Abstract
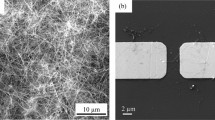
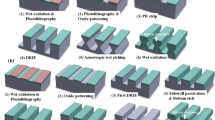
The article presents production methods and test results of field-effect transistor based on silicon nanowire made of heterogeneously arsenic-doped silicon on insulator (SOI). Dopant concentration has been varied over the depth of the silicon layer with a depth of 100 nm from higher than 1020 cm−3 to about 1017 cm−3. The field-effect transistor was manufactured from SOI using electron beam lithography and reactive ion etching. The upper highly conducting part of silicon layer has been used as a substrate for input electrodes and contact pads. The lower sublayer has been used for the formation of semiconductor nanowire. The current-voltage and gate characteristics of the transistor have been measured at 77 and 300 K. The possibility of using a field-effect transistor based on silicon nanowire as a highly sensitive local field-effect and charge sensor with nanometric spatial resolution for application in various fields of physics, technology and medicine has been analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui, Y. et al., Nanowire Nanosensors for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Biological and Chemical Species, Science, 2001, vol. 293, no. 5533, pp. 1289–1292.
Stern, E. et al., Label-Free Immunodetection with CMOS-Compatible Semiconducting Nanowires, Nature, 2007, vol. 445, no. 7127, pp. 519–522.
Patolsky, F. et al., Electrical Detection of Single Viruses, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, vol. 101, no. 39, pp. 14017.
Curreli, M. et al., Real-Time, Label-Free Detection of Biological Entities Using Nanowire-Based FETs, IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 2008, vol. 7, pp. 651–667.
Stern, E. et al., Label-Free Electronic Detection of the Antigen-Specific T-Cell Immune Response, Nano Lett., 2008, vol. 8, no. 10, pp. 3310–3314.
Salfi, J. et al., Direct Observation of Single-Charge-Detection Capability of Nanowire Field-Effect Transistors, Nature Nanotech., 2010, vol. 5, no. 10, pp. 737–741.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.V. Amitonov, D.E. Presnov, V.I. Rudakov, V.A. Krupenin, 2013, published in Mikroelektronika, 2013, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 200–205.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amitonov, S.V., Presnov, D.E., Rudakov, V.I. et al. Field-effect transistor with nanowire channel based on heterogeneously doped SOI. Russ Microelectron 42, 160–164 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739713030025
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739713030025