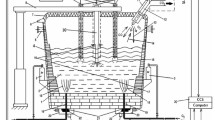
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the possibility of recovery of energy, efficiently, from the off-gases of an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). The system adopted provides the utilization of a phase change materials (PCMs) apparatus matched with an Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) for electrical energy production. The solution proposed allows reduction of the temperature and mass flow rate variability of the off-gases. Results show an excellent reduction of the range of wall-temperatures, close to the off-gases and a relevant energy recovery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kleimt, B., Köhle, S., Kühn, R., and Zisser, S., Application of Models for Electrical Energy Consumption to Improve EAF Operation and Dynamic Control, Proc. 8th European Electric Steelmaking Conf., Birmingham, 2005, pp. 183–197.
Balladino, W., Nardin, G., Pozzetto, D., and Tommasi, S., Ricerca sperimentale sulla fattibilità del recupero energetico e sul controllo antinquinamento nel forno elettrico ad arco durante le fasi di fusione e di affinazione, 2nd European Electric Steel Congress, Florence, 1986.
Jones, J., Understanding Electric Arc Furnace Operations, Tech Commentary, EPRI Center for Materials Production (CMP), 1997.
De Beer, J., Worrel, E., and Blok, K., Long Term Energy Efficiency Improvements in the Iron and Steel Industry, Panels of the ECEEE 1995 Summer Study (Panel 3), 1995.
Mehling, H. and Cabeza, L., Heat and Cold Storage with PCM, Springer, 2008.
Abhat, A., Low Temperature Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage: Heat Storage Materials, Solar Energy, 1983, vol. 30, pp. 313–332.
Zalba, B., Marìn, J.M., Cabeza, L.F., and Mehling, H., Review on Thermal Energy Storage with Phase Change: Materials, Heat Transfer Analysis and Applications, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2003.
Mehling, H., Cabeza, L.F., Hippeli, S., and Hiebler, S., PCM-Module to Improve Hot Water Heat Stores with Stratification, Renewable Energy, 2003, vol. 28, pp. 699–711.
Ravikumar, M. and Srinivasan, Dr. Pss., Phase Change Material as a Thermal Energy Storage for Cooling of Building, J. Theor. Appl. Inform. Technol., 2008.
Heinz, A. and Streicher, W., Application of Phase Change Materials and PCM-Slurries for Thermal Energy Storage, Institute of Thermal Engineering, Graz University of Technology, 2006.
Öttinger, O., PCM/Graphitverbund-Produkte für Hochleistungswärmespeicher, ZAE Symposium, Wärmeund Kältespeicherung mit Phasenwechselmaterialien (PCM), München, 2004.
Cabeza, L., Storage Techniques with Phase Change Materials, Thermal Energy Storage for Solar and Low Energy Buildings, State of the Art by the IEA Solar Heating and Cooling Task 32, 2005, pp. 77–105.
Maruoka, N. and Akiyama, T., Development of PCM for High Temperature Application in the Steelmaking Industry, Dept. Chem. Eng., Graduate School of OSAKA Prefecture University, 2006.
Nishimori, H. and Ortiz, G., Elements of Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena, OxfordUniversity Press, 2011.
Alexiades, V. and Solomon, D., Mathematical Modeling of Melting and Freezing Processes, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, 1993.
Fasano, A. and Primicerio, M., Il Problema di Stefan con condizioni al contorno non lineari, Scuola Normale Superiore Pisa, 1972.
Ansys Fluent Theory Guide 12.0, Ansys, 2009.
Comini, G., Croce, G., and Nobile, E., Fondamenti di Termofluidodinamica Computazionale, SGE Padova, 2004.
Voller, V.R. and Swaminathan, C.R., Generalized Source-Based Method for Solidification Phase Change Numer, Heat Transfer B, 1991, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 175–189.
ECO-D Environmental Systems Srl, Udine (Italy), http://www.eco-d.com/.
Data available at http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/.
Sobolev, V., Thermophysical Properties of Lead and Lead-Bismuth Eutectic, Elsevier J. NuclearMaterials, 2007.
Nicodemi, W., Acciai e Leghe non Ferrose, Zanichelli, 2004.
Miliozzi, A., Giannuzzi, G.M., Taquini, P., and La Barbera, A., Fluido Termovettore: Dati di Base Della Miscela di Nitrati di Sodio e Potassio, ENEA, 2001.
Incropera, F.P., Bergman, T.L., Lavine, A.S., and Dewitt, D.P., Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th ed., Wiley, 2011.
Comini, G. and Cortella, G., Fondamenti di Trasmissione del Calore, SGE Padova, 2005.
Smith, T.F., Shen, Z.F., and Friedman, J.N., Evaluation of Coefficients for theWeighted Sum of Grey Gases Model, 20th National Heat Transfer Conf., Milwaukee, WI, 1981.
Rhine, J.M. and Tucker, R.J., Modeling of Gas-Fired Furnaces and Boilers, McGraw-Hill, 1991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saro, O., De Angelis, A., D’Elia, S. et al. Utilization of phase change materials (PCM) for energy recovery in the steelmaking industry. J. Engin. Thermophys. 22, 93–110 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232813020021
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1810232813020021