Abstract
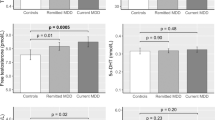
We present a comprehensive clinical and biological study of 46 patients with depressive disorder (F32-F33: depressive episode and recurrent depressive disorder) during pharmacotherapy. Neurohumoral factors (cortisol, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, serotonin, DHEA and its sulfated form) were determined in serum by ELISA. The severity of the current depressive episode was evaluated using the 17-point Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS-17); the pharmacotherapy efficacy was evaluated using the scale of the Clinical Global Impression (CGI Scale). We showed that before prescription of pharmacotherapy peripheral blood neurohumoral markers that characterize the state of stress-realizing and stress-limiting systems of the body may be considered as biological predictors of the effective pharmacotherapy of a current depressive episode and used as additional paraclinical examination methods. At higher concentrations of cortisol and serotonin associated with a decrease in the content of neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone, the high efficiency of the pharmacotherapy of depressive episode is predicted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krasnov, V.N., Rasstroistva affektivnogo spektra (Affective Disorders), Moscow: Prakticheskaya Meditsina, 2011.
Jentsch, M.C., Van Buel, E.M., Bosker, F.J., Gladkevich, A.V., Klein, H.C., Oude, Voshaar R.C., Ruhe, H.G., Eisel, U.L.M., and Schoevers, R.A., Biomark. Med, 2015, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 277–297.
Thase, M.E., Dialogues Clin. Neurosci, 2014, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 539–544.
Uzbekov, M.G., Gurovich, I.Ya., and Ivanova, S.A., Sots. I klin. psikhiatr, 2016, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 77–94.
Ryadovaya, L.A., Gutkevich, E.V., Stoyanova, I.Ya., and Ivanova, S.A., TSPU Bulletin, 2009, no. 3, pp. 49–53.
Bokhan, N.A., Ivanova, S.A., and Levchuk, L.A., Serotoninovaya sistema v modulyatsii depressivnogo i agressivnogo povedeniya (Serotoninergic System in the Modulation of Agression), Tomsk, 2013.
Markopoulou, K., Papadopoulos, A., Juruena, M.F., Poon, L., Pariante, C.M., and Cleare, A.J., Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2009, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 19–26.
Rivera-Baltanas, T., Olivares, J.M., Calado-Otero, M., Kalynchuk, L.E., Martinez-Villamarin, J.R., and Caruncho, H.J., J. Affect Disord, 2014, vol. 163, pp. 47–55.
Eckert, A., Mikoteit, T., Beck, J., Hemmeter, U.M., Brand, S., Schmitt, K., Bischof, R., Delini-Stula, A., and Holsboer-Trachsler, E., European Psychiatry, 2016, vol. 33, p. 410.
Yoshimura, R., Kishi, T., and Suzuki, A., Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 2011, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 1022–1025.
Morita, T., Senzaki, K., Ishihara, R., Umeda, K., Iwata, N., Nagai, T., Hida, H., Nabeshima, T., Yukawa, K., Ozaki, N., and Noda, Y., Hum. Psychopharmacol, 2014, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 280–286.
Shutov, A.A. and Bystrova, O.V., Zhurn. Nevrol. i psikhiatr. im. S.S. Korsakova, 2008, no. 10, pp. 49–54.
Dzyuba, A.N., Khaustova, E.A., and Bezsheiko, V.G., Ukr. Med. chasopi, vol. 88, pp. 121–125.
Levchuk, L.A., Vyalova, N.M., Simutkin, G.G., Ivanova, S.A., and Bokhan, N.A., Vestnik Ural’Skoi akademicheskoi meditsinskoi nauki, 2014, no. 3, pp. 217–219.
Levchuk, L.A., Vyalova, N.M., Ivanova, S.A., Simutkin, G.G., Lebedeva, E.V., and Bokhan, N.A., Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 2015, vol. 158, no. 5, pp. 638–640.
Levchuk, L.A., Ivanova, S.A., Simutkin, G.G., Lebedeva, E.V., Vyalova, N.M., Losenkov, I.S., and Bokhan, N.A., RF Patent No. 2530635 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.A. Levchuk, N.M. Vyalova, G.G. Simutkin, N.A. Bokhan, S.A. Ivanova, 2017, published in Neirokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 177–180.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levchuk, L.A., Vyalova, N.M., Simutkin, G.G. et al. Neurohumoral markers that predict the efficiency of pharmacologic therapy of depressive disorders. Neurochem. J. 11, 185–187 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712417020088
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712417020088