Abstract
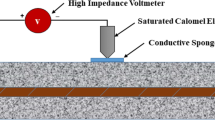
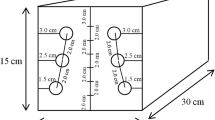
As is well known, the corrosion of embedded steel reinforced depends strongly of the concrete resistivity, which is related directly with the water contained into its porous network. Environment plays an important role on resistivity, due to have a direct correspondence with the relative humidity and temperature. In these terms, ingress or output of water is favored or hampered by the environmental parameters, as well as its fluctuations. This work presents a proposal of instrumented system to generate a map of electrical resistivity at concrete samples by using superficial and embedded electrodes. Mathematical analysis of equivalent circuit revealed the importance of the impedance of electrodes utilized, to simplify measures. Concrete samples were exposed to different relative humidity focused to try to obtain the relation between relative humidity and resistivity. An array of two electrodes distributed in a matrix was manufactured to apply a signal of direct current at first electrode and measure the resultant current at second electrode. The system applies a programmed sequence of switch to turn on and turn off to realize measurements over established zone and, in this form, allows identify zones with potentials gradients. Also, do easy the monitoring of concrete resistivity evolution in function of time and humidity conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCarter W. J., Venesland O. Sensor system for use in reinforced concrete structures. Construction and Building Materials 18 (2004) 351–358
Acosta Torres, Pérez Quiroz J. Estudio de la corrosión en barras de acero inoxidable en concreto contaminado por cloruros cuando se le aplican esfuerzos residuales. Publicación Técnica No 287 IMT, 2006
Abu-Zeid N., Balducci M., Bartocci F., Regni R., Santarato G., Indirect estimation of injected mortar volume in historical walls using the electrical resistivity tomography. Journal of Cultural Heritage 11 (2010) 220–227
Manfore G. E. (1968) A review of fiber reinforcement of Portland cement paste mortar concrete. Journal, PCA Research and Development Laboratories, 3, 36–42 direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) [Monfore, 1968].
Polder R. B., Test methods for on-site measurement of resistivity of concrete – a RILEM TC-154 Technical recommendation. Construction and Building Materials 15 (2001) 125–131.
Ramírez Muñoz D., Casans Berga S. An analog electronic interface to measure electrical conductivity in liquids. Measurement 38 (2005) 181–187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan Blanco, K.S., Jesús Moo Yam, V.M., López, T.P. et al. Instrumented System for Analysis of Concrete Resistivity. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1815, 93 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2016.93
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2016.93