Abstract
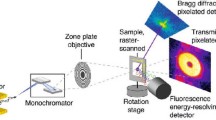
The correlations in multi-modal microscopy data can be systematically reduced by the distinct probe-sample interactions and signal collection geometry for each modality. Extracting scientific insights from correlative datasets thus requires careful consideration of the mode-specific, and often non-overlapping, sampling volume used in the correlative microscopy. Here we describe a pencil beam, ray tracing method that accounts for the finite extent and roughness of thin-films and nanomaterials in synchrotron-based X-ray microscopy measurements, creating a first approximation of the probe-sample interaction for each modality that tightens correlations in multi-modal X-ray nanoprobe characterization. As a demonstrative example we analyze structure–function correlations in sequential microscopy data acquired for a Eu:CsPbBr3 halide perovskite thin-film crystal across three distinct measurement modes. Our ray-traced corrections account for local fluorescence matrix effects and sampling volume discrepancies and unveil structural, compositional, and optoelectronic relationships hidden in the raw data.
Graphic abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
The code described in this work is available at https://github.com/rekumar/XRayTracer.
References
M. Kreuzer, S. Stamenković, S. Chen, P. Andjus, T. Dučić, Lipids status and copper in a single astrocyte of the rat model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Correlative synchrotron-based X-ray and infrared imaging. J. Biophoton. 13(10), e202000069 (2020)
B. De Samber, R. Evens, K. De Schamphelaere, G. Silversmit, B. Masschaele, T. Schoonjans, B. Vekemans, C.R. Janssen, L. Van Hoorebeke, I. Szalóki, F. Vanhaecke, G. Falkenberg, L. Vincze, A combination of synchrotron and laboratory X-ray techniques for studying tissue-specific trace level metal distributions in Daphnia magna. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 23(6), 829 (2008)
A. Conti, R. Sinibaldi, S. Capuani, T. Traini, G.L. Romani, S. Della Penna, Co-registration of Synchrotron Radiation-microCT and micro-MRI images: a new method for the complete characterization of newly-formed bone. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med 22, 1176 (2014)
N. Li, Y. Luo, Z. Chen, X. Niu, X. Zhang, J. Lu, R. Kumar, J. Jiang, H. Liu, X. Guo, B. Lai, G. Brocks, Q. Chen, S. Tao, D. P. Fenning, H. Zhou, Microscopic degradation in formamidinium-cesium lead iodide perovskite solar cells under operational stressors. Joule 4(8), 1743–1758 (2020)
X.L. Quinn, R.E. Kumar, M. Kodur, D.N. Cakan, Z. Cai, T. Zhou, M.V. Holt, D. P. Fenning, Europium addition reduces local structural disorder and enhances photoluminescent yield in perovskite CsPbBr3. Adv. Optical Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202002221
M. Kodur, R.E. Kumar, Y. Luo, D.N. Cakan, X. Li, M. Stuckelberger, D.P. Fenning, X-Ray Microscopy of Halide Perovskites: Techniques, Applications, and Prospects. Adv. Energy Mater. 10(26), 1–25 (2020)
Y. Luo, S. Aharon, M. Stuckelberger, E. Magaña, B. Lai, M.I. Bertoni, L. Etgar, D.P. Fenning, The relationship between chemical flexibility and nanoscale charge collection in hybrid halide perovskites. Adv. Func. Mater. 28(18), 1706995 (2018)
B.M. West, M. Stuckelberger, H. Guthrey, L. Chen, B. Lai, J. Maser, V. Rose, W. Shafarman, M. Al-Jassim, M.I. Bertoni, Grain engineering: How nanoscale inhomogeneities can control charge collection in solar cells. Nano Energy 32, 488–493 (2017)
M. Stuckelberger, B. West, T. Nietzold, B. Lai, J.M. Maser, V. Rose, M.I. Bertoni, Engineering solar cells based on correlative X-ray microscopy. J. Mater. Res. 32(10), 1825–1854 (2017)
Y. Zhou, H. Zhou, J. Deng, W. Cha, Z. Cai, Decisive structural and functional characterization of halide perovskites with synchrotron. Matter 2, 360–377 (2020)
B. Beckhoff, B. Kanngießer, N. Langhoff, R. Wedell, H. Wolff, Handbook of Practical X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis (Springer, New York, 2007)
P. Pfalzer, J.P. Urbach, M. Klemm, S. Horn, M.L. Den Boer, A.I. Frenkel, J.P. Kirkland, Elimination of self-absorption in fluorescence hard-x-ray absorption spectra. Phys. Rev. B 60(13), 9335–9339 (1999)
B.M. West, M. Stuckelberger, A. Jeffries, S. Gangam, B. Lai, B. Stripe, J. Maser, V. Rose, S. Vogt, M.I. Bertoni, X-ray fluorescence at nanoscale resolution for multicomponent layered structures: a solar cell case study. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 24(1), 288–295 (2017)
S.-M. Bak, Z. Shadike, R. Lin, X. Yu, X.-Q. Yang, In situ/operando synchrotron-based X-ray techniques for lithium-ion battery research. NPG Asia Mater. 10(7), 563–580 (2018)
D.A. Shapiro, Y.-S.S. Yu, T. Tyliszczak, J. Cabana, R. Celestre, W. Chao, K. Kaznatcheev, A.L.D.D. Kilcoyne, F. Maia, S. Marchesini, Y.S. Meng, T. Warwick, L.L. Yang, H.A. Padmore, Chemical composition mapping with nanometre resolution by soft X-ray microscopy. Nat. Photon. 8(10), 765–769 (2014)
F. Meirer, B.M. Weckhuysen, Spatial and temporal exploration of heterogeneous catalysts with synchrotron radiation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3(9), 324–340 (2018)
J. Becher, T.L. Sheppard, Y. Fam, S. Baier, W. Wang, D. Wang, S. Kulkarni, T.F. Keller, M. Lyubomirskiy, D. Brueckner, M. Kahnt, A. Schropp, C.G. Schroer, J.-D. Grunwaldt, Mapping the pore architecture of structured catalyst monoliths from nanometer to centimeter scale with electron and X-ray tomographies. J. Phys. Chem. C 123(41), 25197–25208 (2019)
J. Deng, Y.H. Lo, M. Gallagher-Jones, S. Chen, A. Pryor, Q. Jin, Y.P. Hong, Y.S.G.G. Nashed, S. Vogt, J. Miao, C. Jacobsen, Correlative 3D x-ray fluorescence and ptychographic tomography of frozen-hydrated green algae. Sci. Adv. 4(11), 1–11 (2018)
J. Bruley, M.J. Highland, S.O. Hruszkewycz, I. McNulty, C.E. Murray, M.V. Holt, A. Tripathi, P.H. Fuoss, O.G. Shpyrko, J. Holt, C.E. Murray, J. Bruley, J. Holt, A. Tripathi, O.G. Shpyrko, I. McNulty, M.J. Highland, P.H. Fuoss, S.O. Hruszkewycz, I. McNulty, C.E. Murray, M.V. Holt, A. Tripathi, P.H. Fuoss, O.G. Shpyrko, J. Holt, C.E. Murray, J. Bruley, J. Holt, A. Tripathi, O.G. Shpyrko, I. McNulty, M.J. Highland, P.H. Fuoss, Quantitative nanoscale imaging of lattice distortions in epitaxial semiconductor heterostructures using nanofocused X-ray Bragg projection ptychography. Nano Lett. 12(10), 5148–5154 (2012)
M.S. del Rio, L. Rebuffi, OASYS: a software for beamline simulations and synchrotron virtual experiments. AIP Conference Proceedings 2054, 060081 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5084712
B. Lai, F. Cerrina, SHADOW: a synchrotron radiation ray tracing program. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 246(1–3), 337–341 (1986)
M.S. del Rio, N. Canestrari, F. Jiang, F. Cerrina, SHADOW3: a new version of the synchrotron X-ray optics modelling package. J Synchrotron Radiat 18(Pt 5), 708–716 (2011)
P. Khoram, S. Brittman, W.I. Dzik, J.N.H. Reek, E.C. Garnett, Growth and Characterization of PDMS-Stamped Halide Perovskite Single Microcrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 120(12), 6475–6481 (2016)
B.L. Henke, E.M. Gullikson, J.C. Davis, X-ray interactions: photoabsorption, scattering, transmission, and reflection at E= 50–30,000 eV, Z= 1–92. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 54(2), 181–342 (1993)
D. Pettit, P. Fontana, Comparison of sodium chloride hopper cubes grown under microgravity and terrestrial conditions. NPJ Microgravity 5, 25 (2019)
A. Kuczumow, Z. Rzaçzyńska, M. Szewczak, Matrix effects in the x-ray fluorescence method. X-Ray Spectrom. 11(3), 135–139 (1982)
M. Franzini, L. Leoni, M. Saitta, A simple method to evaluate the matrix effects in X-ray fluorescence analysis. X-Ray Spectrom. 1(4), 151–154 (1972)
J.G. Nagy, D.P. O’Leary, Restoring images degraded by spatially variant blur. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19(4), 1063–1082 (1998)
K. Novak, A.T. Watnik, Imaging through deconvolution with a spatially variant point spread function. Comput. Imag. VI (2021)
A. Shajkofci, M. Liebling, Semi-blind spatially-variant deconvolution in optical microscopy with local point spread function estimation by use of convolutional neural networks, vol. 2018. 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, no. ICIP, pp. 3818–3822 (2018)
É. Thiébaut, L. Denis, F. Soulez, R. Mourya, Spatially variant PSF modeling and image deblurring. Adapt. Opt. Syst. V (2016)
T.R. Lauer, Deconvolution with a spatially-variant PSF. Astron. Data Anal. II 4847(520), 167 (2002)
X. Chen, C. Dejoie, T. Jiang, C.-S. Ku, N. Tamura, Quantitative microstructural imaging by scanning Laue x-ray micro- and nanodiffraction. MRS Bull. 41(6), 445–453 (2016)
T.W. Cornelius, O. Thomas, Progress of in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction studies on the mechanical behavior of materials at small scales. Prog. Mater Sci. 94, 384–434 (2018)
F. Hofmann, R.J. Harder, W. Liu, Y. Liu, I.K. Robinson, Y. Zayachuk, Glancing-incidence focussed ion beam milling: a coherent X-ray diffraction study of 3D nano-scale lattice strains and crystal defects. Acta Mater. 154, 113–123 (2018)
G.E. Ice, B.C. Larson, J.Z. Tischler, W. Liu, W. Yang, X-ray microbeam measurements of subgrain stress distributions in polycrystalline materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 399(1–2), 43–48 (2005)
H.F. Poulsen, X. Fu, E. Knudsen, E.M. Lauridsen, L. Margulies, S. Schmidt, 3DXRD—mapping grains and their dynamics in 3 dimensions. Mater. Sci. Forum 467–470, 1363–1372 (2004)
H. Simons, A.C. Jakobsen, S.R. Ahl, C. Detlefs, H.F. Poulsen, Multiscale 3D characterization with dark-field x-ray microscopy. MRS Bull. 41(6), 454–459 (2016)
T. Tian, R. Morusupalli, H. Shin, H.-Y. Son, K.-Y. Byun, Y.-C. Joo, R. Caramto, L. Smith, Y.-L. Shen, M. Kunz, N. Tamura, A.S. Budiman, On the mechanical stresses of Cu through-silicon via (TSV) samples fabricated by SK Hynix vs. SEMATECH—enabling robust and reliable 3-D interconnect/integrated circuit (IC) technology. Procedia Eng. 139, 101–111 (2016)
M. Holt, R. Harder, R. Winarski, V. Rose, Nanoscale hard X-ray microscopy methods for materials studies. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 43(1), 183–211 (2013)
J. Deng, D.J. Vine, S. Chen, Q. Jin, Y.S.G. Nashed, T. Peterka, S. Vogt, C. Jacobsen, X-ray ptychographic and fluorescence microscopy of frozen-hydrated cells using continuous scanning. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–10 (2017)
W.S. Drisdell, L. Leppert, C.M. Sutter-Fella, Y. Liang, Y. Li, Q.P. Ngo, L.F. Wan, S. Gul, T. Kroll, D. Sokaras, A. Javey, J. Yano, J.B. Neaton, F.M. Toma, D. Prendergast, I.D. Sharp, Determining atomic-scale structure and composition of organo-lead halide perovskites by combining high-resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy and first-principles calculations. ACS Energy Lett. 2(5), 1183–1189 (2017)
F. Pfeiffer, R. Article, F. Pfeiffer, X-ray ptychography. Nat. Photonics 12(1), 9–17 (2018)
T.W. Victor, L.M. Easthon, M. Ge, K.H. O’Toole, R.J. Smith, X. Huang, H. Yan, K.N. Allen, Y.S. Chu, L.M. Miller, X-ray fluorescence nanotomography of single bacteria with a sub-15 nm beam. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–8 (2018)
D.J. Vine, D. Pelliccia, C. Holzner, S.B. Baines, A. Berry, I. McNulty, S. Vogt, A.G. Peele, K.A. Nugent, Simultaneous X-ray fluorescence and ptychographic microscopy of Cyclotella meneghiniana. Opt. Express 20(16), 18287 (2012)
Y.S. Chu, W.-K. Lee, R. Tappero, M. Ge, X. Huang, X. Xiao, H. Yan, P. Northrup, J. Thieme, A.M. Kiss, G.J. Williams, Y. Yang, S.L. Nicholas, A. Pattammattel, R. Smith, P. Ilinski, Y. Du, Multimodal, multidimensional, and multiscale X-ray imaging at the national synchrotron light source II. Synchrotron Radiat. News 33(3), 29–36 (2020)
T. Link, S. Zabler, A. Epishin, A. Haibel, M. Bansal, X. Thibault, Synchrotron tomography of porosity in single-crystal nickel-base superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 425(1–2), 47–54 (2006)
L. Helfen, T. Baumbach, P. Mikulík, D. Kiel, P. Pernot, P. Cloetens, J. Baruchel, High-resolution three-dimensional imaging of flat objects by synchrotron-radiation computed laminography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(7), 071915 (2005)
L. Helfen, A. Myagotin, A. Rack, P. Pernot, P. Mikulík, M. Di Michiel, T. Baumbach, Synchrotron-radiation computed laminography for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of flat devices. Phys. Status Solidi A 204(8), 2760–2765 (2007)
L.P. Hunter, Direct measurement of the angular dependence of the imaginary part of the atomic scattering factor of germanium. IBM J. Res. Dev. 3(2), 106–113 (1959)
N.W.M. Ritchie, Efficient simulation of secondary fluorescence via NIST DTSA-II Monte Carlo. Microsc. Microanal. 23(3), 618–633 (2017)
A.G. Karydas, Self-element secondary fluorescence enhancement in XRF analysis. X-Ray Spectrom. 34(5), 426–431 (2005)
A. Shajkofci, M. Liebling, Spatially-variant CNN-based point spread function estimation for blind deconvolution and depth estimation in optical microscopy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 5848–5861 (2020)
M. Weigert, U. Schmidt, T. Boothe, A. Müller, A. Dibrov, A. Jain, B. Wilhelm, D. Schmidt, C. Broaddus, S. Culley, M. Rocha-Martins, F. Segovia-Miranda, C. Norden, R. Henriques, M. Zerial, M. Solimena, J. Rink, P. Tomancak, L. Royer, F. Jug, E.W. Myers, Content-aware image restoration: pushing the limits of fluorescence microscopy. Nat Methods 15(12), 1090–1097 (2018)
D. He, D. Cai, J. Zhou, J. Luo, S.-L. Chen, Restoration of out-of-focus fluorescence microscopy images using learning-based depth-variant deconvolution. IEEE Photon. J. 12(2), 1–13 (2020)
Acknowledgments
Thank you to Moses Kodur at UC San Diego for his help in taking the μPL data, and to Tao Zhou, Martin V. Holt, and Zhonghou Cai from the Center for Nanoscale Materials at Argonne National Laboratory for their assistance during and valuable discussion about our synchrotron measurements. This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. DMR-1848371. Use of the Center for Nanoscale Materials and the Advanced Photon Source, both Office of Science user facilities, was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. This work was performed in part at the San Diego Nanotechnology Infrastructure (SDNI) of UCSD, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure, which was supported by the National Science Foundation (Grant ECCS-1542148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R.E., Quinn, X.L. & Fenning, D.P. Accounting for sample morphology in correlative X-ray microscopy via ray tracing. MRS Advances 6, 547–553 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-021-00114-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-021-00114-0