Abstract
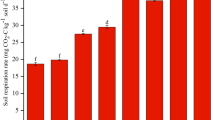
In order to reveal the mechanism of silicon (Si) fertilizer in improving nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) nutrient availability in paddy soil, we designed a series of soil culture experiments by combining application of varying Si fertilizer concentrations with fixed N and P fertilizer concentrations. Following the recommendations of fertilizer manufacturers and local farmers, we applied Si in concentrations of 0, 5.2, 10.4, 15.6, and 20.8 µg/kg. At each concentration of added Si, the availability of soil N and P nutrients, soil microbial activity, numbers of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and P-decomposing bacteria which means that the organic P is decomposed into inorganic nutrients which can be absorbed and utilized by plants, and urease and phosphatase activity first increased, and then decreased, as Si was added to the soil. These indicators reached their highest levels with a Si application rate of 15.6 µg/kg, showing values respectively 19.78%, 105.09%, 8.34%, 73.12%, 130.36%, 28.12%, and 20.15% higher than those of the controls. Appropriate Si application (10.4 to 15.6 µg/kg) could significantly increase the richness of the soil microbial community involved in cycling of N and P nutrients in the soil. When the Si application rate was 15.6 µg/kg, parameters for characterizing microbial abundance such as sequence numbers, operational taxonomic unit (OTU) number, and correlation indices of microbial community richness such as Chao1 index, the adaptive coherence estimator (ACE) index, Shannon index, and Simpson index all reached maximum values, with amounts increased by 14.46%, 10.01%, 23.80%, 30.54%, 0.18%, and 2.64%, respectively, compared with the control group. There is also a good correlation between N and P mineralization and addition of Si fertilizer. The correlation coefficients between the ratio of available P/total P (AP/TP) and the number of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, AP/TP and acid phosphatase activity (AcPA), AP/TP and the Shannon index, the ratio of available N/total amount of N (AN/TN) and the number of ammoniated bacteria, and AN/TN and AcPA were 0.9290, 0.9508, 0.9202, 0.9140, and 0.9366, respectively. In summary, these results revealed that enhancement of soil microbial community structure diversity and soil microbial activity by appropriate application of Si is the key ecological mechanism by which application of Si fertilizer improves N and P nutrient availability.
摘要
目的
揭示适量硅养分的添加对促进水稻土中氮(N)和磷(P)养分有效性增加的作用及其生态机制.
创新点
发现添加适量的硅养分可有效地提高稻田土壤N和P养分的有效性, 其核心生态机制是由于适量硅养分的添加可显著增加稻田土壤的土壤微生物活性, 氨化细菌和解磷菌的数量, 脲酶和磷酸酶的活性以及与N和P养分循环有关的微生物群落群落, 进而促进土壤N和P养分土壤养分矿化.
方法
设计了一系列不同硅肥浓度和固定氮磷肥配合施用的土培试验, 施硅设置为五个梯度:0, 5.2, 10.4, 15.6和20.8 µg/kg. 在25 ℃培养一个月, 分析收获后土壤有效态N和P的含量, 土壤微生物活性, 氨化细菌和解磷菌的数量, 脲酶和磷酸酶的活性以及与土壤微生物群落结构多样性, 最后统计分析硅的添加对水稻土N和P养分有效性, 土壤微生物活性, 氨化细菌和解磷菌的数量, 脲酶和磷酸酶的活性以及与土壤微生物群落结构多样性的影响及其相互关系.
结论
适量硅养分的添加可显著增加稻田土壤的土壤微生物活性, 氨化细菌和解磷菌的数量, 脲酶和磷酸酶的活性以及与N和P养分循环有关的微生物群落群落, 进而促进N和P养分土壤养分矿化. 当硅施用量为15.6µg/kg时, 土壤N和P养分的有效性达到最大值, 同时土壤微生物活性, 氨化细菌和解磷菌的数量, 脲酶和磷酸酶的活性以及与N和P养分循环有关的微生物群落群落也均达到最高水平. 另外, 土壤速效磷比例(有效磷/总磷(AP/TP))与氨化细菌数, AP/TP和酸性磷酸酶活性, AP/TP和Shannon指数, 速效氮比例(有效氮/总氮(AN/TN))与氨化细菌数, AN/TN与酸性磷酸酶活性的相关系数分别为0.9290, 0.9508, 0.9202, 0.9140, 0.9366. 综上所述, 适当补充硅养分可提高稻田土壤N和P养分有效性, 有助于提高稻田土壤N和P养分的水稻利用效率.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao SD, 2011. Analytical Methods of Agricultural Soil Chemistry. Chinese Agricultured Science and Technology Press, Beijing, China, p.39–61, 264–268 (in Chinese).
Blaxter M, Mann J, Chapman T, et al., 2005. Defining operational taxonomic units using DNA barcode data. Philos Trans Roy Soc B Biol Sci, 360(1462):1935–1943. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1725
Cai DL, 2017. Research and application development of silicon fertilizer at home and abroad. Phos Comp Fert, 32(1):37–39 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2017.01.014
Chao AN, 1984. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Stat, 11(4):265–270.
Chao AN, Yang MCK, 1993. Stopping rules and estimation for recapture debugging with unequal failure rates. Biometrika, 80(1):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/80.1.193.
Chen XF, Li ZP, Liu M, et al., 2015. Effect of long-term fertilizations on microbial community structure and functional diversity in paddy soil of subtropical China. Chin J Ecol, 34(7):1815–1822 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.20150615.001
Cusack DF, Silver WL, Torn MS, et al., 2011. Changes in microbial community characteristics and soil organic matter with nitrogen additions in two tropical forests. Ecology, 92(3):621–632. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-0459.1
Du YF, Lv LF, He ZQ, et al., 2016. Effect of mineral conditioners on improvement of acid red soil. J Soil Water Conserv, 30(3):351–354 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2016.03.059
Eneji AE, Inanaga S, Muranaka S, et al., 2008. Growth and nutrient use in four grasses under drought stress as mediated by silicon fertilizers. J Plant Nutr, 31(2):355–365. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160801894913
Frankenberger WT, Dick WA, 1983. Relationships between enzyme activities and microbial growth and activity indices in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J, 47(5):945–951. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1983.03615995004700050021x
Guan SY, 1986. Soil Enzymes and Their Research Methods. Agricultural Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
He JZ, Zheng Y, Chen CR, et al., 2008. Microbial composition and diversity of an upland red soil under long-term fertilization treatments as revealed by culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. J Soils Sed, 8(5):349–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-008-0025-1
Hömberg A, Obst M, Knorr KH, et al., 2020. Increased silicon concentration in fen peat leads to a release of iron and phosphate and changes in the composition of dissolved organic matter. Geoderma, 374:114422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114422
Li CH, Jia ZJ, Tang LS, et al., 2012. Effect of model of fertilization on microbial abundance and enzyme activity in oasis farmland soil. Acta Pedol Sin, 49(3):567–574 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11766/trxb201101070011
Li FD, Yu ZN, He SJ, 1996. Agricultural Microbiology Experimental Technology. China Agricultural Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Liao M, Fang ZP, Liang YQ, et al., 2020. Effects of supplying silicon nutrient on utilization rate of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients by rice and its soil ecological mechanism in a hybrid rice double-cropping system. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(6):474–484. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900516
Liu HF, Ma JH, Jin L, et al., 2009. Determination of activity of FDA hydrolysis in paddy soils and its application in Taihu Lake region. Acta Pedol Sin, 46(2):365–367 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2009.02.026
Mehrabanjoubani P, Abdolzadeh A, Sadeghipour HR, et al., 2015. Impacts of silicon nutrition on growth and nutrient status of rice plants grown under varying zinc regimes. Theor Exp Plant Physiol, 27(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-014-0028-9
Mendes R, Kruijt M, de Bruijn I, et al., 2011. Deciphering the rhizosphere microbiome for disease-suppressive bacteria. Science, 332(6033):1097–1100. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1203980
Meng FQ, Qiao YH, Wu WL, et al., 2017. Environmental impacts and production performances of organic agriculture in China: a monetary valuation. J Environ Manage, 188: 49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.11.080
Nannipieri P, 1994. The potential use of soil enzymes as indicators of productivity, sustainability and pollution. In Pankhurst CE, Double BM, Gupta VVSR, et al. (Eds.), Soil Biota: Management in Sustainable Farming Systems. CSIRO, East Melbourne, p.238–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-14225-3_16
Neu S, Schaller J, Dudel GE, 2017. Silicon availability modifies nutrient use efficiency and content, C:N:P stoichiometry, and productivity of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci Rep, 7:40829. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40829
Pace NR, 1997. A molecular view of microbial diversity and the biosphere. Science, 276(5313):734–740. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5313.734
Pati S, Pal B, Badole S, et al., 2016. Effect of silicon fertilization on growth, yield, and nutrient uptake of rice. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 47(3):284–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2015.1122797
Saudy HS, Mubarak M, 2015. Mitigating the detrimental impacts of nitrogen deficit and fenoxaprop-p-ethyl herbicide on wheat using silicon. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal, 46(7): 897–907. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2015.1011753
Schaller J, Brackhage C, Gessner MO, et al., 2012. Silicon supply modifies C:N:P stoichiometry and growth of Phragmites australis. Plant Biol, 14(2):392–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2011.00537.x
Schaller J, Schoelynck J, Struyf E, et al., 2016. Silicon affects nutrient content and ratios of wetland plants. Silicon, 8(4): 479–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-015-9302-y
Schaller J, Faucherre S, Joss H, et al., 2019. Silicon increases the phosphorus availability of Arctic soils. Sci Rep, 9:449. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37104-6
Schneider T, Keiblinger KM, Schmid E, et al., 2012. Who is who in litter decomposition? Metaproteomics reveals major microbial players and their biogeochemical functions. ISME J, 6(9):1749–1762. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012.11
Schnitzer SA, Klironomos JN, HilleRisLambers J, et al., 2011. Soil microbes drive the classic plant diversity-productivity pattern. Ecology, 92(2):296–303. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-0773.1
Shannon CE, 1948a. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J, 27(3):379–423.
Shannon CE, 1948b. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J, 27(4):623–656.
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Guo JF, et al., 2010. Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in Northeast China. Appl Soil Ecol, 46(1):119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.06.015
Simpson EH, 1949. Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163(4148): 688. https://doi.org/10.1038/163688a0
Su D, Zhang K, Chen FL, et al., 2014. Effects of nitrogen application on soil microbial community structure and function of eucalyptus forests with different organic carbon levels. Ecol Environ Sci, 23(3): 423–429 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.03.009
Waldrop MP, Zak DR, Sinsabaugh RL, 2004. Microbial community response to nitrogen deposition in northern forest ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem, 36(9):1443–1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.04.023
Wang F, Yuan T, Gu SK, et al., 2015. Effects of organic and inorganic slow-release compound fertilizer on different soils microbial community structure. Environ Sci, 36(4): 1461–1467 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.04.045
Wei W, Xu YL, Zhu L, et al., 2013. Effect of long-term fertilization on soil microbial community in black soil farmland. Acta Pedol Sin, 50(2):372–380 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11766/trxb201202290053
Yu ZH, Li YS, Wang GH, et al., 2016. Effectiveness of elevated CO2 mediating bacterial communities in the soybean rhizosphere depends on genotypes. Agric Ecosyst Environ, 231:229–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.06.043
Zhong WH, Gu T, Wang W, et al., 2010. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil, 326(1–2):511–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9988-y
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support for this research from the National Key Research and Development Project of China (No. 2016YFD0200800) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41571226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Author contributions
Yuqi LIANG contributed to data analysis and writing of the manuscript. Min LIAO and Xiaomei XIE contributed to study design, data analysis, and writing and editing of the manuscript. Yuqi LIANG, Zhiping FANG, Jiawen GUO, Xiaomei XIE, and Changxu XU carried out the experimental work. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Yuqi LIANG, Min LIAO, Zhiping FANG, Jiawen GUO, Xiaomei XIE, and Changxu XU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Liao, M., Fang, Z. et al. How silicon fertilizer improves nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient availability in paddy soil?. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 22, 521–532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000708
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000708
Key words
- Silicon
- Paddy soil
- Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient availability
- Microbial community structure nutrient