Abstract
Objectives
Smoking has many deleterious consequences on health, one of which can be sleep-related issues. Therefore, a meta-analysis was performed with the aim of pooling results from studies on the relationship between smoking and sleep-related issues.
Methods
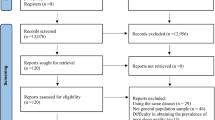
The present study follows PRISMA guidelines. Databases were searched by both researchers to find the articles. The review was done up to December 2018. In order to analyze the results of the screened articles, statistical indexes were converted to logarithms and the studies were combined with each other. Finally, several analyses were conducted with respect to various subgroups. In the subgroup analysis, the pool index of the studies was determined and the degree of heterogeneity in each subgroup was presented. Meta-regression was also used.
Results
Smoking is associated with a risk of developing sleep-related issues. Risk ratio (1.47; 1.20–1.79) for smokers was higher than for non-smokers. Egger’s test and Begg’s test indicated publication bias.
Conclusions
Smoking is associated with sleep-related issues. Informing smokers about the effects of smoking on sleep issues can be effective in reducing and preventing its consequences.
Résumé
Objectifs
Le tabagisme a de nombreuses conséquences délétères sur la santé, et les problèmes liés au sommeil peuvent en faire partie. Nous avons effectué une méta-analyse en vue de regrouper les résultats d’études sur la relation entre le tabagisme et les problèmes liés au sommeil.
Méthode
Notre étude suit les lignes directrices PRISMA. Les deux chercheurs ont interrogé des bases de données pour trouver les articles. La revue a été menée jusqu’en décembre 2018. Pour analyser les résultats des articles filtrés, des indices statistiques ont été convertis en logarithmes, et les études ont été combinées entre elles. Enfin, plusieurs analyses ont été effectuées pour divers sous-groupes. Dans les analyses des sous-groupes, nous avons déterminé l’indice des études regroupées et présenté le degré d’hétérogénéité dans chaque sous-groupe. Nous avons aussi utilisé la méta-régression.
Résultats
Le tabagisme est associé à un risque de contracter des problèmes liés au sommeil. Le risque relatif (1,47; 1,20-1,79) des fumeurs était supérieur à celui des non-fumeurs. Le test d’Egger et le test de Begg ont montré un biais de publication.
Conclusions
Le tabagisme est associé à des problèmes liés au sommeil. Informer les fumeurs des effets du tabagisme sur les problèmes de sommeil peut être un moyen efficace d’en réduire et d’en prévenir les conséquences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Lawati, N. M., Patel, S. R., & Ayas, N. T. (2009). Epidemiology, risk factors, and consequences of obstructive sleep apnea and short sleep duration. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 51(4), 285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.08.001.
Anothaisintawee, T., Reutrakul, S., Van Cauter, E., & Thakkinstian, A. (2016). Sleep disturbances compared to traditional risk factors for diabetes development: systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 30, 11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.10.002.
Antman, E. M., Lau, J., Kupelnick, B., Mosteller, F., & Chalmers, T. C. (1992). A comparison of results of meta-analyses of randomized control trials and recommendations of clinical experts. Treatments for myocardial infarction. Jama, 268(2), 240–248.
Armijo-Olivo, S., Stiles, C. R., Hagen, N. A., Biondo, P. D., & Cummings, G. G. (2012). Assessment of study quality for systematic reviews: a comparison of the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias Tool and the Effective Public Health Practice Project Quality Assessment Tool: methodological research. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, 18(1), 12–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2753.2010.01516.x.
Baglioni, C., Battagliese, G., Feige, B., Spiegelhalder, K., Nissen, C., Voderholzer, U., et al. (2011). Insomnia as a predictor of depression: a meta-analytic evaluation of longitudinal epidemiological studies. Journal of Affective Disorders, 135(1–3), 10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2011.01.011.
Ban, D. J., & Lee, T. J. (2001). Sleep duration, subjective sleep disturbances and associated factors among university students in Korea. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 16(4), 475–480. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2001.16.4.475.
Bartel, K. A., Gradisar, M., & Williamson, P. (2015). Protective and risk factors for adolescent sleep: a meta-analytic review. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 21, 72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2014.08.002.
Beccuti, G., & Pannain, S. (2011). Sleep and obesity. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 14(4), 402–412. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283479109.
Begg, C. B., & Mazumdar, M. (1994). Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics, 50(4), 1088–1101.
Brook, D. W., Rubenstone, E., Zhang, C., & Brook, J. S. (2012). Trajectories of cigarette smoking in adulthood predict insomnia among women in late mid-life. Sleep Medicine, 13(9), 1130–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2012.05.008.
Chen, L. J., Steptoe, A., Chen, Y. H., Ku, P. W., & Lin, C. H. (2017). Physical activity, smoking, and the incidence of clinically diagnosed insomnia. Sleep Medicine, 30, 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2016.06.040.
Cohen, A., Ben Abu, N., & Haimov, I. (2018). The interplay between tobacco dependence and sleep quality among young adults. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15402002.2018.1546707.
Conway, S. G., Roizenblatt, S. S., Palombini, L., Castro, L. S., Bittencourt, L. R., Silva, R. S., & Tufik, S. (2008). Effect of smoking habits on sleep. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 41(8), 722–727.
Custodio, L., Carlson, C. R., Upton, B., Okeson, J. P., Harrison, A. L., & de Leeuw, R. (2015). The impact of cigarette smoking on sleep quality of patients with masticatory myofascial pain. Journal of Oral & Facial Pain and Headache, 29(1), 15–23. https://doi.org/10.11607/ofph.1266.
Davila, D. G., Hurt, R. D., Offord, K. P., Harris, C. D., & Shepard Jr., J. W. (1994). Acute effects of transdermal nicotine on sleep architecture, snoring, and sleep-disordered breathing in nonsmokers. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 150(2), 469–474. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.150.2.8049831.
Ditre, J. W., Heckman, B. W., Butts, E. A., & Brandon, T. H. (2010). Effects of expectancies and coping on pain-induced motivation to smoke. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 119(3), 524–533. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019568.
Doll, R., Peto, R., Boreham, J., & Sutherland, I. (2004). Mortality in relation to smoking: 50 years’ observations on male British doctors. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 328(7455), 1519. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38142.554479.AE.
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics, 56(2), 455–463.
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj, 315(7109), 629–634.
Espiritu, J. R. (2008). Aging-related sleep changes. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine, 24(1), 1–14, v. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2007.08.007.
Foley, D. J., Monjan, A. A., Brown, S. L., Simonsick, E. M., Wallace, R. B., & Blazer, D. G. (1995). Sleep complaints among elderly persons: an epidemiologic study of three communities. Sleep, 18(6), 425–432.
Ford, D. E., & Kamerow, D. B. (1989). Epidemiologic study of sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders. An opportunity for prevention? Jama, 262(11), 1479–1484.
Forouzanfar, M. H., Afshin, A., Alexander, L. T., Anderson, H. R., Bhutta, Z. A., Biryukov, S., et al. (2016). Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet, 388(10053), 1659–1724. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8.
Fritsch Montero, R., Lahsen Martinez, P., Romeo Gomez, R., Araya Baltra, R., & Rojas Castillo, G. (2010). Sleep disorders in the adult population of Santiago of Chile and its association with common psychiatric disorders. Actas Españolas de Psiquiatría, 38(6), 358–364.
Gillin, J. C., Lardon, M., Ruiz, C., Golshan, S., & Salin-Pascual, R. (1994). Dose-dependent effects of transdermal nicotine on early morning awakening and rapid eye movement sleep time in nonsmoking normal volunteers. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 14(4), 264–267.
Gomes Felden, E. P., Barbosa, D. G., Junior, G. J. F., Santos, M. O., Pelegrini, A., & Silva, D. A. S. (2017). Factors associated with sleep duration in Brazilian high school students. Chronobiology International, 34(6), 773–781. https://doi.org/10.1080/07420528.2017.1323759.
Haario, P., Rahkonen, O., Laaksonen, M., Lahelma, E., & Lallukka, T. (2013). Bidirectional associations between insomnia symptoms and unhealthy behaviours. Journal of Sleep Research, 22(1), 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01043.x.
Haddaway, N. R., & Watson, M. J. (2016). On the benefits of systematic reviews for wildlife parasitology. International Journal for Parasitology, 5(2), 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2016.05.002.
Haheim, L. L., Holme, I., Hjermann, I., & Leren, P. (1996). Smoking habits and risk of fatal stroke: 18 years follow up of the Oslo Study. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 50(6), 621–624.
Hamidovic, A., & de Wit, H. (2009). Sleep deprivation increases cigarette smoking. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 93(3), 263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.12.005.
Hargens, T. A., Kaleth, A. S., Edwards, E. S., & Butner, K. L. (2013). Association between sleep disorders, obesity, and exercise: a review. Nature and Science of Sleep, 5, 27–35. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSS.S34838.
Harma, M., Tenkanen, L., Sjoblom, T., Alikoski, T., & Heinsalmi, P. (1998). Combined effects of shift work and life-style on the prevalence of insomnia, sleep deprivation and daytime sleepiness. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health, 24(4), 300–307.
Hertenstein, E., Feige, B., Gmeiner, T., Kienzler, C., Spiegelhalder, K., Johann, A., et al. (2018). Insomnia as a predictor of mental disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 43, 96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2018.10.006.
Hestetun, I., Svendsen, M. V., & Oellingrath, I. M. (2018). Sleep problems and mental health among young Norwegian adolescents. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 72(8), 578–585. https://doi.org/10.1080/08039488.2018.1499043.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Higgins, J. P., & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 21(11), 1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186.
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., & Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj, 327(7414), 557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557.
Huxley, R. R., & Woodward, M. (2011). Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for coronary heart disease in women compared with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Lancet, 378(9799), 1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60781-2.
Ioannidis, J. P., Patsopoulos, N. A., & Evangelou, E. (2007). Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses. Bmj, 335(7626), 914–916. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39343.408449.80.
Jaehne, A., Loessl, B., Barkai, Z., Riemann, D., & Hornyak, M. (2009). Effects of nicotine on sleep during consumption, withdrawal and replacement therapy. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 13(5), 363–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2008.12.003.
Jaehne, A., Unbehaun, T., Feige, B., Lutz, U. C., Batra, A., & Riemann, D. (2012). How smoking affects sleep: a polysomnographical analysis. Sleep Medicine, 13(10), 1286–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2012.06.026.
Jaehne, A., Unbehaun, T., Feige, B., Cohrs, S., Rodenbeck, A., Schutz, A. L., et al. (2015). Sleep changes in smokers before, during and 3 months after nicotine withdrawal. Addiction Biology, 20(4), 747–755. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12151.
Janson, C., Gislason, T., De Backer, W., Plaschke, P., Bjornsson, E., Hetta, J., et al. (1995). Prevalence of sleep disturbances among young adults in three European countries. Sleep, 18(7), 589–597.
Janson, C., Lindberg, E., Gislason, T., Elmasry, A., & Boman, G. (2001). Insomnia in men-a 10-year prospective population based study. Sleep, 24(4), 425–430.
Jayes, L., Haslam, P. L., Gratziou, C. G., Powell, P., Britton, J., Vardavas, C., et al. (2016). SmokeHaz: systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the effects of smoking on respiratory health. Chest, 150(1), 164–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2016.03.060.
Kageyama, M., Odagiri, K., Mizuta, I., Yamamoto, M., Yamaga, K., Hirano, T., et al. (2017). Health-related behaviors associated with subjective sleep insufficiency in Japanese workers: a cross-sectional study. Journal of Occupational Health, 59(2), 139–146. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.16-0038-OA.
Kim, T. K., Lee, H. C., Lee, S. G., Han, K. T., & Park, E. C. (2016). The combined effect of sleep duration and quality on mental health among Republic of Korea Armed Forces. Military Medicine, 181(11), e1581–e1589. https://doi.org/10.7205/milmed-d-15-00538.
Kishimoto, T., & Domino, E. F. (1998). Effects of tobacco smoking and abstinence on middle latency auditory evoked potentials. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 63(5), 571–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9236(98)90108-4.
Lee, J. Y., Brook, J. S., Finch, S. J., & Brook, D. W. (2016). Trajectories of cigarette smoking beginning in adolescence predict insomnia in the mid thirties. Substance Use & Misuse, 51(5), 616–624. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2015.1126747.
Li, L., Wu, C., Gan, Y., Qu, X., & Lu, Z. (2016). Insomnia and the risk of depression: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMC Psychiatry, 16(1), 375. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-016-1075-3.
Li, J., Vitiello, M. V., & Gooneratne, N. S. (2018). Sleep in normal aging. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 13(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2017.09.001.
Liu, X., & Liu, L. (2005). Sleep habits and insomnia in a sample of elderly persons in China. Sleep, 28(12), 1579–1587.
Liu, X., Bragg, F., Yang, L., Kartsonaki, C., Guo, Y., Du, H., et al. (2018a). Smoking and smoking cessation in relation to risk of diabetes in Chinese men and women: a 9-year prospective study of 0.5 million people. The Lancet Public Health, 3(4), e167–e176. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-2667(18)30026-4.
Liu, X., Bragg, F., Yang, L., Kartsonaki, C., Guo, Y., Du, H., et al. (2018b). Smoking and smoking cessation in relation to risk of diabetes in Chinese men and women: a 9-year prospective study of 0·5 million people. The Lancet Public Health, 3(4), e167–e176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(18)30026-4.
Maggi, S., Langlois, J. A., Minicuci, N., Grigoletto, F., Pavan, M., Foley, D. J., & Enzi, G. (1998). Sleep complaints in community-dwelling older persons: prevalence, associated factors, and reported causes. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 46(2), 161–168.
Martinez-Gomez, D., Guallar-Castillon, P., Leon-Munoz, L. M., Lopez-Garcia, E., & Rodriguez-Artalejo, F. (2013). Combined impact of traditional and non-traditional health behaviors on mortality: a national prospective cohort study in Spanish older adults. BMC Medicine, 11, 47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-47.
Milojevich, H. M., & Lukowski, A. F. (2016). Sleep and mental health in undergraduate students with generally healthy sleep habits. PLoS One, 11(6), e0156372. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156372.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The, P. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.
Mong, J. A., & Cusmano, D. M. (2016). Sex differences in sleep: impact of biological sex and sex steroids. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 371(1688), 20150110–20150110. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0110.
Mong, J. A., Baker, F. C., Mahoney, M. M., Paul, K. N., Schwartz, M. D., Semba, K., & Silver, R. (2011). Sleep, rhythms, and the endocrine brain: influence of sex and gonadal hormones. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(45), 16107–16116. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4175-11.2011.
Newcomb, P. A., & Carbone, P. P. (1992). The health consequences of smoking. Cancer Medical Clinics of North America, 76(2), 305–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30355-8.
Nordmann, S., Lions, C., Vilotitch, A., Michel, L., Mora, M., Spire, B., et al. (2016). A prospective, longitudinal study of sleep disturbance and comorbidity in opiate dependence (the ANRS Methaville study). Psychopharmacology, 233(7), 1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4202-4.
O’Keeffe, L. M., Taylor, G., Huxley, R. R., Mitchell, P., Woodward, M., & Peters, S. A. E. (2018). Smoking as a risk factor for lung cancer in women and men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open, 8(10), e021611. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021611.
Office of the Surgeon General, Office on Smoking and Health. (2004). Reports of the surgeon general. In The health consequences of smoking: a report of the surgeon general. Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US).
Ohayon, M. M., & Bader, G. (2010). Prevalence and correlates of insomnia in the Swedish population aged 19-75 years. Sleep Medicine, 11(10), 980–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2010.07.012.
Ohayon, M. M., Zulley, J., Guilleminault, C., Smirne, S., & Priest, R. G. (2001). How age and daytime activities are related to insomnia in the general population: consequences for older people. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 49(4), 360–366.
Oxman, A. D., & Guyatt, G. H. (1993). The science of reviewing research. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 703, 125–133; discussion 133-124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26342.x.
Pandi-Perumal, S. R., Verster, J. C., Kayumov, L., Lowe, A. D., Santana, M. G., Pires, M. L., et al. (2006). Sleep disorders, sleepiness and traffic safety: a public health menace. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 39(7), 863–871.
Patten, C. A., Choi, W. S., Gillin, J. C., & Pierce, J. P. (2000). Depressive symptoms and cigarette smoking predict development and persistence of sleep problems in US adolescents. Pediatrics, 106(2), E23.
Patterson, A. L., Gritzner, S., Resnick, M. P., Dobscha, S. K., Turk, D. C., & Morasco, B. J. (2012). Smoking cigarettes as a coping strategy for chronic pain is associated with greater pain intensity and poorer pain-related function. The Journal of Pain, 13(3), 285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2011.11.008.
Peters, S. A., Huxley, R. R., & Woodward, M. (2013). Smoking as a risk factor for stroke in women compared with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 81 cohorts, including 3,980,359 individuals and 42,401 strokes. Stroke, 44(10), 2821–2828. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.113.002342.
Phillips, B., & Mannino, D. (2005). Correlates of sleep complaints in adults: the ARIC study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 1(3), 277–283.
Reichenheim, M. E., & Coutinho, E. S. (2010). Measures and models for causal inference in cross-sectional studies: arguments for the appropriateness of the prevalence odds ratio and related logistic regression. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-10-66.
Reitsma, M. B., Fullman, N., Ng, M., Salama, J. S., Abajobir, A., Abate, K. H., et al. (2017). Smoking prevalence and attributable disease burden in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet, 389(10082), 1885–1906. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30819-X.
Revicki, D., Sobal, J., & DeForge, B. (1991). Smoking status and the practice of other unhealthy behaviors. Family Medicine, 23(5), 361–364.
Roberts, R. E., Roberts, C. R., & Duong, H. T. (2009). Sleepless in adolescence: prospective data on sleep deprivation, health and functioning. Journal of Adolescence, 32(5), 1045–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2009.03.007.
Sakamoto, N., Gozal, D., Smith, D. L., Yang, L., Morimoto, N., Wada, H., et al. (2017). Sleep duration, snoring prevalence, obesity, and behavioral problems in a large cohort of primary school students in Japan. Sleep, 40(3). https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsw082.
Shahar, E., & Shahar, D. J. (2013). Causal diagrams and the cross-sectional study. Clinical Epidemiology, 5, 57–65. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S42843.
Short, N. A., Mathes, B. M., Gibby, B., Oglesby, M. E., Zvolensky, M. J., & Schmidt, N. B. (2017). Insomnia symptoms as a risk factor for cessation failure following smoking treatment. Addiction Research and Theory, 25(1), 17–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/16066359.2016.1190342.
Sivertsen, B., Salo, P., Mykletun, A., Hysing, M., Pallesen, S., Krokstad, S., et al. (2012). The bidirectional association between depression and insomnia: the HUNT study. Psychosomatic Medicine, 74(7), 758–765. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e3182648619.
Sivertsen, B., Lallukka, T., Salo, P., Pallesen, S., Hysing, M., Krokstad, S., & Simon, O. (2014). Insomnia as a risk factor for ill health: results from the large population-based prospective HUNT Study in Norway. Journal of Sleep Research, 23(2), 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12102.
Smagula, S. F., Stone, K. L., Fabio, A., & Cauley, J. A. (2016). Risk factors for sleep disturbances in older adults: evidence from prospective studies. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 25, 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.01.003.
Smith, M. T., Wickwire, E. M., Grace, E. G., Edwards, R. R., Buenaver, L. F., Peterson, S., et al. (2009). Sleep disorders and their association with laboratory pain sensitivity in temporomandibular joint disorder. Sleep, 32(6), 779–790. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/32.6.779.
Sugawara, Y., Tsuji, I., Mizoue, T., Inoue, M., Sawada, N., Matsuo, K., et al. (2018). Cigarette smoking and cervical cancer risk: an evaluation based on a systematic review and meta-analysis among Japanese women. Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyy158.
Taveira, K. V. M., Kuntze, M. M., Berretta, F., de Souza, B. D. M., Godolfim, L. R., Demathe, T., et al. (2018). Association between obstructive sleep apnea and alcohol, caffeine and tobacco: a meta-analysis. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 45(11), 890–902. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12686.
Theorell-Haglow, J., Akerstedt, T., Schwarz, J., & Lindberg, E. (2015). Predictors for development of excessive daytime sleepiness in women: a population-based 10-year follow-up. Sleep, 38(12), 1995–2003. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.5258.
Thomas, K. M., Redd, L. A., Wright, J. D., & Hartos, J. L. (2017). Sleep and mental health in the general population of elderly women. The Journal of Primary Prevention, 38(5), 495–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10935-017-0484-5.
Thorpy, M. J. (2012). Classification of sleep disorders. Neurotherapeutics, 9(4), 687–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-012-0145-6.
Tom, S. E., Kuh, D., Guralnik, J. M., & Mishra, G. D. (2010). Self-reported sleep difficulty during the menopausal transition: results from a prospective cohort study. Menopause, 17(6), 1128–1135. https://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e3181dd55b0.
Townsend, J., Wilkes, H., Haines, A., & Jarvis, M. (1991). Adolescent smokers seen in general practice: health, lifestyle, physical measurements, and response to antismoking advice. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 303(6808), 947–950. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.303.6808.947.
Troxel, W. M., Robles, T. F., Hall, M., & Buysse, D. J. (2007). Marital quality and the marital bed: examining the covariation between relationship quality and sleep. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 11(5), 389–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2007.05.002.
van de Wouw, E., Evenhuis, H. M., & Echteld, M. A. (2012). Prevalence, associated factors and treatment of sleep problems in adults with intellectual disability: a systematic review. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 33(4), 1310–1332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2012.03.003.
Vitiello, M. V. (2006). Sleep in normal aging. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 1(2), 171–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2006.04.007.
Wetter, D. W., & Young, T. B. (1994). The relation between cigarette smoking and sleep disturbance. Preventive Medicine, 23(3), 328–334. https://doi.org/10.1006/pmed.1994.1046.
Wetter, D. W., Fiore, M. C., Baker, T. B., & Young, T. B. (1995). Tobacco withdrawal and nicotine replacement influence objective measures of sleep. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 63(4), 658–667. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-006x.63.4.658.
Xiaolin Gu, M. M. (2017). Risk factors of sleep disorder after stroke: a meta-analysis. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation, 24(1), 34–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/10749357.2016.1188474.
Yang, Y., Shin, J. C., Li, D., & An, R. (2017). Sedentary behavior and sleep problems: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 24(4), 481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12529-016-9609-0.
Zhang, H. S., Li, Y., Mo, H. Y., Qiu, D. X., Zhao, J., Luo, J. L., et al. (2017). A community-based cross-sectional study of sleep quality in middle-aged and older adults. Quality of Life Research, 26(4), 923–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-016-1408-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, S., Behnezhad, S. Smoking and risk of sleep-related issues: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Can J Public Health 111, 775–786 (2020). https://doi.org/10.17269/s41997-020-00308-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17269/s41997-020-00308-3