Abstract
Background and aim:In the UK, the current management of high-grade gliomas consists of maximal surgical debulking, where possible, followed by radiotherapy. A large, randomized, multicenter trial assessing the addition of temozolomide to radiotherapy found a significant increase in median survival of the order of 2.5 months in favor of the combined treatment (14.6 vs 12.1 months; p < 0.001). Our center has considerable experience with temozolomide and has treated patients with a regimen similar to that used in the above trial. The aim of this study was to confirm whether these results are translated into a benefit when used in clinical practice in the UK.
Material and methods:We present a retrospective study of 86 patients treated for glioblastoma with radiotherapy with or without temozolomide between 1998 and 2003. A search of our radiotherapy database was undertaken and patient records were accessed for histopathology, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy information. Patients who were diagnosed with glioblastoma and who did not receive radiotherapy or only received a palliative dose were excluded from the study. Radiotherapy was administered at a dosage of 60–65Gy in 30–37 fractions over 6 weeks. Temozolomide was administered orally at a dosage of 75 mg/m2daily for 6 weeks throughout the radiotherapy, followed by adjuvant temozolomide given for 6 cycles on days 1–5 of a 28-day cycle (150–200 mg/m2/day).
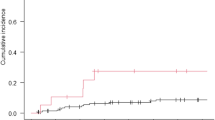
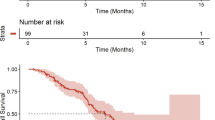
Results:Eighty-six patients (59 male and 27 female; mean age = 55.1 years, range 25–72) with glioblastoma were planned to receive treatment with a radical dosage of radiotherapy. Forty-eight patients (56%) underwent surgical debulking. Forty-nine patients (57%) received concurrent temozolomide and radiotherapy followed by adjuvant temozolomide (median number of cycles received was three). Thirty-seven patients (43%) initially received radiotherapy alone, although nine of those received chemotherapy on further disease progression. Three patients died before treatment was completed. The decision to treat with temozolomide was influenced by the availability of the drug. There were no identifiable patient factors influencing the decision for radical radiotherapy alone or combined radiotherapy and temozolomide. Patients treated with concurrent temozolomide and radiotherapy had a significantly better median survival of 13 months compared with 8 months for those treated with radiotherapy alone (p < 0.003).
Conclusion:The addition of temozolomide to the standard treatment of radiotherapy for glioblastoma improved overall survival. This study shows that the published phase III results in a selective group of patients can be replicated in everyday practice and that the combined regimen is both practical and effective.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levin V, Leibel S, Gutin P. Neoplasms of the central nervous system. In: DeVita V, Hellmen S, Rosenburg S, editors. Cancer: principles and practice of oncology, edition. 5thed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott-Raven, 1997: 2022–82
Kristiansen K, Hagen S, Kollevold T, et al. Combined modality therapy of operated astrocytomas grade III and IV: confirmation of the value of postoperative irradiation and lack of potentiation of bleomycin on survival time: a prospective multicenter trial of the Scandinavian Glioblastoma Study Group. Cancer 1981; 47: 649–52
Stewart LA. Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet 2002; 359: 1011–8
Newlands ES, Foster T, Zaknoen S. Phase I study of temozolamide (TMZ) combined with procarbazine (PCB) in patients with gliomas. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 248–51
Newlands ES, Stevens MF, Wedge SR, et al. Temozolomide: a review of its discovery, chemical properties, pre-clinical development and clinical trials. Cancer Treat Rev 1997; 23: 35–61
Chibbaro S, Benvenuti L, Caprio A, et al. Temozolomide as first-line agent in treating high-grade gliomas: phase II study. J Neurooncol 2004; 67: 77–81
Yung WK, Albright RE, Olson J, et al. A phase II study of temozolomide vs procarbazine in patients with glioblastoma multiforme at first relapse. Br J Cancer 2000; 83: 588–93
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Guidance on the use of temozolomide for the treatment of recurrent malignant glioma [Technology Appraisal Guidance no. 23]. London: NICE, 2001
Stupp R, Dietrich PY, Ostermann Kraljevic S, et al. Promising survival for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 1375–82
Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, et al. The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2002; 61: 215–25
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, et al. CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 2003Jul; 13(3): 176–81
Stupp R, Mason WP, van denBent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 987–96
Jackson RJ, Fuller GN, Abi-Said D, et al. Limitations of stereotactic biopsy in the initial management of gliomas. Neurooncol 2001; 3: 193–200
Schonekaes K, Mucke R, Panke J, et al. Combined radiotherapy and temozolomide in patients with recurrent high grade glioma. Tumori 2002; 88: 28–31
Acknowledgments
No sources of funding were used to assist in the preparation of this study. The author has no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this study
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beresford, M.J., Power, D., Alexander, E. et al. Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma with Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide and Radiotherapy. Am J Cancer 5, 427–432 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2165/00024669-200605060-00008
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00024669-200605060-00008