Abstract
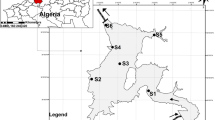
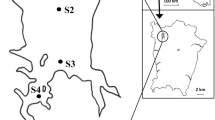
Zooplankton community and its relationship to environmental variables were investigated seasonally between autumn 2006 and summer 2008 in the Gulf of Bandırma (the Sea of Marmara). In the Gulf, we identified nine Copepoda, three Cladocera, one Hydrozoa, one Cydippida, Appendicularia, Bivalvia, Chaetognatha, Cirripedia, Decapoda, Echinodermata, Gastropoda, Polychaeta, Pisces larvae, and Pisces eggs at three sampling stations. Shannon-Weaver diversity index and Pielou’s evenness value ranged between 0.00–2.72 and 0.00–1.00, respectively. The first two components of the redundancy analysis (RDA) explained 81.9% of the variance as the main factors (generally the longest arrows) affecting the spatial and temporal distributions of zooplankton in the Gulf of Bandırma, with dissolved oxygen (DO), nitrite+nitrate (NO3 + NO2-N) and phosphate (PO4-P). Liriope tetraphylla, Oithona nana, Paracalanus parvus, Penilia avirostris, Appendicularia and veliger larvae (Gastropoda) were positively related to DO and salinity, and negatively correlated with temperature, chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), Trophic State Index (Trix), PO4-P, and NO3 + NO2-N. According to Spearman’s rank correlation analysis, there was a strong positive correlation between the number of zooplankton individuals and temperature, and the number of zooplankton individuals negatively correlated with salinity and Chl-a. In order to determine similarities among seasons in the samples, the Bray-Curtis similarity index was calculated using species diversity and abundance values, while Euclidean distances were calculated using ecological parameters. Overall, the diversity of zooplankton in the Gulf of Bandırma was higher in the first sampling year and decreased due to the effect of mucilage in the second sampling year.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Aker HV (2015) Zooplankton of the Aegean Sea. In: Katağan T, Tokaç A, Beşiktepe Ş, Öztürk B (eds) The Aegean Sea marine biodiversity, fisheries, conservation and governance. Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TUDAV), Istanbul, pp 176–187
Altuğ G, Aktan Y, Oral M, Topaloğlu B, Dede A, Keskin Ç, İşinibilir M, Çardak M, Çiftçi PS (2011) Biodiversity of the northern Aegean Sea and southern part of the Sea of Marmara, Turkey. Mar Biodivers Rec 4:e65. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1755267211000662
Atienza D, Saiz E, Calbet A (2006) Feeding ecology of the marine cladoceran Penilia avirostris: natural diet, prey selectivity and daily ration. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 315:211–220. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps315211
Atienza D, Saiz E, Skovgaard A, Trepat I, Calbet A (2008) Life history and population dynamics of the marine cladoceran Penilia avirostris (Branchiopoda: Cladocera) in the Catalan Sea (NW Mediterranean). J Plankton Res 30(4):345–357. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbm109
Balci M, Balkis N, Durmus T, Sivri N (2014) Seasonal variations of nutrients and chlorophyll-a in the coastal waters of the Kapidag peninsula (Marmara Sea). Fresenius Environ Bull 23(12b):3391–3399
Balkis N, Atabay H, Türetgen I, Albayrak S, Balkis H, Tüfekçi V (2011) Role of single-celled organisms in mucilage formation on the shores of Büyükada Island (the Marmara Sea). J Mar Biol Assoc UK 91:771–781. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315410000081
Balkis N, Toklu-Alicli B, Balci M (2012) Evaluation of ecological quality status with the trophic index (TRIX) values in the coastal waters of the gulfs of Erdek and Bandırma in the Marmara Sea. In: Voudouris K (ed) Ecological water quality - water treatment and reuse. InTech, Rijeka, Croatia, pp 1–22. https://doi.org/10.5772/33698
Belmonte G, Rubino F (2019) Resting cysts from coastal marine plankton. In: Hawkins SJ, Allcock AL, Bates AE, Firth LB, Smith IP, Swearer SE, Todd PA (eds) Oceanography and marine biology: an annual review (57). CRC Press, Florida, pp 1–88
Benli H, Tarkan A, Sever T (2001) Comparison of the mesozooplankton composition the southwestern Black Sea, sea of Marmara and eastern Aegean Sea. Turkish J Mar Sci 7(3):163–179
Beşiktepe ŞT, Sur HI, Özsoy E, Abdul Latif M, Oǧuz T, Ünlüata Ü (1994) The circulation and hydrography of the Marmara Sea. Prog Oceanogr 34:285–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6611(94)90018-3
Chiba S, Batten S, Martin CS, Ivory S, Miloslavich P, Weatherdon LV (2018) Zooplankton monitoring to contribute towards addressing global biodiversity conservation challenges. J Plankton Res 40(5):509–518. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fby030
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. PRIMER-E, Plymouth-UK
Hafferssas A, Seridji R (2010) Relationships between the hydrodynamics and changes in copepod structure on the Algerian coast. Zool Stud 49(3):353–366
Isinibilir M (2010) Spatial and temporal variation of zooplankton in two bays in the southern sea of Marmara. Crustaceana 83(2):233–244. https://doi.org/10.1163/001121609X12512848343568
Isinibilir M, Yilmaz IN (2016) Jellyfish species of the sea of Marmara. In: Özsoy E, Çağatay MN, Balkıs N, Balkıs N, Öztürk B (eds) The sea of Marmara marine biodiversity, fisheries, conservation and governance. Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TUDAV), Istanbul, pp 390–400
Isinibilir M, Kideys AE, Tarkan AN, Yilmaz IN (2008) Annual cycle of zooplankton abundance and species composition in Izmit Bay (the northeastern Marmara Sea). Estuar Coast Shelf S 78(4):739–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2008.02.013
Isinibilir M, Yilmaz IN, Piraino S (2010) New contributions to the jellyfish fauna of the Marmara Sea. Ital J Zool 77:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250000902895766
İşinibilir-Okyar M, Üstün F, Orun DA (2015) Changes in abundance and community structure of the zooplankton population during the 2008 mucilage event in the northeastern Marmara Sea. Turk J Zool 39:28–38. https://doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1308-11
Kasapidis P, Siokou I, Khelifi-Touhami M et al (2018) Revising the taxonomic status and distribution of the Paracalanus parvus species complex (Copepoda, Calanoida) in the Mediterranean and black seas through an integrated analysis of morphology and molecular taxonomy. J Plankton Res 40(5):595–605. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fby036
Leps J, Smilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO, multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511615146
Najdek M (1997) Unusual changes of zooplankton fatty acid composition in the northern Adriatic during the 1991 mucilage event. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 159:143–150. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps159143
Öğdül RG, Ergüven H (1992) A study on the abundance and composition of zooplankton groups in the Bay of Beykoz (Bosphorus). Istanbul Univ J Aquat Prod 6:105–120 (in Turkish)
Pielou EC (1966) The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J Theor Biol 13:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-5193(66)90013-0
Sever TM (2009) Pelagic Copepoda fauna of the Aegean Sea and the distribution of the common species. Ege J Fish Aquat Sci 26(3):203–209
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1964) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, USA
Siegel S (1956) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York-USA
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature 163:688. https://doi.org/10.1038/163688a0
Siokou-Frangou I, Papathanassiou E, Lepretre A, Frontier S (1998) Zooplankton assemblages and influence of environmental parameters on them in a Mediterranean coastal area. J Plankton Res 20:847–870. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/20.5.847
Svetlichny LS, Hubareva ES, Kideys AE, İsinibilir M, Shmeleva A (2006) Zooplankton community state in the northeastern Marmara Sea during early autumn with comments on mass mortality of the Black Sea species due to the salinity gradient. J Black Sea/Medit Environ 12(3):213–231
Tarkan AN, Isinibilir M, Tarkan AS (2005) Seasonal variations of the zooplankton composition and abundance in the Istanbul Strait. Pak J Biol Sci 8:1327–1336. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2005.1327.1336
Ter Braak CJF (1986) Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67:1167–1179. https://doi.org/10.2307/1938672
Ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (1998) CANOCO reference manual and user’s guide to Canoco for windows: software for canonical community ordination (version 4). Centre for Biometry, Wageningen, the Netherlands
Terbiyik Kurt T, Polat S (2015) Zooplankton abundance, biomass, and size structure in the coastal waters of the northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Turk J Zool 39:378–387. https://doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1311-14
Toklu Alıçlı B, Sarihan E (2016) Seasonal changes of zooplankton species and groups composition in Iskenderun Bay (north east Levantine, Mediterranean Sea). Pak J Zool 48(5):1395–1405
Toklu-Alıçlı B, Balkis N, Balci M (2014) Seasonal distribution of zooplankton in the Gulf of Erdek (the Marmara Sea) and the impact of ecological variables. Fresenius Environ Bull 23(12):3013–3021
Tüfekci V, Balkis N, Polat Beken C, Ediger D, Mantikci M (2010) Phytoplankton composition and environmental conditions of a mucilage event in the sea of Marmara. Turk J Biol 34(2):199–210. https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-0812-1
Ullyott P, Pektaş H (1952) Çanakkale Boğazı’ndaki yıllık temperatür ve tuzluluk değişmeleri hakkında ilk araştırmalar. Hidrobiyoloji Mecmuası Serie A:19–33 (in Turkish)
Unal E, Shmeleva A, Zagorodnyaya J, Kideys AE (2000) Zooplankton structure and copepod species of the sea of Marmara in spring 1998. In: Öztürk B, Kadıoğlu M, Öztürk H (eds) Marmara Sea 2000 Symposium. Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TUDAV), Istanbul-Turkey, pp 450–460
Uriarte I, Villate F (2005) Differences in the abundance and distribution of copepods in two estuaries of the Basque coast (Bay of Biscay) in relation to pollution. J Plankton Res 27(9):863–874. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbi059
Villate F (1994) Temporal variability of the spatial distribution of the zooplankton community in a coastal embayment of the Basque Country in relation to physical phenomena. Hydrobiologia 288:79–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007128
Wang Y, Zhang W, Lin Y, Cao W, Zheng L, Yang J (2014) Phosphorus, nitrogen and chlorophyll-a are significant factors controlling ciliate communities in summer in the northern Beibu gulf, South China Sea. PLoS One 9(7):e101121. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101121
Weng KC, Pedersen MW, Del Raye GA, Caselle JE, Gray AE (2015) Umbrella species in marine systems: using the endangered humphead wrasse to conserve coral reefs. Endanger Spec Res 27:251–263. https://doi.org/10.3354/esr00663
WoRMS. (2020). Animalia. http://www.marinespecies.org. Accessed 30 May 2020
Yilmaz IN (2015) Collapse of zooplankton stocks during Liriope tetraphylla (hydromedusa) blooms and dense mucilaginous aggregations in a thermohaline stratified basin. Mar Ecol 36:595–610. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12166
Yilmaz IN, Isinibilir M (2016) Zooplankton of the Sea of Marmara. In: Özsoy E, Çağatay MN, Balkıs N, Balkıs N, Öztürk B (eds) The sea of Marmara marine biodiversity, fisheries, conservation and governance. Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TUDAV), Istanbul, pp 376–389
Zar J (2010) Biostatistical analysis. Pearson Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, USA
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Dr. Hüsamettin BALKIS from Istanbul University, Faculty of Science for their valuable assistance. This work was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University, Project Number 541.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University, Project Number 541.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toklu-Alicli, B., Balkis-Ozdelice, N., Durmus, T. et al. Relationship between environmental factors and zooplankton diversity in the Gulf of Bandırma (the Sea of Marmara). Biologia 76, 1727–1736 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00668-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00668-8