Abstract
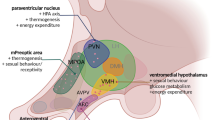
To evaluate whether Orthosiphon stamineus (OS) reduces appetite and fat deposition, food intake and visceral fat mass following treatment with OS (450 mg/kg/day, per oral) for 2 weeks in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were measured. Hypothalamic neuropeptides associated with appetite regulation was also analyzed. Two weeks of OS treatment reduced food intake and visceral fat mass compared to saline-treated SD rats. OS treatment for 2 weeks elevated the expression of proopiomelanocortin (POMC) in the hypothalamus, whereas neuropeptide Y (NPY) expression was decreased, which may be associated with the elevation of plasma leptin concentration in OStreated rats. Methanol and butanol extracts of OS increased leptin mRNA expression in 3T3-L1 cells in dose-dependent manner. Acute study showed intraperitoneal injection of various concentrations of OS increased POMC expression in the hypothalamus, whereas NPY expression decreased dose-dependently. These results suggest that OS reduces appetite, which may have resulted from the increased expression of POMC and decreased expression of NPY in the hypothalamus in association with the elevation of leptin. OS could be a medicinal food applicable for body weight control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah NR, Ismail Z, and Ismail Z (2009) Acute toxicity of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth standardized extract in Sprague Dawley rats. Phytomedicine 16, 222–226.
Adam Y, Somchit MN, Sulaiman MR, Nasaruddin AA, Zuraini A, Bustamam AA, and Zakaria ZA (2009) Diuretic properties of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. J Ethnopharmacol 124, 154–158.
Arafat OM, Tham SY, Sadikun A, Zhari I, Haughton PJ, and Asmawi MZ (2008) Studies on diuretic and hypouricemic effects of Orthosiphon stamineus methanol extracts in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 118, 354–360.
Awale S, Tezuka Y, Banskota AH, Adnyana IK, and Kadota S (2003a) Nitric oxide inhibitory isopimarane-type diterpense from Orthosiphon stamineus of Indonesia. J Nat Prod 66, 255–258.
Awale S, Tezuka Y, Banskota AH, and Kadota S (2003b) Highly-oxygenated isopimarane-type diterpense from Orthosiphon stamineus of Indonesia and their nitric oxide inhibitory activity. Chem Pharm Bull 51, 268–275.
Awale S, Tezuka Y, Banskota AH, and Kadota S (2003c) Siphonols A-E: novel nitric oxide inhibitors from Orthosiphon stamineus of Indonesia. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13, 31–35.
Beaux D, Fleurentin J, and Mortier F (1999) Effect of extracts of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth, Hieracium pilosella L., Sambucus nigra L. and Arctostaphylos uva-ursi (L.) Spreng. in rats. Phytother Res 13, 222–225.
Chin JH, Abas HH, and Sabariah I (2008) Toxicity study of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth (Misai Kucing) on Sprague Dawley rats. Trop Biomed 25, 9–16.
Covasa M and Ritter RC (2001) Attenuated satiation response to intestinal nutrients in rats that do not express CCK-A receptors. Peptides 22, 1339–1348.
de Melo CL, Queiroz MG, Arruda Filho AC, Rodrigues AM, de Sousa DF, Almeida JG, Pessoa OD, Silveira ER, Menezes DB, Melo TS, Santos FA, and Rao VS (2009) Betulinic acid, a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid, prevents abdominal fat accumulation in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Agric Food Chem 57, 8776–8781.
de Melo CL, Queiroz MG, Fonseca SG, Bizerra AM, Lemos TL, Melo TS, Santos FA, and Rao VS (2010) Oleanolic acid, a natural triterpenoid improves blood glucose tolerance in normal mice and ameliorates visceral obesity in mice fed a high-fat diet. Chem Biol Interact 185, 59–65.
Halaas JL, Boozer C, Blair-West J, Fidahusein N, Denton DA, and Friedman JM (1997) Physiological response to longterm peripheral and central leptin infusion in lean and obese mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94, 8878–8883.
Han CJ, Hussin AH, and Ismail S (2008) Toxicity study of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth (Misai Kucing) on Sprague Dawley rats. Trop Biomed 25, 9–16.
Jayaprakasam B, Olson LK, Schutzki RE, Tai MH, and Nair MG (2006) Amelioration of obesity and glucose intolerance in high-fat-fed C57BL/6 mice by anthocyanins and ursolic acid in Cornelian cherry (Cornus mas). J Agric Food Chem 54, 243–248.
Jeffery RW, Drewnowski A, Epstein LH, Stunkard AJ, Wilson GT, Wing RR, and Hill DR (2000) Longterm maintenance of weight loss: current status. Health Psychol 19 (suppl), 5–16.
Kim YW, Kim JY, Park YH, Park SY, Won KC, Choi KH, Huh JY, and Moon KH (2006) Metformin restores leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed obese rats with leptin resistance. Diabetes 55, 716–724.
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Orte D, Seeley RJ, and Baskin DG (2000) Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404, 661–671.
Sriplang K, Adisakwattana S, and Rungsipipiat A (2007) Effects of Orthosiphon stamineus aqueous extract on plasma glucose concentration and lipid profile in normal and stretozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 109, 510–514.
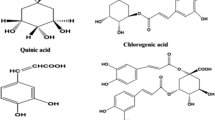
Tezuka Y, Stampoulis P, Banskota AH, Awale S, Tran KQ, Saiki I, and Kadota S (2000) Constituents of the Vietnamese medicinal plant Orthosiphon stamineus. Chem Pharm Bull 48, 1711–1719.
Wadden TA, Crerand CE, and Brock J (2005) Behavioral treatment of obesity. Psychiatr Clin North Am 28, 151–170.
Wang Y and Beydoun MA (2007) The obesity epidemic in the United States-gender, age, socioeconomic, racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev 29, 6–28.
Xiong Y, Shen L, Liu KJ, Tso P, Xiong Y, Wang G, Woods SC, and Liu M (2010) Antiobesity and antihyperglycemic effects of ginsenoside Rb1 in rats. Diabetes 59, 2505–2512.
Yam MF, Asmawi MZ, and Basir R (2008) An investigation of the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Orthosiphon stamineus leaf extract. J Med Food 11, 362–368.
Yam MF, Basir R, Asmawi MZ, and Ismail Z (2007) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. standardized extract. Am J Chin Med 35, 115–126.
Yang DJ, Chang YY, Hsu CL, Liu CW, Lin YL, Lin YH, Liu KC, and Chen YC (2010) Antiobesity and hypolipidemic effects of polyphenol-rich longan (Dimocarpus longans Lour.) flower water extract in hypercaloric-dietary rats. J Agric Food Chem 58, 2020–2027.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, JY., Park, SY., Kim, JY. et al. Orthosiphon stamineus reduces appetite and visceral fat in rats. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 54, 200–205 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.033
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2011.033