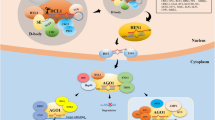
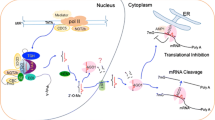
Abstract
miRNAs in plant plays crucial role in controlling proper growth, development and fitness by modulating the expression of their target genes. Therefore to modulate the expression of any stress/development related gene specifically, it is better to modulate expression of the miRNA that can target that gene. To modulate the expression level of miRNA, it is prerequisite to uncover the underlying molecular mechanism of its biogenesis. The biogenesis pathway consists of two major steps, transcription of MIR gene to pri-MIRNA and processing of pri-MIRNA into mature miRNA via sequential cleavage steps. Both of these pathways are tightly controlled by several different factors involving structural and functional molecules. This review is mainly focused on different aspects of pri-MIRNA processing mechanism to emphasize on the fact that to modulate the level of a miRNA in the cell only over-expression or knock-down of that MIR gene is not always sufficient rather it is also crucial to take processing regulation into consideration. The data collected from the recent and relevant literatures depicts that processing regulation is controlled by several aspects like structure and size of the pri-MIRNA, presence of introns in MIR gene and their location, interaction of processing factors with the core components of processing machinery etc. These detailed information can be utilized to figure out the particular point which can be utilized to modulate the expression of the miRNA which would ultimately be beneficial for the scientist and researcher working in this field to generate protocol for engineering plant with improved yield and stress tolerance.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- pri-MIRNA :
-
Primary microRNA
- DCL1:
-
Dicer like 1
- RISC:
-
RNA-induced silencing complex
- CBC:
-
cap-binding complex
- SE:
-
Serrate
- HYL1:
-
Hyponastic leaves 1
- DDL:
-
Dawdle
- TGH:
-
TOUGH
- HEN1:
-
HUA ENHANCER1
- HST:
-
HASTY
- AGO1:
-
ARGONAUTE
- hnRNPs:
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins
- XCT:
-
XAP5 CIRCADIAN TIMEKEEPER
- RACK1:
-
RECEPTOR FOR ACTIVATED C KINASE 1
- RCF3:
-
REGULATOR OF CBF GENE EXPRESSION 3
- PP4:
-
Protein Phosphatase 4
- MAC:
-
MOS4-Associated Complex
- SIC:
-
SICKLE
- STA1:
-
STABILIZED1
- HOS5:
-
HIGH OSMOTIC STRESS GENE EXPRESSION 5
- DOG1:
-
DELAY OF GERMINATION1
- EMU:
-
ERECTA mRNA UNDER-EXPRESSED
- MTA:
-
MRNA adenosine methylase
- HESO1:
-
HEN1 SUPPRESSOR 1
- SDN1:
-
SMALL-RNA-DEGRADING NUCLEASES
- EMA1:
-
ENHANCED miRNA ACTIVITY1
- TRN1:
-
TRANSPORTIN1
References
Achkar NP, Cho SK, Poulsen C, Arce AL, Re DA, Giudicatti AJ et al (2018) A Quick HYL1-dependent reactivation of MicroRNA production is required for a proper developmental response after extended periods of light deprivation. Dev Cell 46:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2018.06.014
Addo-Quaye C, Snyder JA, Park YB, Li YF, Sunkar R, Axtell MJ (2009) Sliced microRNA targets and precise loop-first processing of MIR319 hairpins revealed by analysis of the Physcomitrella patens degradome. RNA 15:2112–2121. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1774909
Bai M, Yang GS, Chen WT, Mao ZC, Kang HX, Chen GH, Yang YH, Xie BY (2012) Genome-wide identification of Dicer-like, Argonaute and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene families and their expression analyses in response to viral infection and abiotic stresses in Solanum lycopersicum. Gene 501:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.02.009
Bajczyk M, Lange H, Bielewicz D, Szewc L, Bhat SS, Dolata J, Kuhn L, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Gagliardi D, Jarmolowski A (2020) SERRATE interacts with the nuclear exosome targeting (NEXT) complex to degrade primary miRNA precursors in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 48:6839–6854. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa373
Baranauskė S, Mickutė M, Plotnikova A, Finke A, Venclovas Č, Klimašauskas S, Vilkaitis G (2015) Functional mapping of the plant small RNA methyltransferase: HEN1 physically interacts with HYL1 and DICER-LIKE 1 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 43:2802–2812. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv102
Basso MF, Ferreira PC, Kobayashi AK, Harmon FG, Nepomuceno AL, Molinari HB, Grossi-de-Sa MF (2019) Micro RNA s and new biotechnological tools for its modulation and improving stress tolerance in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 17(8):1482–1500. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13116
Ben Chaabane S, Liu R, Chinnusamy V, Kwon Y, Park JH, Kim SY, Zhu JK, Yang SW, Lee BH (2013) STA1, an Arabidopsis pre-mRNA processing factor 6 homolog, is a new player involved in miRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 41:1984–1997. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1309
Bhat SS, Bielewicz D, Grzelak N, Gulanicz T, Bodi Z, Szewc L, Bajczyk M, Dolata J, Smolinski D, Fray RG, Jarmolowski A (2019) mRNA adenosine methylase (MTA) deposits m6A on pri-miRNAs to modulate miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2003733117
Bielewicz D, Kalak M, Kalyna M, Windels D, Barta A, Vazquez F, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A (2013) Introns of plant pri-miRNAs enhance miRNA biogenesis. EMBO Rep 14:622–628. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2013.62
Bologna NG, Mateos JL, Bresso EG, Palatnik JF (2009) A loop-to-base processing mechanism underlies the biogenesis of plant microRNAs miR319 and miR159. EMBO J 28:3646–3656. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.292
Bologna NG, Schapire AL, Palatnik JF (2013a) Processing of plant microRNA precursors. Brief Funct Genomics 12:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/els050
Bologna NG, Schapire AL, Zhai J, Chorostecki U, Boisbouvier J, Meyers BC, Palatnik JF (2013b) Multiple RNA recognition patterns during microRNA biogenesis in plants. Genome Res 23:1675–1689. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.153387.112
Bologna NG, Iselin R, Abriata LA, Sarazin A, Pumplin N, Jay F, Grentzinger T, Dal Peraro M, Voinnet O (2018) Nucleo-cytosolic Shuttling of ARGONAUTE1 prompts a revised model of the plant MicroRNA Pathway. Mol Cell 69:709–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.007
Bouché N, Lauressergues D, Gasciolli V, Vaucheret H (2006) An antagonistic function for Arabidopsis DCL2 in development and a new function for DCL4 in generating viral siRNAs. EMBO J 25:3347–3356. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601217
Budak H, Akpinar BA (2015) Plant miRNAs: biogenesis, organization and origins. Funct Integr Genomics 15:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0451-2
Calderon-Villalobos LI, Kuhnle C, Dohmann EM, Li H, Bevan M, Schwechheimer C (2005) The evolutionarily conserved TOUGH protein is required for proper development of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 17:2473–2485. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.031302
Carbonell A, Fahlgren N, Garcia-Ruiz H, Gilbert KB, Montgomery TA, Nguyen T, Cuperus JT, Carrington JC (2012) Functional analysis of three Arabidopsis ARGONAUTES using slicer-defective mutants. Plant Cell 24:3613–3629. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099945
Chand SK, Nanda S, Mishra R, Joshi RK (2017) Multiple garlic (Allium sativum L.) microRNAs regulate the immunity against the basal rot fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cepae. Plant Sci 257:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.01.007
Chen L, Luan Y, Zhai J (2015a) Sp-miR396a-5p acts as a stress-responsive genes regulator by conferring tolerance to abiotic stresses and susceptibility to Phytophthora nicotianae infection in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 34:2013–2025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1847-0
Chen T, Cui P, Xiong L (2015b) The RNA-binding protein HOS5 and serine/arginine-rich proteins RS40 and RS41 participate in miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 43:8283–8298. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv751
Chen J, Liu L, You C, Gu J, Ruan W, Zhang L, Gan J, Cao C, Huang Y, Chen X, Ma J (2018) Structural and biochemical insights into small RNA 3′ end trimming by Arabidopsis SDN1. Nat Commun 9:3585. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05942-7
Cho SK, Chaabane SB, Shah P, Poulsen CP, Yang SW (2014) COP1 E3 ligase protects HYL1 to retain microRNA biogenesis. Nat Commun 5:5867. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6867
Cho SK, Ryu MY, Poulsen C, Kim JH, Oh TR, Choi SW, Kim M, Yang JY, Boo KH, Geshi N, Kim WT (2017) HIGLE is a bifunctional homing endonuclease that directly interacts with HYL1 and SERRATE in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 591:1383–1393. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12628
Chorostecki U, Moro B, Rojas AM, Debernardi JM, Schapire AL, Notredame C, Palatnik JF (2017) Evolutionary footprints reveal insights into plant microRNA biogenesis. Plant Cell 29:1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00272
Cui Y, Fang X, Qi Y (2016) TRANSPORTIN1 promotes the association of MicroRNA with ARGONAUTE1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 28:2576–2585. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00384
Cui X, Yan Q, Gan S, Xue D, Dou D, Guo N, Xing H (2017) Overexpression of gma-miR1510a/b suppresses the expression of a NB-LRR domain gene and reduces resistance to Phytophthora sojae. Gene 621:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.04.015
Djami-Tchatchou AT, Sanan-Mishra N, Ntushelo K, Dubery IA (2017) Functional roles of microRNAs in agronomically important plants—potential as targets for crop improvement and protection. Front Plant Sci 22(8):378. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00378
Dolata J, Bajczyk M, Bielewicz D, Niedojadlo K, Niedojadlo J, Pietrykowska H, Walczak W, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A (2016) Salt stress reveals a new role for ARGONAUTE1 in miRNA biogenesis at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Plant Physiol 172:297–312. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00830
Drusin SI, Suarez IP, Gauto DF, Rasia RM, Moreno DM (2016) dsRNA–protein interactions studied by molecular dynamics techniques. Unravelling dsRNA recognition by DCL1. Arch Biochem Biophys 596:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2016.03.013
Fang Y, Spector DL (2007) Identification of nuclear dicing bodies containing proteins for microRNA biogenesis in living Arabidopsis plants. Curr Biol 17:818–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.04.005
Fang X, Cui Y, Li Y, Qi Y (2015a) Transcription and processing of primary microRNAs are coupled by Elongator complex in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 1:15075. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.75
Fang X, Shi Y, Lu X, Chen Z, Qi Y (2015b) CMA33/XCT Regulates small RNA production through modulating the transcription of dicer-like genes in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 8:1227–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.03.002
Finnegan EJ, Matzke MA (2003) The small RNA world. J Cell Sci 116:4689–4693. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00838
Francisco-Mangilet AG, Karlsson P, Kim MH, Eo HJ, Oh SA, Kim JH, Kulcheski FR, Park SK, Manavella PA (2015) THO2, a core member of the THO/TREX complex, is required for microRNA production in Arabidopsis. Plant J 82:1018–1029. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12874
Fujioka Y, Utsumi M, Ohba Y, Watanabe Y (2007) Location of a possible miRNA processing site in SmD3/SmB nuclear bodies in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1243–1253. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcm099
Fukudome A, Fukuhara T (2017) Plant dicer-like proteins: double-stranded RNA-cleaving enzymes for small RNA biogenesis. J Plant Res 130:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-016-0877-1
Furumizu C, Tsukaya H, Komeda Y (2010) Characterization of EMU, the Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast THO complex member HPR1. RNA 16:1809–1817. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2265710
Gao S, Wang J, Jiang N, Zhang S, Wang Y, Zhang J, Li N, Fang Y, Yang L, Chen S, Yan B (2020) Hyponastic Leaves 1 protects pri-miRNAs from nuclear exosome attack. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:17429–17437. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2007203117
Guil S, Cáceres JF (2007) The multifunctional RNA-binding protein hnRNP A1 is required for processing of miR-18a. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:591–596. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1250
Ha M, Kim VN (2014) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:509–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3838
Huang J, Yang M, Zhang X (2016) The function of small RNAs in plant biotic stress response. J Integr Plant Biol 58:312–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12463
Huo H, Wei S, Bradford KJ (2016) DELAY OF GERMINATION1 (DOG1) regulates both seed dormancy and flowering time through microRNA pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:2199–2206. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1600558113
Jagtap S, Shivaprasad PV (2014) Diversity, expression and mRNA targeting abilities of Argonaute-targeting miRNAs among selected vascular plants. BMC Genom 15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1049
Jia T, Zhang B, You C, Zhang Y, Zeng L, Li S, Johnson KC, Yu B, Li X, Chen X (2017) The Arabidopsis MOS4-associated complex promotes microRNA biogenesis and precursor messenger RNA splicing. Plant Cell 29:2626–2643. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00370
Jodder J, Basak S, Das R, Kundu P (2017) Coherent regulation of miR167a biogenesis and expression of auxin signaling pathway genes during bacterial stress in tomato. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 100:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.08.001
Jodder J, Das R, Sarkar D, Bhattacharjee P, Kundu P (2018) Distinct transcriptional and processing regulations control miR167a level in tomato during stress. RNA Biol 15:130–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2017.1391438
Karlsson P, Christie MD, Seymour DK, Wang H, Wang X, Hagmann J, Kulcheski F, Manavella PA (2015) KH domain protein RCF3 is a tissue-biased regulator of the plant miRNA biogenesis cofactor HYL1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:14096–14101. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512865112
Kim S, Yang JY, Xu J, Jang IC, Prigge MJ, Chua NH (2008) Two cap-binding proteins CBP20 and CBP80 are involved in processing primary MicroRNAs. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1634–1644. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcn146
Kim W, Benhamed M, Servet C, Latrasse D, Zhang W, Delarue M, Zhou DX (2009) Histone acetyltransferase GCN5 interferes with the miRNA pathway in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 19:899–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.59
Kim W, Jun AR, Ahn JH (2016a) Proximal disruption of base pairing of the second stem in the upper stem of pri-miR156a caused ambient temperature-sensitive flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 11:e1226455. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2016.1226455
Kim W, Kim HE, Jun AR, Jung MG, Jin S, Lee JH, Ahn JH (2016b) Structural determinants of miR156a precursor processing in temperature-responsive flowering in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 67:4659–4670. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw248
Kim HE, Kim W, Lee AR, Jin S, Jun AR, Kim NK, Lee JH, Ahn JH (2017a) Base-pair opening dynamics of the microRNA precursor pri-miR156a affect temperature-responsive flowering in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 484:839–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.185
Kim W, Kim HE, Lee AR, Jun AR, Jung MG, Ahn JH, Lee JH (2017b) Base-pair opening dynamics of primary miR156a using NMR elucidates structural determinants important for its processing level and leaf number phenotype in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 45:875–885. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw747
Köster T, Meyer K, Weinholdt C, Smith LM, Lummer M, Speth C, Grosse I, Weigel D, Staiger D (2014) Regulation of pri-miRNA processing by the hnRNP-like protein AtGRP7 in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 42:9925–9936. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku716
Kurihara Y, Takashi Y, Watanabe Y (2006) The interaction between DCL1 and HYL1 is important for efficient and precise processing of pri-miRNA in plant microRNA biogenesis. RNA 12:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2146906
Laubinger S, Sachsenberg T, Zeller G, Busch W, Lohmann JU, Rätsch G, Weigel D (2008) Dual roles of the nuclear cap-binding complex and SERRATE in pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA processing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:8795–8800. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0802493105
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek SH, Kim VN (2004) MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J 23:4051–4060. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600385
Lee WC, Lu SH, Lu MH, Yang CJ, Wu SH, Chen HM (2015) Asymmetric bulges and mismatches determine 20-nt microRNA formation in plants. RNA Biol 12:1054–1066. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1079682
Li J, Yang Z, Yu B, Liu J, Chen X (2005) Methylation protects miRNAs and siRNAs from a 3’-end uridylation activity in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 15:1501–1507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.029
Li Z, Wang S, Cheng J, Su C, Zhong S, Liu Q, Fang Y, Yu Y, Lv H, Zheng Y, Zheng B (2016) Intron Lariat RNA Inhibits MicroRNA Biogenesis by Sequestering the Dicing Complex in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 12:e1006422. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006422
Li S, Liu K, Zhang S, Wang X, Rogers K, Ren G, Zhang C, Yu B (2017) STV1, a ribosomal protein, binds primary microRNA transcripts to promote their interaction with the processing complex in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:1424–1429. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1613069114
Li S, Liu K, Zhou B, Li M, Zhang S, Zeng L, Zhang C, Yu B (2018a) MAC3A and MAC3B, two core subunits of the MOS4-associated complex, positively influence miRNA biogenesis. Plant Cell 30:481–494. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00953
Li S, Xu R, Li A, Liu K, Gu L, Li M, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhuang S, Wang Q, Gao G (2018b) SMA1, a homolog of the splicing factor Prp28, has a multifaceted role in miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 46:9148–9159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky591
Lin Z, Yin K, Zhu D, Chen Z, Gu H, Qu LJ (2007) AtCDC5 regulates the G2 to M transition of the cell cycle and is critical for the function of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem. Cell Res 17:815–828. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.71
Liu N, Wu S, Van Houten J, Wang Y, Ding B, Fei Z, Clarke TH, Reed JW, Van Der Knaap E (2014) Down-regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORS 6 and 8 by microRNA 167 leads to floral development defects and female sterility in tomato. J Exp Bot 65:2507–2520. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru141
Llave C, Kasschau KD, Rector MA, Carrington JC (2002) Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14:1605–1619. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.003210
Lobbes D, Rallapalli G, Schmidt DD, Martin C, Clarke J (2006) SERRATE: a new player on the plant microRNA scene. EMBO Rep 7:1052–1058. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400806
Lowder LG, Paul JW, Qi Y (2017) Multiplexed transcriptional activation or repression in plants using CRISPR-dCas9-based systems. Methods Mol Biol 1629:167–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7125-1_12
Lu C, Fedoroff N (2000) A mutation in the Arabidopsis HYL1 gene encoding a dsRNA binding protein affects responses to abscisic acid, auxin, and cytokinin. Plant Cell 12:2351–2366. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.12.2351
Machida S, Yuan YA (2013) Crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana Dawdle forkhead-associated domain reveals a conserved phospho-threonine recognition cleft for dicer-like 1 binding. Mol Plant 6:1290–1300. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst007
Machida S, Chen HY, Adam Yuan Y (2011) Molecular insights into miRNA processing by Arabidopsis thaliana SERRATE. Nucleic Acids Res 39:7828–7836. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr428
Manavella PA, Hagmann J, Ott F, Laubinger S, Franz M, Macek B, Weigel D (2012) Fast-forward genetics identifies plant CPL phosphatases as regulators of miRNA processing factor HYL1. Cell 151:859–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.09.039
Mateos JL, Bologna NG, Chorostecki U, Palatnik JF (2010) Identification of microRNA processing determinants by random mutagenesis of Arabidopsis MIR172a precursor. Curr Biol 20:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.072
Narjala A, Nair A, Tirumalai V, Hari Sundar GV, Shivaprasad PV (2020) A conserved sequence signature is essential for robust plant miRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 48:3103–3118. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa077
Pan J, Huang D, Guo Z, Kuang Z, Zhang H, Xie X, Ma Z, Gao S, Lerdau MT, Chu C, Li L (2018) Overexpression of microRNA408 enhances photosynthesis, growth, and seed yield in diverse plants. J Integr Plant Biol 60:323–340. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12634
Park MY, Wu G, Gonzalez-Sulser A, Vaucheret H, Poethig RS (2005) Nuclear processing and export of microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3691–3696. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405570102
Plotnikova A, Baranauskė S, Osipenko A, Klimašauskas S, Vilkaitis G (2013) Mechanistic insights into small RNA recognition and modification by the HEN1 methyltransferase. Biochem J 453:281–290. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20121699
Prigge MJ, Wagner DR (2001) The Arabidopsis serrate gene encodes a zinc-finger protein required for normal shoot development. Plant Cell 13:1263–1279. https://doi.org/10.1105/TPC.010095
Raghuram B, Sheikh AH, Rustagi Y, Sinha AK (2015) MicroRNA biogenesis factor DRB1 is a phosphorylation target of mitogen activated protein kinase MPK3 in both rice and Arabidopsis. FEBS J 282:521–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13159
Ramachandran V, Chen X (2008) Degradation of microRNAs by a family of exoribonucleases in Arabidopsis. Science 321:1490–1492. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1163728
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16:1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1004402
Ren G, Chen X, Yu B (2012a) Uridylation of miRNAs by hen1 suppressor1 in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 22:695–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.02.052
Ren G, Xie M, Dou Y, Zhang S, Zhang C, Yu B (2012b) Regulation of miRNA abundance by RNA binding protein TOUGH in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:12817–12821. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1204915109
Ren G, Xie M, Zhang S, Vinovskis C, Chen X, Yu B (2014) Methylation protects microRNAs from an AGO1-associated activity that uridylates 5’ RNA fragments generated by AGO1 cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6365–6370. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405083111
Rogers K, Chen X (2013) Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 25:2383–2399. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.113159
Rojas AML, Drusin SI, Chorostecki U, Mateos JL, Moro B, Bologna NG, Bresso EG, Schapire A, Rasia RM, Moreno DM, Palatnik JF (2020) Identification of key sequence features required for microRNA biogenesis in plants. Nat Commun 11:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19129-6
Salvador-Guirao R, Baldrich P, Weigel D, Rubio-Somoza I, San Segundo B (2018) The microRNA miR773 is involved in the Arabidopsis immune response to fungal pathogens. Mol Plant–Microbe Interact 15 31(2):249–259. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-17-0108-R
Schwab R, Speth C, Laubinger S, Voinnet O (2013) Enhanced microRNA accumulation through stemloop-adjacent introns. EMBO Rep 14:615–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2013.58
Slezak-Prochazka I, Durmus S, Kroesen BJ, van den Berg A (2010) MicroRNAs, macrocontrol: regulation of miRNA processing. RNA 16:1087–1095. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1804410
Song L, Han MH, Lesicka J, Fedoroff N (2007) Arabidopsis primary microRNA processing proteins HYL1 and DCL1 define a nuclear body distinct from the Cajal body. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5437–5442. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701061104
Song L, Axtell MJ, Fedoroff NV (2010) RNA secondary structural determinants of miRNA precursor processing in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 20:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.076
Song JB, Gao S, Wang Y, Li BW, Zhang YL, Yang ZM (2016) miR394 and its target gene LCR are involved in cold stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Gene 5:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2015.12.001
Speth C, Willing EM, Rausch S, Schneeberger K, Laubinger S (2013) RACK1 scaffold proteins influence miRNA abundance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 76:433–445. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12308
Starega-Roslan J, Krol J, Koscianska E, Kozlowski P, Szlachcic WJ, Sobczak K, Krzyzosiak WJ (2011) Structural basis of microRNA length variety. Nucleic Acids Res 39:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq727
Stepien A, Knop K, Dolata J, Taube M, Bajczyk M, Barciszewska-Pacak M, Pacak A, Jarmolowski A, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2017) Posttranscriptional coordination of splicing and miRNA biogenesis in plants. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1403
Su C, Li Z, Cheng J, Li L, Zhong S, Liu L, Zheng Y, Zheng B (2017) The Protein Phosphatase 4 and SMEK1 complex dephosphorylates HYL1 to promote miRNA biogenesis by Antagonizing the MAPK cascade in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 41:527–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.05.008 (e5)
Sun Z, Guo T, Liu Y, Liu Q, Fang Y (2015) The roles of Arabidopsis CDF2 in transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of primary MicroRNAs. PLoS Genet 11:e1005598. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005598
Tomassi AH, Ré DA, Romani F, Cambiagno DA, Gonzalo L, Moreno JE, Arce AL, Manavella PA (2020) The intrinsically disordered protein CARP9 bridges HYL1 to AGO1 in the nucleus to promote MicroRNA activity. Plant Physiol 184:316–329. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.20.00258
Tu B, Liu L, Xu C, Zhai J, Li S, Lopez MA, Zhao Y, Yu Y, Ramachandran V, Ren G, Yu B (2015) Distinct and cooperative activities of HESO1 and URT1 nucleotidyl transferases in microRNA turnover in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 11:e1005119. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005119
Wang JJ, Guo HS (2015) Cleavage of INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE28 mRNA by microRNA847 upregulates auxin signaling to modulate cell proliferation and lateral organ growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27:574–590. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00101
Wang W, Ye R, Xin Y, Fang X, Li C, Shi H, Zhou X, Qi Y (2011) An importin β protein negatively regulates MicroRNA activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23:3565–3576. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.091058
Wang L, Song X, Gu L, Li X, Cao S, Chu C, Cui X, Chen X, Cao X (2013) NOT2 proteins promote polymerase II-dependent transcription and interact with multiple MicroRNA biogenesis factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:715–727. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.105882
Wang B, Duan CG, Wang X, Hou YJ, Yan J, Gao C, Kim JH, Zhang H, Zhu JK (2015a) HOS1 regulates Argonaute1 by promoting transcription of the microRNA gene MIR168b in Arabidopsis. Plant J 81:861–870. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12772
Wang Y, Li K, Chen L, Zou Y, Liu H, Tian Y, Li D, Wang R, Zhao F, Ferguson BJ, Gresshoff PM (2015b) MicroRNA167-directed regulation of the auxin response factors GmARF8a and GmARF8b Is required for soybean nodulation and lateral root development. Plant Physiol 168:984–999. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00265
Wang X, Wang Y, Dou Y, Chen L, Wang J, Jiang N, Guo C, Yao Q, Wang C, Liu L, Yu B (2018a) Degradation of unmethylated miRNA/miRNA* s by a DEDDy-type 3′ to 5′ exoribonuclease Atrimmer 2 in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 10 115(28):E6659–E6667. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721917115
Wang Z, Ma Z, Castillo-González C, Sun D, Li Y, Yu B, Zhao B, Li P, Zhang X (2018b) SWI2/SNF2 ATPase CHR2 remodels pri-miRNAs via Serrate to impede miRNA production. Nature 557:516–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0135-x
Wang J, Chen S, Jiang N, Li N, Wang X, Li Z, Li X, Liu H, Li L, Yang Y, Ni T (2019a) Spliceosome disassembly factors ILP1 and NTR1 promote miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:7886–7900. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz526
Wang J, Mei J, Ren G (2019b) Plant microRNAs: biogenesis, homeostasis, and degradation. Front Plant Sci 10:360. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00360
Wang S, Quan L, Li S, You C, Zhang Y, Gao L, Zeng L, Liu L, Qi Y, Mo B, Chen X (2019c) The PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE4 complex promotes transcription and processing of primary microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 31:486–501. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00556
Werner S, Wollmann H, Schneeberger K, Weigel D (2010) Structure determinants for accurate processing of miR172a in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 20:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.073
Wu L, Zhou H, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Ni F, Liu C, Qi Y (2010) DNA methylation mediated by a microRNA pathway. Mol Cell 38:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.008
Wu X, Shi Y, Li J, Xu L, Fang Y, Li X, Qi Y (2013) A role for the RNA-binding protein MOS2 in microRNA maturation in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 23:645–657. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.23
Xie M, Zhang S, Yu B (2015) microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7
Yan J, Wang P, Wang B, Hsu CC, Tang K, Zhang H, Hou YJ, Zhao Y, Wang Q, Zhao C, Zhu X (2017) The SnRK2 kinases modulate miRNA accumulation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 13:e1006753. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006753
Yang L, Liu Z, Lu F, Dong A, Huang H (2006a) SERRATE is a novel nuclear regulator in primary microRNA processing in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:841–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02835.x
Yang Z, Ebright YW, Yu B, Chen X (2006b) HEN1 recognizes 21–24 nt small RNA duplexes and deposits a methyl group onto the 2’ OH of the 3’ terminal nucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res 34:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj474
Yang X, Ren W, Zhao Q, Zhang P, Wu F, He Y (2014) Homodimerization of HYL1 ensures the correct selection of cleavage sites in primary miRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 42:12224–12236. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku907
Yu B, Bi L, Zheng B, Ji L, Chevalier D, Agarwal M, Ramachandran V, Li W, Lagrange T, Walker JC, Chen X (2008) The FHA domain proteins DAWDLE in Arabidopsis and SNIP1 in humans act in small RNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10073–10078. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804218105
Yu Y, Jia T, Chen X (2017a) The ‘how’and ‘where’of plant micro RNAs. New Phytol 216:1002–1017. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14834
Yu Y, Ji L, Le BH, Zhai J, Chen J, Luscher E, Gao L, Liu C, Cao X, Mo B, Ma J (2017b) ARGONAUTE10 promotes the degradation of miR165/6 through the SDN1 and SDN2 exonucleases in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 15:e2001272. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2001272
Yu C, Chen Y, Cao Y, Chen H, Wang J, Bi YM, Tian F, Yang F, Rothstein SJ, Zhou X, He C (2018) Overexpression of miR169o, an overlapping microRNA in response to both nitrogen limitation and bacterial infection, promotes nitrogen use efficiency and susceptibility to bacterial blight in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol 59:1234–1247. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy060
Zhan X, Wang B, Li H, Liu R, Kalia RK, Zhu JK, Chinnusamy V (2012) Arabidopsis proline-rich protein important for development and abiotic stress tolerance is involved in microRNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:18198–18203. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1216199109
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2006) Plant microRNA: a small regulatory molecule with big impact. Dev Biol 289:3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.036
Zhang H, He X, Zhu JK (2013a) RNA-directed DNA methylation in plants: Where to start? RNA Biol 10:1593–1596. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.26312
Zhang S, Xie M, Ren G, Yu B (2013b) CDC5, a DNA binding protein, positively regulates posttranscriptional processing and/or transcription of primary microRNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:17588–17593. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1310644110
Zhang S, Liu Y, Yu B (2014a) PRL1, an RNA-binding protein, positively regulates the accumulation of miRNAs and siRNAs in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 10:e1004841. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004841
Zhang X, Niu D, Carbonell A, Wang A, Lee A, Tun V, Wang Z, Carrington JC, Chia-en AC, Jin H (2014b) ARGONAUTE PIWI domain and microRNA duplex structure regulate small RNA sorting in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 5:5468. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6468
Zhang T, Zhao YL, Zhao JH, Wang S, Jin Y, Chen ZQ, Fang YY, Hua CL, Ding SW, Guo HS (2016) Cotton plants export microRNAs to inhibit virulence gene expression in a fungal pathogen. Nature Plants 2(10):16153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2016.153
Zhang Z, Guo X, Ge C, Ma Z, Jiang M, Li T, Koiwa H, Yang SW, Zhang X (2017) KETCH1 imports HYL1 to nucleus for miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:4011–4016. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1619755114
Zhang S, Dou Y, Li S, Ren G, Chevalier D, Zhang C, Yu B (2018) DAWDLE interacts with DICER-LIKE proteins to mediate small RNA biogenesis. Plant Physiol 177:1142–1151. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00354
Zhang B, You C, Zhang Y, Zeng L, Hu J, Zhao M, Chen X (2020) Linking key steps of microRNA biogenesis by TREX-2 and the nuclear pore complex in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 6:957–969. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-020-0726-z
Zhou J, Deng K, Cheng Y, Zhong Z, Tian L, Tang X, Tang A, Zheng X, Zhang T, Qi Y, Zhang Y (2017) CRISPR-Cas9 based genome editing reveals new insights into microRNA function and regulation in rice. Front Plant Sci 13(8):1598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01598
Zhu H, Zhou Y, Castillo-González C, Lu A, Ge C, Zhao YT, Duan L, Li Z, Axtell MJ, Wang XJ, Zhang X (2013) Bidirectional processing of pri-miRNAs with branched terminal loops by Arabidopsis Dicer-like1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20:1106–1115. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2646
Zuber H, Scheer H, Joly AC, Gagliardi D (2018) Respective contributions of URT1 and HESO1 to the uridylation of 5′ fragments produced From RISC-cleaved mRNAs. Front Plant Sci 9:1438. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01438
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JJ had the idea for the article, performed the literature search and data analysis, drafted and critically revised the work.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Wusheng Liu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jodder, J. Regulation of pri-MIRNA processing: mechanistic insights into the miRNA homeostasis in plant. Plant Cell Rep 40, 783–798 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02660-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02660-7