Abstract
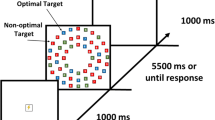
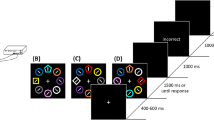
Aversive conditioning has been shown to influence the control of attention, such that aversively conditioned stimuli receive elevated priority. Although aversively conditioned but task-irrelevant distractors are known to capture attention during speeded search in rapid orienting tasks, it is unclear whether this bias extends to situations where orienting can be more deliberate. We demonstrate that punishment, via electric shock, does not give rise to oculomotor capture by shock-associated stimuli during a foraging task; rather, such aversively conditioned stimuli are actively avoided when searching through a display. On the other hand, even during a foraging task, we found some evidence for a covert attentional bias to threat. Our findings indicate that the previously described effects of aversive conditioning on visual search may not generalize beyond the initial glance and can be suppressed when conditions allow for more deliberate search strategies. More generally, our findings reveal that sustained attentional avoidance of aversively conditioned stimuli is possible during active search.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
Raw data and experiment code for both experiments is available on the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/kgp45/).
References
Anderson, B. A. (2016). Value-driven attentional capture in the auditory domain. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 78(1), 242–250.
Anderson, B. A. (2018). Controlled information processing, automaticity, and the burden of proof. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(5), 1814–1823.
Anderson, B. A., & Britton, M. K. (2019). On the automaticity of attentional orienting to threatening stimuli. Emotion. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000596
Anderson, B. A., & Halpern, M. (2017). On the value-dependence of value-driven attentional capture. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 79(4), 1001–1011.
Anderson, B. A., & Kim, H. (2019). On the relationship between value-driven and stimulus-driven attentional capture. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics, 81(3), 607–613.
Anderson, B. A., & Yantis, S. (2012). Value-driven attentional and oculomotor capture during goal-directed, unconstrained viewing. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 74(8), 1644–1653.
Awh, E., Belopolsky, A. V., & Theeuwes, J. (2012). Top–down versus bottom–up attentional control: A failed theoretical dichotomy. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 16(8), 437–443.
Bannerman, R. L., Milders, M., & Sahraie, A. (2010). Attentional bias to brief threat-related faces revealed by saccadic eye movements. Emotion, 10(5), 733–738.
Brainard, D. H. (1997). The psychophysics toolbox. Spatial Vision, 10, 433–436.
Cain, M. S., & Mitroff, S. R. (2013). Memory for found targets interferes with subsequent performance in multiple-target visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 39(5), 1398–1408.
Chukoskie, L., Snider, J., Mozer, M. C., Krauzlis, R. J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (2013). Learning where to look for a hidden target. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110, 10438–10445.
Cisler, J. M., & Koster, E. H. W. (2010). Mechanisms of attentional biases towards threat in the anxiety disorders: An integrative review. Clinical Psychology Review, 30(2), 203–216.
Cunningham, C. A., & Egeth, H. E. (2016). Taming the white bear: Initial costs and eventual benefits of distractor inhibition. Psychological Science, 27(4), 476–485.
Donk, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2001). Visual marking beside the mark: Prioritizing selection by abrupt onsets. Perception & Psychophysics, 63(5), 891–900.
Donk, M., & van Zoest, W. (2008). Effects of salience are short-lived. Psychological Science, 19(7), 733–739.
Failing, M., Nissens, T., Pearson, D., Le Pelley, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2015). Oculomotor capture by stimuli that signal the availability of reward. Journal of Neurophysiology, 114(4), 2316–2327.
Hermans, D., Vansteenwegen, D., & Eelen, P. (1999). Eye movement registration as a continuous index of attention deployment: Data from a group of spider anxious students. Cognition and Emotion, 13(4), 419–434.
Hickey, C., & van Zoest, W. (2012). Reward creates oculomotor salience. Current Biology, 22(7), R219–R220.
Hopkins, L. S., Helmstetter, F. J., & Hannula, D. E. (2016). Eye movements are captured by a perceptually simple conditioned stimulus in the absence of explicit contingency knowledge. Emotion, 16(8), 1157–1171.
Koster, E. H., Crombez, G., Van Damme, S., Verschuere, B., & De Houwer, J. (2004). Does imminent threat capture and hold attention? Emotion, 4(3), 312–317.
Koster, E. H. W., Crombez, G., Verschuere, B., Van Damme, S., & Wiersema, J. R. (2006). Components of attentional bias to threat in high trait anxiety: Facilitated engagement, impaired disengagement, and attentional avoidance. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 44(12), 1757–1771.
Le Pelley, M. E., Watson, P., Pearson, D., Abeywickrama, R. S., & Most, S. B. (2018). Winners and losers: Reward and punishment produce biases in temporal selection. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 45(5), 822–833.
Mogg, K., Bradley, B., Miles, F., & Dixon, R. (2004). Brief report time course of attentional bias for threat scenes: Testing the vigilance-avoidance hypothesis. Cognition and Emotion, 18(5), 689–700.
Moher, J., & Egeth, H. E. (2012). The ignoring paradox: Cueing distractor features leads first to selection, then to inhibition of to-be-ignored items. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics, 74(8), 1590–1605.
Mulckhuyse, M. (2018). The influence of emotional stimuli on the oculomotor system: A review of the literature. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 18(3), 411–425.
Mulckhuyse, M., Crombez, G., & Van der Stigchel, S. (2013). Conditioned fear modulates visual selection. Emotion, 13(3), 529–536.
Mulckhuyse, M., & Dalmaijer, E. S. (2016). Distracted by danger: Temporal and spatial dynamics of visual selection in the presence of threat. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 16(2), 315–324.
Mulckhuyse, M., Van der Stigchel, S., & Theeuwes, J. (2009). Early and late modulation of saccade deviations by target distractor similarity. Journal of Neurophysiology, 102(3), 1451–1458.
Mulckhuyse, M., van Zoest, W., & Theeuwes, J. (2008). Capture of the eyes by relevant and irrelevant onsets. Experimental Brain Research, 186(2), 225–235.
Nissens, T., Failing, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2017). People look at the object they fear: Oculomotor capture by stimuli that signal threat. Cognition and Emotion, 31(8), 1707–1714.
Öhman, A., & Mineka, S. (2001). Fears, phobias, and preparedness: Toward an evolved module of fear and fear learning. Psychological Review, 108(3), 483–522.
Pearson, D., Osborn, R., Whitford, T. J., Failing, M., Theeuwes, J., & Le Pelley, M. E. (2016). Value-modulated oculomotor capture by task-irrelevant stimuli is a consequence of early competition on the saccade map. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 78(7), 2226–2240.
Rinck, M., & Becker, E. S. (2006). Spider fearful individuals attend to threat, then quickly avoid it: Evidence from eye movements. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 115(2), 231–238.
Rouder, J. N., Speckman, P. L., Sun, D., Morey, R. D., & Iverson, G. (2009). Bayesian t tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(2), 225–237.
Sagliano, L., Trojano, L., Amoriello, K., Migliozzi, M., & D’Olimpio, F. (2014). Attentional biases toward threat: The concomitant presence of difficulty of disengagement and attentional avoidance in low trait anxious individuals. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 685.
Sali, A. W., Anderson, B. A., Yantis, S., Mostofsky, S. H., & Rosch, K. S. (2018). Reduced value-driven attentional capture among children with ADHD compared to typically developing controls. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 46(6), 1187–1200.
Sawaki, R., & Luck, S. J. (2010). Capture versus suppression of attention by salient singletons: Electrophysiological evidence for an automatic attend-to-me signal. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 72(6), 1455–1470.
Schmidt, L. J., Belopolsky, A. V., & Theeuwes, J. (2012). The presence of threat affects saccade trajectories. Visual Cognition, 20(3), 284–299.
Schmidt, L. J., Belopolsky, A. V., & Theeuwes, J. (2015). Attentional capture by signals of threat. Cognition and Emotion, 29(4), 687–694.
Schmidt, L. J., Belopolsky, A. V., & Theeuwes, J. (2017). The time course of attentional bias to cues of threat and safety. Cognition and Emotion, 31(5), 845–857.
Smith, S. D., Most, S. B., Newsome, L. A., & Zald, D. H. (2006). An emotion-induced attentional blink elicited by aversively conditioned stimuli. Emotion, 6(3), 523–527.
Theeuwes, J., de Vries, G. J., & Godijn, R. (2003). Attentional and oculomotor capture with static singletons. Perception & Psychophysics, 65(5), 735–746.
Thigpen, N. N., Bartsch, F., & Keil, A. (2017). The malleability of emotional perception: Short-term plasticity in retinotopic neurons accompanies the formation of perceptual bias to threat. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 146(4), 464–471.
Van der Stigchel, S., & Theeuwes, J. (2007). The relationship between covert and overt attention in endogenous cuing. Perception & Psychophysics, 69(5), 719–731.
van Zoest, W., Donk, M., & Theeuwes, J. (2004). The role of stimulus-driven and goal-driven control in saccadic visual selection. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 30(4), 746–759.
Vuilleumier, P. (2005). How brains beware: Neural mechanisms of emotional attention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(12), 585–594.
Wang, L., Yu, H., & Zhou, X. (2013). Interaction between value and perceptual salience in value-driven attentional capture. Journal of Vision, 13(3), 1–13.
Weaver, M. D., van Zoest, W., & Hickey, C. (2017). A temporal dependency account of attentional inhibition in oculomotor control. NeuroImage, 147, 880–894.
Weierich, M. R., Treat, T. A., & Hollingworth, A. (2008). Theories and measurement of visual attentional processing in anxiety. Cognition and Emotion, 22(6), 985–1018.
Wentura, D., Muller, P., & Rothermund, K. (2014). Attentional capture by evaluative stimuli: Gain- and loss-connoting colors boost the additional singleton effect. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 21(3), 701–707.
Wolfe, J. M., Butcher, S. J., Lee, C., & Hyle, M. (2003). Changing your mind: On the contributions of top-down and bottom-up guidance in visual search for feature singletons. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 29(2), 483–502.
Wolfe, J. M., Cain, M. S., & Aizenman, A. M. (2019). Guidance and selection history in hybrid foraging visual search. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 81(3), 637–653.
Yantis, S., & Jonides, J. (1984). Abrupt visual onsets and selective attention: Evidence from visual search. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 10(5), 601–621.
Funding
This study was supported by Grants from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (NARSAD 26008) and NIH (R01-DA046410) to BAA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Texas A&M University Institutional Review Board and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Britton, M.K., Anderson, B.A. Attentional avoidance of threatening stimuli. Psychological Research 85, 82–90 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-019-01255-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-019-01255-6