Abstract
Purpose
Naringin is a natural dietary flavonoid compound. We aimed to evaluate the effects of naringin on intestinal tumorigenesis in the adenomatous polyposis coli multiple intestinal neoplasia (Apc Min/+) mouse model.
Methods
Apc Min/+ mice were given either naringin (150 mg/kg) or vehicle by p.o. gavage daily for 12 consecutive weeks. Mice were killed with ether, and blood samples were collected to assess the concentrations of IL-6 and PGE2. Total intestines were removed, and the number of polyps was examined. Tissue samples of intestinal polyps were subjected to the assays of histopathology, immunohistochemical analysis and Western blotting analysis.
Results
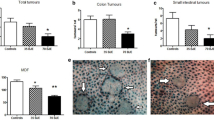
Apc Min/+ mice fed with naringin developed less and smaller polyps in total intestines. Naringin prevented intestinal tumorigenesis without adverse effects. Histopathologic analysis revealed the reduction of dysplastic cells and dysplasia in the adenomatous polyps. The treatments’ effects might arise from its anti-proliferation, induction of apoptosis and modulation of GSK-3β and APC/β-catenin signaling pathways. Naringin also exerted its effects on tumorigenesis through anti-chronic inflammation.
Conclusion
Naringin prevented intestinal tumorigenesis likely through a collection of activities including anti-proliferation, induction of apoptosis, modulation of GSK-3β and APC/β-catenin pathways and anti-inflammation. Naringin is a potential chemopreventive agent for reducing the risk of colonic cancers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeniyi AO, Olubolade AO, Owira PM (2015) Naringin mitigates cardiac hypertrophy by reducing oxidative stress and inactivating c-Jun Nuclear Kinase (JNK-1) protein in type I diabetes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000000325
Adil M, Kandhare AD, Visnagri A, Bodhankar SL (2015) Naringin ameliorates sodium arsenite-induced renal and hepatic toxicity in rats: decisive role of KIM-1, Caspase-3, TGF-β, and TNF-α. Ren Fail 37:1396–1407
Annema N, Heyworth JS, McNaughton SA, Iacopetta B, Fritschi L (2011) Fruit and vegetable consumption and the risk of proximal colon, distal colon, and rectal cancers in a case–control study in Western Australia. J Am Diet Assoc 111:1479–1490
Arvelo F, Sojo F, Cotte C (2015) Biology of colorectal cancer. Ecancermedicalscience 9:520
Banjerdpongchai R, Wudtiwai B, Khaw-On P, Rachakhom W, Duangnil N, Kongtawelert P (2015) Hesperidin from Citrus seed induces human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell apoptosis via both mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3774-7
Boo JH, Song H, Kim JE, Kang DE, Mook-Jung I (2009) Accumulation of phosphorylated β-catenin enhances ROS-induced cell death in presenilin-deficient cells. PLoS ONE 4:e4172
Bosman F, Yan P (2014) Molecular pathology of colorectal cancer. Pol J Pathol 65:257–266
Cheung KL, Lee JH, Khor TO, Wu TY, Li GX, Chan J, Yang CS, Kong AN (2014) Nrf2 knockout enhances intestinal tumorigenesis in Apc(min/+) mice due to attenuation of anti-oxidative stress pathway while potentiates inflammation. Mol Carcinog 53:77–84
Chtourou Y, Aouey B, Kebieche M, Fetoui H (2015) Protective role of naringin against cisplatin induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and apoptosis in rat striatum via suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB and P53 signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact 239:76–86
Cordenonsi LM, Bromberger NG, Raffin RP, Scherman EE (2015) Simultaneous separation and sensitive detection of naringin and naringenin in nanoparticles by chromatographic method indicating stability and photodegradation kinetics. Biomed Chromatogr. doi:10.1002/bmc.3531
Diab S, Fidanzi C, Léger DY, Ghezali L, Millot M, Martin F, Azar R, Esseily F, Saab A, Sol V et al (2015) Berberis libanotica extract targets NF-κB/COX-2, PI3K/Akt and mitochondrial/caspase signalling to induce human erythroleukemia cell apoptosis. Int J Oncol 47:220–230
Fujisawa T, Sugiyama M, Tomimoto A, Wada K, Endo H, Takahashi H, Yoneda K, Yoneda M, Inamori M, Saito S (2008) Inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma promotes tumorigenesis through activation of the beta-catenin/T cell factor (TCF) pathway in the mouse intestine. J Pharmacol Sci 108:535–544
Greene ER, Huang S, Serhan CN, Panigrahy D (2011) Regulation of inflammation in cancer by eicosanoids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 96:27–36
Huang J, Zhang D, Xie F, Lin D (2015) The potential role of COX-2 in cancer stem cell-mediated canine mammary tumor initiation: an immunohistochemical study. J Vet Sci 16:225–231
Jamieson T, Clarke M, Steele CW, Samuel MS, Neumann J, Jung A, Huels D, Olson MF, Das S, Nibbs RJ et al (2012) Inhibition of CXCR2 profoundly suppresses inflammation-driven and spontaneous tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 122:3127–3144
Khare V, Dammann K, Asboth M, Krnjic A, Jambrich M, Gasche C (2015) Overexpression of PAK1 promotes cell survival in inflammatory bowel diseases and colitis-associated cancer. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21:287–296
Klampfer L (2011) Cytokines, inflammation and colon cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11:451–464
Kulasekaran G, Ganapasam S (2015) Neuroprotective efficacy of naringin on 3-nitropropionic acid-induced mitochondrial dysfunction through the modulation of Nrf2 signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Mol Cell Biochem 409:199–211
Kumar A, Pandurangan AK, Lu F, Fyrst H, Zhang M, Byun HS, Bittman R, Saba JD (2012) Chemopreventive sphingadienes downregulate Wnt signaling via a PP2A/Akt/GSK3β pathway in colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 33:1726–1735
Kwong LN, Dove WF (2009) APC and its modifiers in colon cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 656:85–106
Lee J, Kim JC, Lee SE, Quinley C, Kim H, Herdman S, Corr M, Raz E (2012) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein suppresses adenoma-to-carcinoma transition in Apcmin/+ mice via regulation of Snail-1 (SNAI) protein stability. J Biol Chem 287:18182–18189
Leoz ML, Carballal S, Moreira L, Ocaña T, Balaguer F (2015) The genetic basis of familial adenomatous polyposis and its implications for clinical practice and risk management. Appl Clin Genet 8:95–107
Lewinska A, Siwak J, Rzeszutek I, Wnuk M (2015) Diosmin induces genotoxicity and apoptosis in DU145 prostate cancer cell line. Toxicol In Vitro 29:417–425
Li H, Yang B, Huang J, Xiang T, Yin X, Wan J, Luo F, Zhang L, Li H, Ren G (2013) Naringin inhibits growth potential of human triple-negative breast cancer cells by targeting β-catenin signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett 220:219–228
Liu HP, Gao ZH, Cui SX, Wang Y, Li BY, Lou HX, Qu XJ (2013) Chemoprevention of intestinal adenomatous polyposis by acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid in APC(Min/+) mice. Int J Cancer 132:2667–2681
McAlpine CA, Barak Y, Matise I, Cormier RT (2006) Intestinal-specific PPARgamma deficiency enhances tumorigenesis in ApcMin/+ mice. Int J Cancer 119:2339–2346
Meidenbauer JJ, Ta N, Seyfried TN (2014) Influence of a ketogenic diet, fish-oil, and calorie restriction on plasma metabolites and lipids in C57BL/6J mice. Nutr Metab (Lond) 11:23
Merritt AJ, Gould KA, Dove WF (1997) Polyclonal structure of intestinal adenomas in ApcMin/+ mice with concomitant loss of Apc+ from all tumor lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13927–13931
O’Callaghan G, Kelly J, Shanahan F, Houston A (2008) Prostaglandin E2 stimulates Fas ligand expression via the EP1 receptor in colon cancer cells. Br J Cancer 99:502–512
Pierre CC, Longo J, Mavor M, Milosavljevic SB, Chaudhary R, Gilbreath E, Yates C, Daniel JM (2015) Kaiso overexpression promotes intestinal inflammation and potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis in ApcMin/+ mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:1846–1855
Qi Z, Xu Y, Liang Z, Li S, Wang J, Wei Y, Dong B (2015) Naringin ameliorates cognitive deficits via oxidative stress, proinflammatory factors and the PPARγ signaling pathway in a type 2 diabetic rat model. Mol Med Rep. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4232
Raha S, Yumnam S, Hong GE, Lee HJ, Saralamma VV, Park HS, Heo JD, Lee SJ, Kim EH, Kim JA, Kim GS (2015) Naringin induces autophagy-mediated growth inhibition by downregulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR cascade via activation of MAPK pathways in AGS cancer cells. Int J Oncol 47:1061–1069
Rajamanickam S, Velmurugan B, Kaur M, Singh RP, Agarwal R (2010) Chemoprevention of intestinal tumorigenesis in APCmin/+ mice by silibinin. Cancer Res 70:2368–2378
Rigby RJ, Simmons JG, Greenhalgh CJ, Alexander WS, Lund PK (2007) Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) limits damage-induced crypt hyper-proliferation and inflammation-associated tumorigenesis in the colon. Oncogene 26:4833–4841
Schneikert J, Vijaya Chandra SH, Ruppert JG, Ray S, Wenzel EM, Behrens J (2013) Functional comparison of human adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and APC-like in targeting beta-catenin for degradation. PLoS ONE 8:e68072
Shih IM, Wang TL, Traverso G, Romans K, Hamilton SR, Ben-Sasson S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (2001) Top-down morphogenesis of colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2640–2645
Tarapore RS, Siddiqui IA, Mukhtar H (2012) Modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by bioactive food components. Carcinogenesis 33:483–491
van Noort M, Meeldijk J, van der Zee R, Destree O, Clevers H (2002) Wnt signaling controls the phosphorylation status of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 277:17901–17905
Wang R, Wang Y, Gao Z, Qu X (2014) The comparative study of acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA) and aspirin in the prevention of intestinal adenomatous polyposis in APC(Min/+) mice. Drug Discov Ther 8:25–32
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (91229113, 81173090, 81373435) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR2009CQ019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We confirm that there is no potential conflict of interest or financial dependence regarding this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YS., Li, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Naringin, a natural dietary compound, prevents intestinal tumorigenesis in Apc Min/+ mouse model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 913–925 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2097-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2097-9