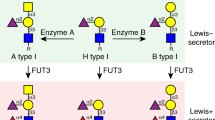
Abstract
Together, norovirus and rotavirus are responsible for the majority of gastroenteritis cases worldwide, leading to a large number of deaths of children in low-income countries. Both attach to glycans of the histo-blood group antigen type (HBGAs) widely expressed in the digestive tract of vertebrates, albeit with interspecies differences. In humans, their synthesis is performed by glycosyltransferases encoded by the highly polymorphic ABO, FUT2 and FUT3 genes that are under long-term balanced selection. The combination of functional and null or weak alleles at these loci provides a diversity of glycan structures that define the ABO, Secretor and Lewis phenotypes. At the initial stage of infection norovirus and rotavirus attach to these glycans, although distinct strains of each virus present different specificities for individual glycans, hence exhibiting preferences for different human phenotypes. Absence or low expression of the recognized glycan motifs due to genetic polymorphism is associated with resistance to the disease, showing that the HBGA polymorphisms provide a population-based innate protection. Epidemiologically dominant strains of either norovirus or rotavirus display specificity for glycan motifs present in large fractions of the population, which may differ between geographical areas in accordance with the frequency of the ABO, FUT2, FUT3 gene polymorphisms. Evidence for virus adaptation to these geographical differences is amounting, indicative of a host–pathogen co-evolution and suggesting that enteric pathogens such as norovirus and rotavirus are likely the driving forces behind the balanced HBGA polymorphisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrantes J, Posada D, Guillon P, Esteves PJ, Le Pendu J (2009) Widespread gene conversion of alpha-2-fucosyltransferase genes in mammals. J Mol Evol 69:22–31
Alfajaro MM, Kim J-Y, Barbé L, Cho EH, Park J-G, Soliman M, Baek Y-B, Kang M-I, Kim SH, Kim G-J, Park S-I, Le Pendu J, Cho KO (2019) Dual recognition of sialic acid and aGal epitopes by the VP8* domains of the bovine rotavirus G6P[5] WC3 and of its monoreassortant G4P[5] RotaTeq vaccines strains. J Virol 93:e00941-19
Ao Y, Wang J, Ling H, He Y, Dong X, Wang X, Peng J, Zhang H, Jin M, Duan Z (2017) Norovirus GII.P16/GII.2-associated gastroenteritis, China, 2016. Emerg Infect Dis 23:1172–1175
Ayouni S, Sdiri-Loulizi K, de Rougemont A, Estienney M, Ambert-Balay K, Aho S, Hamami S, Aouni M, Neji-Guediche M, Pothier P, Belliot G (2015) Rotavirus P[8] Infections in persons with secretor and nonsecretor phenotypes, Tunisia. Emerg Infect Dis 21:2055–2058
Azevedo L, Serrano C, Amorim A, Cooper DN (2015) Trans-species polymorphism in humans and the great apes is generally maintained by balancing selection that modulates the host immune response. Human Genom. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-015-0043-1
Banyai K, Estes MK, Martella V, Parashar UD (2018) Viral gastroenteritis. Lancet 392:175–186
Barbé L, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Echasserieau K, Bernardeau K, Carton T, Bovin N, Nordgren J, Svensson L, Ruvoën-Clouet N, Le Pendu J (2018) Histo-blood group antigen-binding specificities of human rotaviruses are associated with gastroenteritis but not with in vitro infection. Sci Rep 8:12961
Bu W, Mamedova A, Tan M, Xia M, Jiang X, Hegde RS (2008) Structural basis for the receptor binding specificity of Norwalk virus. J Virol 82:5340–5347
Bucardo F, Nordgren J, Reyes Y, Gonzalez F, Sharma S, Svensson L (2018) The Lewis A phenotype is a restriction factor for RotaTeq and Rotarix vaccine-take in Nicaraguan children. Sci Rep 8:1502
Calafell F, Roubinet F, Ramirez-Soriano A, Saitou N, Bertanpetit J, Blancher A (2008) Evolutionary dynamics of the human ABO gene. Hum Genet 124:123–135
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucl Acid Res 37:D233–D238
Cao S, Lou Z, Tan M, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Jiang X, Li X, Rao Z (2007) Structural basis for the recognition of blood group trisaccharides by norovirus. J Virol 81:5949–5957
Chan MC, Lee N, Hung TN, Kwok K, Cheung K, Tin EK, Lai RW, Nelson EA, Leung TF, Chan PK (2015) Rapid emergence and predominance of a broadly recognizing and fast-evolving norovirus GII.17 variant in late 2014. Nat Commun 6:10061
Chen Y, Tan M, Xia M, Hao N, Zhang XC, Huang P, Jiang X, Li X, Rao Z (2011) Crystallography of a Lewis-binding norovirus, elucidation of strain-specificity to the polymorphic human histo-blood group antigens. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002152
Chhabra P, de Graaf M, Parra F, Chan MC, Green KY, Martella V, Wang Q, White PA, Katayama K, Vennema H, Koopmans MPG, Vinjé J (2019) Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J Gen Virol 100:1393–1406
Choi J-M, Hutson AM, Estes MK, Prasad BV (2008) Atomic resolution structural characterisation of recognition of histo-blood group antigens by Norwalk virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:9175–9180
Cooling L (2015) Blood groups in infection and host susceptibility. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:801–870
de Graaf M, van Beek J, Koopmans MP (2016) Human norovirus transmission and evolution in a changing world. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:421–433
de Rougemont A, Ruvoën-Clouet N, Simon B, Estienney M, Elie-Caille C, Aho S, Pothier P, Le Pendu J, Boireau W, Belliot G (2011) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the binding of GII.4 norovirus variants onto human blood group antigens. J Virol 85:4057–4070
Desselberger U (2014) Rotaviruses. Virus Res 190C:75–96
Enard D, Petrov DA (2018) Evidence that RNA viruses drove adaptive introgression between Neanderthals and modern humans. Cell 175:360–371
Ferrer-Admetlla A, Sikora M, Laayouni H, Esteve A, Roubinet F, Blancher A, Calafell F, Bertanpetit J, Calafell F (2009) A natural history of FUT2 polymorphism in humans. Mol Biol Evol 26:1993–2003
Glass RI, Parashar U, Patel M, Gentsch J, Jiang B (2014) Rotavirus vaccines: successes and challenges. J Infect 68(Suppl 1):18
Hansman G, Biertumpfel C, Georgiev I, McLellan J, Chen L, Zhou T, Katayama K, Kwong P (2011) Crystal structures of GII.10 and GII.12 norovirus protruding domains in complex with histo-blood group antigens reveal details for a potential site of vulnerability. J Virol 85:6687–7388
Hu L, Crawford SE, Czako R, Cortes-Penfield NW, Smith DF, Le Pendu J, Estes MK, Prasad BV (2012) Cell attachment protein VP8* of a human rotavirus specifically interacts with A-type histo-blood group antigen. Nature 485:256–259
Hu L, Sankaran B, Laucirica DR, Patil K, Salmen W, Ferreon ACM, Tsoi PS, Lasanajak Y, Smith DF, Ramani S, Atmar RL, Estes MK, Ferreon JC, Prasad BVV (2018) Glycan recognition in globally dominant human rotaviruses. Nat Commun 9:2631
Huang PW, Farkas T, Marionneau S, Zhong WM, Ruvoën-clouet N, Morrow A, Pickering LK, Newburg DS, Le Pendu J, Jiang X (2003) Norwalk-like viruses bind to ABO, Lewis and secretor histo-blood group antigens but different strains bind to distinct antigens. J Infect Dis 188:19–31
Huang P, Farkas T, Zhong W, Tan M, Thornton SA, Morrow AL, Jiang X (2005) Norovirus and histo-blood group antigens: demonstration of a wide spectrum of strain specificities and classification of two major binding groups among multiple binding patterns. J Virol 79:6714–6722
Huang P, Xia M, Tan M, Zhong W, Wei C, Wang L, Morrow A, Jiang X (2012) Spike protein VP8* of human rotavirus recognizes histo-blood group antigens in a type-specific manner. J Virol 86:4833–4843
Hutson AM, Atmar RL, Graham DY, Estes MK (2002) Norwalk virus infection and disease is associated with ABO histo-blood group type. J Infect Dis 185:1335–1337
Imbert-Marcille B-M, Barbé L, Dupé M, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Besse B, Peltier C, Ruvoën-Clouet N, Le Pendu J (2013) A FUT2 gene common polymorphism determines resistance to rotavirus A of the P[8] genotype. J Infect Dis 209:1227–1230
Jiang X, Liu Y, Tan M (2017) Histo-blood group antigens as receptors for rotaivurs, new understanding on rotavirus epidemiology and vaccine strategy. Emerg Microbes Infect 6:e22
Kambhapati A, Payne DC, Costantini V, Lopman BA (2015) Host genetic susceptibility to enteric viruses: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Clin Infect Dis 62:11–18
Kazi AM, Cortese MM, Yu Y, Lopman B, Morrow AL, Fleming JA, McNeal MM, Steele AD, Parashar UD, Zaidi AKM, Ali A (2017) Secretor and salivary ABO blood group antigen status predict rotavirus vaccine take in infants. J Infect Dis 215:786–789
Kirk MD, Pires SM, Black RE, Caipo M, Crump JA, Devleesschauwer B, Dopfer D, Fazil A, Fischer-Walker CL, Hald T, Hall AJ, Keddy KH, Lake RJ, Lanata CF, Torgerson PR, Havelaar AH, Angulo FJ (2015) World health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 22 foodborne bacterial, protozoal, and viral diseases, 2010: a data synthesis. PLoS Med 12:e1001921
Koromyslova AD, Leuthold MM, Bowler MW, Hansman GS (2015) The sweet quartet: binding of fucose to the norovirus capsid. Virology 483:203–208
Kubota T, Kumagai A, Ito H, Furukawa S, Someya Y, Takeda N, Ishii K, Wakita T, Narimatsu H, Shirato H (2012) Structural basis for the recognition of Lewis antigens by genogroup I norovirus. J Virol 86:11138–11150
Kwok K, Niendorf S, Lee N, Hung TN, Chan LY, Jacobsen S, Nelson EAS, Leung TF, Lai RWM, Chan PKS, Chan MCW (2017) Increased detection of emergent recombinant norovirus GII.P16-GII.2 strains in Young Adults, Hong Kong, China, 2016-2017. Emerg Infect Dis 23:1852–1855. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2311.170561
Le Pendu J, Ruvöen-Clouet N, Kindberg E, Svensson L (2006) Mendelian resistance to human norovirus infections. Sem Immunol 18:375–386
Le Pendu J, Nystrom K, Ruvoen-Clouet N (2014) Host-pathogen co-evolution and glycan interactions. Curr Opin Virol 7:88–94
Lee B, Dickson DM, deCamp AC, Ross Colgate E, Diehl SA, Uddin MI, Sharmin S, Islam S, Bhuiyan TR, Alam M, Nayak U, Mychaleckyj JC, Taniuchi M, Petri WA Jr, Haque R, Qadri F, Kirkpatrick BD (2018) Histo-blood group antigen phenotype determines susceptibility to genotype-specific rotavirus infections and impacts measures of rotavirus vaccine efficacy. J Infect Dis 217:1399–1407
Lindesmith L, Moe CL, Marionneau S, Ruvoën-clouet N, Jiang X, Lindblad L, Stewart PA, Le Pendu J, Baric RS (2003) Human susceptibility and resistance to Norwalk virus infection. Nat Med 9:548–553
Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, Perin J, Scott S, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Campbell H, Cibulskis R, Li M, Mathers C, Black RE (2012a) Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 379:2151–2161
Liu Y, Huang P, Tan M, Biesiada J, Meller J, Castello AA, Jiang B, Jiang X (2012b) Rotavirus VP8*: phylogeny, host range, and interaction with histo-blood group antigens. J Virol 86:9899–9910
Liu Y, Ramelot TA, Huang P, Liu Y, Li Z, Feizi T, Zhong W, Wu F-T, Tan M, Kennedy MA, Jiang X (2016) Glycan specificity of P[19] rotavirus and comparison with those of related P genotypes. J Virol 90:9983–9996
Lopez S, Arias CF (2004) Multistep entry of rotavirus into cells: a Versaillesque dance. Trends Microbiol 12:271–278
Macher BA, Galili U (2008) The Galα 1,3Galβ1,4GlcNAc-R (α-Gal) epitope: a carbohydrate of unique evolution and clinical relevance. Biochem Biophys Acta 1780:75–88
Mallory ML, Lindesmith LC, Graham RL, Baric RS (2019) GII.4 Human norovirus: surveying the antigenic landscape. Viruses 11:E177
Marionneau S, Ruvöen-Clouet N, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Clement M, Cailleau-Thomas A, Riuz-Palacios G, Huang PW, Jiang X, Le Pendu J (2002) Norwalk virus binds to histo-blood group antigens on gastro-duodenal epithelial cells of secretor individuals. Gastroenterology 122:1967–1977
Matthijnssens J, Potgieter CA, Ciarlet M, Parreno V, Martella V, Banyai K, Garaicoechea L, Palombo EA, Novo L, Zeller M, Arista S, Gerna G, Rahman M, Van Ranst M (2009) Are human P[14] rotavirus strains the result of interspecies transmissions from sheep or other ungulates that belong to the mammalian order Artiodactyla? J Virol 83:2917–2929
Matthijnssens J, Otto PH, Ciarlet M, Desselberger U, Van Ranst M, Johne R (2012) VP6-sequence-based cutoff values as a criterion for rotavirus species demarcation. Arch Virol 157:1177–1182
Niendorf S, Jacobsen S, Faber M, Eis-Hubinger AM, Hofmann J, Zimmermann O, Hohne M, Bock CT (2017) Steep rise in norovirus cases and emergence of a new recombinant strain GII.P16-GII.2, Germany, winter 2016. Euro Surveill 22:30447
Nordgren J, Svensson L (2019) Genetic susceptibility to human norovirus infection: an update. Viruses 11:E226
Nordgren J, Nitiema LW, Ouermi D, Simpore J, Svensson L (2013) Host genetic factors affect susceptibility to norovirus infections in Burkina Faso. PLoS One 8:e69557
Nordgren J, Sharma SB, Bucardo F, Nasir W, Günaydin G, Ouermi D, Nitiema LW, Becker-Dreps S, Simpore J, Hammarström L, Larson G, Svensson L (2014) Both lewis and secretor status mediate susceptibility to rotavirus infections in a rotavirus genotype dependent manner. Clin Infect Dis 59:1567–1573
Nystrom K, Abrantes J, Lopes AM, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Marchandeau S, Rocher J, Ruvoen-Clouet N, Esteves PJ, Le Pendu J (2015) Neofunctionalization of the Sec1 alpha1,2fucosyltransferase paralogue in leporids contributes to glycan polymorphism and resistance to rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004759
Pang H, Koda Y, Soejima M, Fujitani N, Ogaki T, Saito A, Kawasaki T, Kimura H (2001) Polymorphism of the human ABO-Secretor locus (FUT2) in four populations in Asia: indication of distinct Asian subpopulations. Ann Hum Genet 65:429–437
Patnaik SK, Helmberg W, Blumenfeld OO (2012) BGMUT: NCBI dbRBC database of allelic variations of genes encoding antigens of blood group systems. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1023–D1029
Qian Y, Song M, Jiang X, Xia M, Meller J, Tan M, Chen Y, Li X, Rao Z (2018) Structural adaptations of norovirus GII17/13/21 lineage through two distinct evolutionary paths. J Virol 93:e01655-18
Quintana-Murci L (2019) Human immunology through the lens of evolutionary genetics. Cell 177:184–199
Race RR, Sanger R (1975) Blood groups in man. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Ramani S, Hu L, Venkataram Prasad BV, Estes MK (2016) Diversity in rotavirus-host glycan interactions: a “sweet spectrum”. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:263–273
Roczo-Farkas S, Kirkwood CD, Cowley D, Barnes GL, Bishop RF, Bogdanovic-Sakran N, Boniface K, Donato CM, Bines JE (2018) The impact of rotavirus vaccines on genotype diversity: a comprehensive analysis of 2 decades of Australian surveillance data. J Infect Dis 218:546–554
Ruvöen-Clouet N, Belliot G, Le Pendu J (2013) Noroviruses and histo-blood groups: the impact of common host genetic polymorphisms on virus transmission and evolution. Rev Med Virol 23:355–366
Schroten H, Hanish FG, Hansman GS (2016) Human norovirus interactions with histo-blood group antigens and human milk oligosaccharides. J Virol 90:5855–5859
Segurel L, Thompson EE, Flutre T, Lovstad J, Venkat A, Margulis SW, Moyse J, Ross S, Gamble K, Sella G, Ober C, Przeworski M (2012) The ABO blood group is a trans-species polymorphism in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:18493–18498
Segurel L, Gao Z, Przeworski M (2013) Ancestry runs deeper than blood: the evolutionary history of ABO points to cryptic variation of functional importance. BioEssays 35:862–867
Shanker S, Czako R, Sankaran B, Atmar RL, Estes MK, Prasad BV (2014) Structural analysis of determinants of histo-blood group antigen binding specificity in genogroup I noroviruses. J Virol 88:6168–6180
Silva LM, Carvalho AS, Guillon P, Seixas S, Azevedo M, Almeida R, Ruvoën-Clouet N, Reis CA, Le Pendu J, Rocha J, David L (2010) Infection-associated FUT2 (fucosyltransferase 2) genetic variation and impact on functionality assessed by in vivo studies. Glycoconj J 27:61–68
Singh BK, Koromyslova A, Hefele L, Gürth C, Hansman GS (2015a) Structural evolution of the emerging 2014-2015 GII.17 Noroviruses. J Virol 90:2710–2715
Singh BK, Leuthold MM, Hansman GS (2015b) Human noroviruses’ fondness for histo-blood group antigens. J Virol 89:2024–2040
Sun X, Guo N, Li D, Jin M, Zhou Y, Xie G, Pang L, Zhang Q, Cao Y, Duan Z (2016a) Binding specificity of P[8] VP8* proteins of rotavirus vaccine strains with histo-blood group antigens. Virology 495:129–135
Sun X, Guo N, Li J, Yan X, He Z, Li D, Jin M, Xie G, Pang L, Zhang Q, Liu N, Duan ZJ (2016b) Rotavirus infection and histo-blood group antigens in the children hospitalized with diarrhoea in China. Clin Microbiol Infect 22:740.e1–740.e3
Sun X, Wang L, Qi J, Li D, Wang M, Cong X, Peng R, Chai W, Zhang Q, Wang H, Wen H, Gao GF, Tan M, Duan Z (2018) Human Group C rotavirus VP8*s recognize type a histo-blood group antigens as ligands. J Virol 92:e00442-18
Tan M, Jiang X (2011) Norovirus-host interaction: multi-selections by human histo-blood group antigens. Trends Microbiol 19:382–388
Tan M, Jiang X (2014) Histo-blood group antigens: a common niche for norovirus and rotavirus. Expert Rev Mol Med 16:e5
Tanaka T, Kamiya H, Asada K, Suga S, Ido M, Umemoto M, Ouchi K, Ito H, Kuroki H, Nakano T, Taniguchi K (2017) Changes in rotavirus genotypes before and after vaccine introduction: a multicenter, prospective observational study in three areas of Japan. Jpn J Infect Dis 70:448–452
Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Parashar UD (2016) Global, regional, and national estimates of rotavirus mortality in children < 5 years of age, 2000–2013. Clin Infect Dis 62S:S96–S105
Troeger C, Khalil IA, Rao PC, Cao S, Blacker BF, Ahmed T, Armah G, Bines JE, Brewer TG, Colombara DV, Kang G, Kirkpatrick BD, Kirkwood CD, Mwenda JM, Parashar UD, Petri WA Jr, Riddle MS, Steele AD, Thompson RL, Walson JL, Sanders JW, Mokdad AH, Murray CJL, Hay SI, Reiner RC Jr (2018) Rotavirus vaccination and the global burden of rotavirus diarrhea among children younger than 5 years. JAMA Pediatr 172:958–965
Turcot-Dubois AL, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Despiau S, Roubinet F, Bovin N, Le Pendu J, Blancher A (2007) Long-term evolution of the CAZY glycosyltransferase 6 (ABO) gene family from fishes to mammals: a birth-and-death evolution model. Glycobiology 17:516–528
Van Trang N, Vu HT, Le NT, Huang P, Jiang X, Anh DD (2014) Association between norovirus and rotavirus infection and histo-blood group antigen types in Vietnamese children. J Clin Microbiol 52:1366–1374
Villanea FA, Safi KN, Busch JW (2015) A general model of negative frequency dependent selection explains global patterns of human ABO polymorphism. PLoS One 10:e0125003
Xu S, Liu Y, Tan M, Zhong W, Zhao D, Jiang X, Kennedy MA (2019) Molecular basis of P[6] and P[8] major human rotavirus VP8* domain interactions with histo-blood group antigens. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/512301
Yang T-A, Hou J-Y, Huang Y-C, Chen C-J (2017) Genetic susceptibility to rotavirus gastroenteritis and vaccine effectiveness in Taiwanese children. Sci Rep 7:6412
Zakhour M, Ruvoën-Clouet N, Charpilienne A, Langpap B, Poncet D, Peters T, Bovin N, Le Pendu J (2009) The alphaGal epitope of the histo-blood group antigen family is a ligand for bovine norovirus Newbury2 expected to prevent cross-species prevention. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000504
Zeller M, Heylen E, Damanka S, Pietsch C, Donato C, Tamura T, Kulkarni R, Arora R, Cunliffe N, Maunula L, Potgieter C, Tamim S, Coster SD, Zhirakovskaya E, Bdour S, O’Shea H, Kirkwood CD, Seheri M, Nyaga MM, Mphahlele J, Chitambar SD, Dagan R, Armah G, Tikunova N, Van Ranst M, Matthijnssens J (2015) Emerging OP354-Like P[8] rotaviruses have rapidly dispersed from Asia to other continents. Mol Biol Evol 32:2060–2071
Zhang XF, Huang Q, Long Y, Jiang X, Zhang T, Tan M, Zhang QL, Huang ZY, Li YH, Ding YQ, Hu GF, Tang S, Dai YC (2015) An outbreak caused by GII.17 norovirus with a wide spectrum of HBGA-associated susceptibility. Sci Rep 5:17687
Acknowledgements
The work of the authors’ laboratory on this topic was supported by Inserm (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale), the Région des Pays de la Loire and ANR (Agence Nationale de la Recherche) through several grants. The authors are most grateful to the past and present members of the laboratory Séverine Marionneau, Maha Zakhour, Jézabel Rocher, Béatrice Le Moullac-Vaidye, Laure Barbé, Adrien Breiman, Amira Khachou and Tasnuva Ahmed for their outstanding contributions to the research presented in this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of both authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le Pendu, J., Ruvoën-Clouet, N. Fondness for sugars of enteric viruses confronts them with human glycans genetic diversity. Hum Genet 139, 903–910 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02090-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-019-02090-w