Abstract
Recently, with the high requirement of electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials, micro- or nano-fibrillated cellulose reinforced Ti3C2Tx nanosheets (transition-metal carbides/carbonitrides, MXene) composites have attracted wide attention due to their complementary functional properties. Nevertheless, it is still challenging to overcome a trade-off between EMI shielding performance and mechanical enhancement with the addition of reinforcing fillers. Herein, modified bacterial cellulose nanofiber (BCNF), with well-tuned micro structure, is employed as the unique reinforcing unit to self-assembly with MXene. The mechanical and electrical properties of different cellulose-derived composites were further compared to get insights into the effect of the fiber configuration on reinforcing properties. Particularly, the optimized MXene/BCNF sample simultaneously exhibited high tensile strength (252.2 MPa), excellent folding endurance (> 10,000 times), and high electrical conductivity (443.5 S cm−1). With striking shielding effectiveness (19,652 dB cm2 g−1), the sample effectively interferes with emitted electromagnetic waves, and is therefore a promising candidate for wearable devices and human electronic equipment.
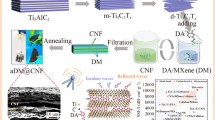
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao WT, Chen FF, Zhu YJ, Zhang YG, Jiang YY, Ma MG, Chen F (2018) Binary strengthening and toughening of MXene/cellulose nanofiber composite paper with nacre-inspired structure and superior electromagnetic interference shielding properties. ACS Nano 12(5):4583–4593. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00997
Cao MS, Cai YZ, He P, Shu JC, Cao WQ, Yuan J (2019a) 2D MXenes: electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 359:1265–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.051
Cao WT, Ma C, Tan S, Ma MG, Wan PB, Chen F (2019b) Ultrathin and flexible CNTs/MXene/cellulose nanofibrils composite paper for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano-Micro Lett 11(1):72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-019-0304-y
Chen WM, Zhang DT, Yang K, Luo M, Yang P, Zhou XY (2020) Mxene (Ti3C2Tx)/cellulose nanofiber/porous carbon film as free-standing electrode for ultrathin and flexible supercapacitors. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127524
Fang XY, Yu XX, Zheng HM, Jin HB, Wang L, Cao MS (2015) Temperature- and thickness-dependent electrical conductivity of few-layer graphene and graphene nanosheets. Phys Lett A 379(37):2245–2251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2015.06.063
Gao MH, Li J, Bao ZX, Hu MD, Nian R, Feng DX, An D, Li X, Xian M, Zhang HB (2019) A natural in situ fabrication method of functional bacterial cellulose using a microorganism. Nature Commun 10(1):437. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07879-3
Geng L, Zhu PX, Wei YJ, Guo RH, Xiang C, Cui C, Li Y (2019) A facile approach for coating Ti3C2Tx on cotton fabric for electromagnetic wave shielding. Cellulose 26(4):2833–2847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02284-5
He P, Cao MS, Shu JC, Cai YZ, Wang XX, Zhao QL, Yuan J (2019a) Atomic layer tailoring titanium carbide MXene to tune transport and polarization for utilization of electromagnetic energy beyond solar and chemical energy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(13):12535–12543. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b00593
He P, Wang XX, Cai YZ, Shu JC, Zhao QL, Yuan J, Cao MS (2019b) Tailoring Ti3C2Tx nanosheets to tune local conductive network as an environmentally friendly material for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanoscale 11(13):6080–6088. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR10489A
Hua JC, Fei B (2019) Super-tough polyacrylamide/iota-carrageenan double-network hydrogels strengthened by bacterial cellulose microclusters. Mater Today: Proc 16:1497–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.330
Huang RK, Cao CY, Liu J, Sun DP, Song WG (2019) N-Doped carbon nanofibers derived from bacterial cellulose as an excellent metal-free catalyst for selective oxidation of arylalkanes. Chem Commun 55(13):1935–1938. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CC00185A
Joseph N, Varghese J, Sebastian MT (2017) Graphite reinforced polyvinylidene fluoride composites an efficient and sustainable solution for electromagnetic pollution. Compos Part B-Eng 123:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.05.030
Krasteva PV, Bernal-Bayard J, Travier L, Martin FA, Kaminski PA, Karimova G, Fronzes R, Ghigo JM (2017) Insights into the structure and assembly of a bacterial cellulose secretion system. Nat Commun 8(1):2065. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01523-2
Kumar P (2019) Ultrathin 2D nanomaterials for electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201901454
Lee SH, Yu SG, Shahzad F, Hong JP, Kim WN, Park C, Hong SM, Koo CM (2017) Highly anisotropic Cu oblate ellipsoids incorporated polymer composites with excellent performance for broadband electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos Sci Technol 144:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.03.016
Liang CB, Song P, Ma AJ, Shi XT, Gu HB, Wang L, Qiu H, Kong J, Gu JW (2019) Highly oriented three-dimensional structures of Fe3O4 decorated CNTs/reduced graphene oxide foam/epoxy nanocomposites against electromagnetic pollution. Compos Sci Technol 181:107683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107683
Liu J, Zhang HB, Sun RH, Liu YF, Liu ZS, Zhou AG, Yu ZZ (2017) Hydrophobic, flexible, and lightweight mxene foams for high-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding. Adv Mater 29(38):1702367. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201702367
Liu J, Zhang HB, Xie X, Yang R, Liu ZS, Liu YF, YU, ZZ, (2018) Multifunctional, superelastic, and lightweight MXene/polyimide aerogels. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201802479
Liu LX, Wei C, Zhang HB, Wang QW, Guan FL, Yu ZZ (2019) Flexible and multifunctional silk textiles with biomimetic leaf-like MXene/silver nanowire nanostructures for electromagnetic interference shielding, humidity monitoring, and self-derived hydrophobicity. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201905197
Luo HL, Xiong GY, Hu D, Ren KJ, Yao FL, Zhu Y, Gao C, Wan YZ (2013) Characterization of TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Mater Chem Phys 143(1):373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.09.012
Ma ZL, Kang SL, Ma JZ, Shao L, Zhang YL, Liu C, Wei AJ, Xiang XL, Wei LF, Gu JW (2020) Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber–Ti3C2Tx MXene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 14(7):8368–8382. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c02401
Ma C, Cao WT, Zhang W, Ma MG, Sun WM, Zhang J, Chen F (2021) Wearable, ultrathin and transparent bacterial celluloses/MXene film with Janus structure and excellent mechanical property for electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem Eng J 403:126438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126438
Malucelli LC, Matos M, Jordão C, Lomonaco D, Lacerda LG, Carvalho Filho MAS, Magalhães WLE (2019) Influence of cellulose chemical pretreatment on energy consumption and viscosity of produced cellulose nanofibers (CNF) and mechanical properties of nanopaper. Cellulose 26(3):1667–1681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2161-0
Nie SX, Hao NK, Zhang K, Xing CY, Wang SF (2020) Cellulose nanofibrils-based thermally conductive composites for flexible electronics: a mini review. Cellulose 27(8):4173–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03103-y
Palazzetti R, Zucchelli A (2017) Electrospun nanofibers as reinforcement for composite laminates materials—a review. Compos Struct 182(12):711–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.09.021
Rahman MM, Puthirath AB, Adumbumkulath A, Tsafack T, Robatjazi H, Barnes M, Wang Z, Kommandur S, Susarla S, Sajadi SM (2019) Fiber reinforced layered dielectric nanocomposite. Adv Funct Mater 29(28):1900056.1-1900056.8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201900056
Sage C, Burgio E (2018) Electromagnetic fields, pulsed radiofrequency radiation, and epigenetics: how wireless technologies may affect childhood development. Child Dev 89(1):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12824
Shahzad F, Alhabeb M, Hatter CB, Anasori B, Man HS, Koo CM, Gogotsi Y (2016) Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353(6304):1137–1140. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aag2421
Shen B, Zhai WT, Zheng WG (2014) Ultrathin flexible graphene film: an excellent thermal conducting material with efficient EMI shielding. Adv Funct Mater 24(28):4542–4548. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201400079
Song P, Qiu H, Wang L, Liu XY, Zhang YL, Zhang JL, Kong J, Gu JW (2020) Honeycomb structural rGO-MXene/epoxy nanocomposites for superior electromagnetic interference shielding performance. SM&T. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2020.e00153
Tang J, Swolfs Y, Longana ML, Yu H, Wisnom MR, Lomov SV, Gorbatikh L (2019) Hybrid composites of aligned discontinuous carbon fibers and self-reinforced polypropylene under tensile loading. Compos Part A- Appl Sci Manuf 123:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.05.003
Tian WQ, Vahidmohammadi A, Reid MS, Wang Z, Hamedi MM (2019) Multifunctional nanocomposites with high strength and capacitance using 2D MXene and 1D nanocellulose. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902977
Valekar AH, Cho KH, Lee UH, Lee JS, Yoon JW, Hwang YK, Lee SG, Cho SJ, Chang JS (2017) Shaping of porous metal–organic framework granules using mesoporous ρ-alumina as a binder. RSC Adv 7(88):55767–55777. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA11764G
Wan YJ, Zhu PL, Yu SH, Sun R, Wong CP, Liao WH (2018) Anticorrosive, ultralight, and flexible carbon-wrapped metallic nanowire hybrid sponges for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Small 14(27):1800534. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201800534
Wang S, Jiang F, Xu X, Kuang YD, Fu K, Hitz E, Hu LB (2017) Super-strong, super-stiff macrofibers with aligned, long bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Adv Mater 29(35):1702498. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201702498
Wang S, Li T, Chen CJ, Kong WQ, Zhu SZ, Dai JQ, Diaz AJ, Hitz E, Solares SD, Li T (2018) Transparent, anisotropic biofilm with aligned bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Adv Funct Mater 28(24):1707491. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201707491
Wang L, Chen LX, Song P, Liang CB, Lu YJ, Qiu H, Zhang YL, Kong J, Gu JW (2019a) Fabrication on the annealed Ti3C2Tx MXene/epoxy nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding application. Compos Part B-Eng 171:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.050
Wang QW, Zhang HB, Liu J, Zhao S, Xie X, Liu LX, Yang R, Noratkar N, Yu ZZ (2019b) Multifunctional and water-resistant MXene-decorated polyester textiles with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding and joule heating performances. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201806819
Wang XX, Shu JC, Cao WQ, Zhang M, Yuan J, Cao MS (2019c) Eco-mimetic nanoarchitecture for green EMI shielding. Chem Eng J 369:1068–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.164
Wang Y, Wang W, Qi QB, Xu N, Yu D (2020) Layer-by-layer assembly of PDMS-coated nickel ferrite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes/cotton fabrics for robust and durable electromagnetic interference shielding. Cellulose 27(5):2829–2845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02949-1
Weng GM, Li JY, Alhabeb M, Karpovich C, Wang H, Lipton J, Maleski K, Kong J, Shaulsky E, Elimelech M, Gogotsi Y, Taylor AD (2018) Layer-by-layer assembly of cross-functional semi-transparent MXene-carbon nanotubes composite films for next-generation electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Funct Mater 28(44):1803360. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201803360
Xie F, Jia F, Zhuo L, Lu Z (2019a) Ultrathin MXene/aramid nanofiber composite paper with excellent mechanical properties for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanoscale 11(48):23382–23391. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr07331k
Xie F, Jia FF, Zhuo LH, Lu ZQ, Si LM, Huang JZ, Zhang MY, Ma Q (2019b) Ultrathin MXene/aramid nanofiber composite paper with excellent mechanical properties for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nanoscale. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR07331K
Xiong DB, Li XF, Bai ZM, Lu SG (2018) Recent advances in layered Ti3C2Tx MXene for electrochemical energy storage. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201703419
Yadav S, Jain CP, Sharma MM (2018) Smartphone frequency shielding with penta-bandstop FSS for security and electromagnetic health applications. IEEE T Electromagn C 61(3):887–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEMC.2018.2839707
Yan DX, Pang H, Li B, Vajtai R, Xu L, Ren PG, Wang JH, Li ZM (2015) Structured reduced graphene oxide/polymer composites for ultra-efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Funct Mater 25(4):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201403809
Yan HQ, Chen XQ, Song HW, Li JC, Feng YH, Shi ZF, Wang XH, Lin Q (2017) Synthesis of bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose nanocrystals for their applications in the stabilization of olive oil pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocolloids 72:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.05.044
Yu WC, Xu JZ, Wang ZG, Huang YF, Yin HM, Xu L, Chen YW, Yan DX, Li ZM (2018) Constructing highly oriented segregated structure towards high-strength carbon nanotube/ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos Part A- Appl S 110:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.05.004
Zeng ZH, Jin H, Chen MJ, Li WW, Zhou LC, Zhang Z (2016) Lightweight and anisotropic porous MWCNT/WPU composites for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Funct Mater 26(2):303–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201503579
Zeng ZH, Jin H, Chen MJ, Li WW, Zhou LC, Xue X, Zhang Z (2017) Microstructure design of lightweight, flexible, and high electromagnetic shielding porous multiwalled carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Small 13(34):1701388. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201701388
Zhang CJ, Anasori B, Seral-Ascaso A, Park SH, Mcevoy N, Shmeliov A, Duesberg GS, Coleman JN, Gogotsi Y, Nicolosi V (2017) Transparent, flexible, and conductive 2D titanium carbide (MXene) films with high volumetric capacitance. Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201702678
Zhang Q, Liang QJ, Zhang Z, Kang Z, Liao QL, Ding Y, Ma M, Gao FF, Zhao X, Zhang Y (2018) Electromagnetic shielding hybrid nanogenerator for health monitoring and protection. Adv Funct Mater 28(1):1703801. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703801
Zhang M, Wang XX, Cao WQ, Yuan J, Cao MS (2019) Electromagnetic functions of patterned 2D materials for micro–nano devices covering GHz, THz, and optical frequency. Adv Opt Mater 7(19):1900689. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201900689
Zhao S, Zhang HB, Luo JQ, Wang QW, Bin S (2018) Highly electrically conductive three-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene/reduced graphene oxide hybrid aerogels with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding performances. ACS Nano. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05739
Zhou B, Zhang Z, Li YL, Han GJ, Feng YZ, Wang B, Zhang DB, Ma JM, Liu CT (2020) Flexible, robust, and multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding film with alternating cellulose nanofiber and MXene layers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(4):4895–4905. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b19768
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52003121), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20200501), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M671497, 2020T130300), and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XX: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft. SW: Data curation, validation. CJ: Investigation. LY: investigation. DL: investigation. YZ: software, visualization. XC: conceptualization, formal analysis, resources, visualization, writing—original draft. KW: supervision, validation, writing—review and editing. DS: supervision, validation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Wu, S., Cui, J. et al. Insights into the microstructures and reinforcement mechanism of nano-fibrillated cellulose/MXene based electromagnetic interference shielding film. Cellulose 28, 3311–3325 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03765-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03765-2