Abstract
Purpose
Obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) may cause pulmonary diseases, and periostin plays an important role on the development of pulmonary diseases. In addition, periostin and pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α can regulate each other in vivo. This study aimed to observe the changes of serum periostin and TNF-α levels in patients with OSAHS compared with healthy volunteers and to investigate their correlation.
Methods
A convenience sample of 67 patients with OSAHS in our hospital from December 2018 to December 2019 was selected and categorized into mild, moderate, and severe groups according to apnea-hypopnea index by polysomnography. In addition, 21 healthy volunteers were selected as the control group. Serum levels of periostin and TNF-α were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results were analyzed using the SPSS software.
Results
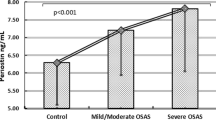
Both serum periostin and TNF-α levels in all the three OSAHS groups were higher than those of the control group and increased with severity of OSAHS. The severe group had significantly higher serum periostin and TNF-α levels than the mild and moderate groups (p < 0.05). For patients with OSAHS, serum periostin and TNF-α levels positively correlated with the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) (p < 0.01) and negatively correlated with the lowest saturation oxygen (LSaO2) and mean saturation oxygen (MSaO2) (both p < 0.01). In addition, there was a positive correlation between serum periostin and TNF-α levels in patients with OSAHS (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Serum periostin and TNF-α levels were significantly increased in patients with OSAHS and may serve as a potential biomarker for severity of OSAHS. These findings suggest that it may be fruitful to study the role of periostin and TNF-α in OSAHS-induced pulmonary diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qaseem A, Holty JC, Owens DK, Dallas P, Starkey M, Shekelle P (2013) Management of obstructive sleep apnea in adults: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med 159:471–483
McNicholas WT, Bonsignore MR (2007) Sleep apnoea as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: current evidence, basic mechanisms and research priorities. Eur Respir J 29:156–178
Dempsey JA, Veasey SC, Morgan BJ, O’Donnell CP (2010) Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol Rev 90:47–112
Young T, Peppard PE, Taheri S (2005) Excess weight and sleep-disordered breathing. J Appl Physiol 99:1592–1599
Dean RT, Wilcox I (1993) Possible atherogenic effects of hypoxia during obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 16:S15–S32
Dyugovskaya L, Lavie P, Lavie L (2002) Increased adhesion molecules expression and production of reactive oxygen species in leukocytes of sleep apnea patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:934–939
Yaggi HK, Concato J, Kernan WN, Lichtman JH, Brass LM, Mohsenin V (2005) Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med 353:2034–2041
Westergren-Thorsson G, Larsen K, Nihlberg K, Andersson-Sjöland A, Hallgren O, Marko-Varga G, Bjermer L (2010) Pathological airway remodelling in inflammation. Clin Respir J 4:1–8
Knight D (2001) Epithelium–fibroblast interactions in response to airway inflammation. Immunol Cell Biol 79:160–164
Bonnet N, Garnero P, Ferrari S (2016) Periostin action in bone. Mol Cell Endocrinol 432:75–82
Coutu DL, Wu JH, Monette A, Rivard GE, Blostein MD, Galipeau J (2008) Periostin, a member of a novel family of vitamin K-dependent proteins, is expressed by mesenchymal stromal cells. J Biol Chem 283:17991–18001
Idolazzi L, Ridolo E, Fassio A, Gatti D, Montagni M, Caminati M, Martignago I, Incorvaia C, Senna G (2017) Periostin: the bone and beyond. Eur J Intern Med 38:12–16
Liu AY, Zheng H, Ouyang G (2014) Periostin, a multifunctional matricellular protein in inflammatory and tumor microenvironments. Matrix Biol 37:150–156
Woodruff PG, Boushey HA, Dolganov GM, Barker CS, Yang YH, Donnelly S, Ellwanger A, Sidhu SS, Dao-Pick TP, Pantoja C, Erle DJ, Yamamoto KR, Fahy JV (2007) Genome-wide profiling identifies epithelial cell genes associated with asthma and with treatment response to corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:15858–15863
Okamoto M, Hoshino T, Kitasato Y, Sakazaki Y, Kawayama T, Fujimoto K, Ohshima K, Shiraishi H, Uchida M, Ono J, Ohta S, Kato S, Izuhara K, Aizawa H (2011) Periostin, a matrix protein, is a novel biomarker for idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur Respir J 37:1119–1127
Nakajima M, Honda T, Miyauchi S, Yamazaki K (2014) Th2 cytokines efficiently stimulate periostin production in gingival fibroblasts but periostin does not induce an inflammatory response in gingival epithelial cells. Arch Oral Biol 59:93–101
Sozmen M, Devrim AK, Kabak YB, Devrim T (2019) Periostin alters transcriptional profile in a rat model of isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity. Hum Exp Toxicol 38:255–266
Kapur VK, Auckley DH, Chowdhuri S, Kuhlmann DC, Mehra R, Ramar K, Harrod CG (2017) Clinical practice guideline for diagnostic testing for adult obstructive sleep apnea: an American Academy of sleep medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med 13:479–504
Meslier N, Gagnadoux F, Giraud P, Person C, Ouksel H, Urban T, Racineux JL (2003) Impaired glucose-insulin metabolism in males with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Eur Respir J 22:156–160
Kanemitsu Y, Matsumoto H, Izuhara K, Tohda Y, Kita H, Horiguchi T, Kuwabara K, Tomii K, Otsuka K, Fujimura M, Ohkura N, Tomita K, Yokoyama A, Ohnishi H, Nakano Y, Oguma T, Hozawa S, Nagasaki T, Ito I, Oguma T, Inoue H, Tajiri T, Iwata T, Izuhara Y, Ono J, Ohta S, Tamari M, Hirota T, Yokoyama T, Niimi A, Mishima M (2013) Increased periostin associates with greater airflow limitation in patients receiving inhaled corticosteroids. J Allergy Clin Immunol 132:305–312
Generoso A, Oppenheimer J (2020) Asthma/obstructive pulmonary disease overlap: update on definition, biomarkers, and therapeutics. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 20:43–47
Desai M, Oppenheimer J, Tashkin DP (2017) Asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap syndrome: what we know and what we need to find out. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 118:241–245
He ZH, Domany KA, Nava-Guerra L, Khoo MCK, DiFrancesco M, Xu YF, McConnell K, Hossain MM, Amin R (2019) Phenotype of ventilatory control in children with moderate to severe persistent asthma and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 42:UNSP zsz130
Ding X, Yu C, Liu Y, Yan S, Li W, Wang D, Sun L, Han Y, Li M, Zhang S, Yun F, Zhao H, Li Y (2014) Chronic obstructive sleep apnea accelerates pulmonary remodeling via TGF-β/miR-185/CoLA1 signaling in a canine model. Oncotarget 7:57545–57555
Broytman O, Braun RK, Morgan BJ, Egelow DF, Hsu PN, Mei LS, Koya AK, Eldridge M, Teodorescu M (2015) Effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia on allergen-induced airway inflammation in rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 52:162–170
Kii I, Nishiyama T, Li M, Matsumoto K, Saito M, Amizuka N, Kudo A (2010) Incroporation of tenascin-C into the extracellular matrix by periostin underlies an extracellular meshwork architecture. J Biol Chen 285:2028–2039
O’Dwyer DN, Moore BB (2017) The role of periostin in lung fibrosis and airway remodeling. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:4305–4314
Li NF, Yao XG, Zhu J, Yang J, Liu KJ, Wang YC, Wang XL, Zu FY (2010) Higher levels of plasma TNF-α and neuropeptide Y in hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Clin Exp Hypertens 32:54–60
Minoguchi K, Tazaki T, Yokoe T, Minoguchi H, Watanabe Y, Yamamoto M, Mitsuru A (2004) Elevated production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by monocytes in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Chest 126:1473–1479
Luo Y, Qu H, Wang H, Wei H, Wu J, Duan Y, Liu D, Deng H (2016) Plasma periostin levels are increased in Chinese subjects with obesity and type 2 diabetes and are positively correlated with glucose and lipid parameters. Mediat Inflamm 2016:6423637
Amara S, Lopez K, Banan B, Brown SK, Whalen M, Myles E, Lvy MT, Johnson T, Schey KL, Tiriveedhi V (2015) Synergistic effect of proinflammatory TNF-α and IL-17 in periostin mediated collagen deposition: potential role in liver fibrosis. Mol Immunol 64:26–35
Funding
The authors received financial support and grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600044), the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (WSN-081), and Xuzhou City Bureau of Science and Technology Project (KC KC18058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee, and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Liu, Y., Liu, P. et al. Serum periostin and TNF-α levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath 25, 331–337 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02124-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-020-02124-y