Abstract
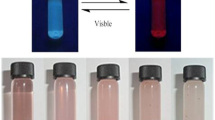
Nanographenes (NGs) are exceptionally hydrophobic. They are insoluble in water, preventing the exploration and utilization of their photophysical properties under aqueous conditions. This work discloses an atomically precise water-soluble synthetic NG 1, featuring a 2 nm sp2 carbon skeleton appended with 12 branched triethylene glycol chains. It synergistically combines low critical solution temperature (LCST) behavior and a photothermal effect to create the first thermo- and photo-responsive atomically precise NG functioning in an aqueous solution. The LCST behavior can be attributed to a delicate balance of hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions, providing a sensitive thermal response to changes over a temperature range of physiological interest (close to 37 °C). Moreover, 1 has considerable photothermal conversion capability, with irradiation of 1 in water by red or near infrared light increasing the solutions temperature to above the clouding point within seconds, leading to a reversible clear-to-turbid transition over many cycles without evident fatigue.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Müllen K. ACS Nano, 2014, 8: 6531–6541
Narita A, Wang XY, Feng X, Müllen K. Chem Soc Rev, 2015, 44: 6616–6643
Segawa Y, Ito H, Itami K. Nat Rev Mater, 2016, 1: 15002
Wang XY, Yao X, Müllen K. Sci China Chem, 2019, 62: 1099–1144
Yin M, Shen J, Pisula W, Liang M, Zhi L, Mullen K. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 14618–14619
Lin HA, Sato Y, Segawa Y, Nishihara T, Sugimoto N, Scott LT, Higashiyama T, Itami K. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 2874–2878
Huang Y, Dou WT, Xu F, Ru HB, Gong Q, Wu D, Yan D, Tian H, He XP, Mai Y, Feng X. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 3366–3371
Zhu Y, Xia Z, Cai Z, Yuan Z, Jiang N, Li T, Wang Y, Guo X, Li Z, Ma S, Zhong D, Li Y, Wang J. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140: 4222–4226
Wang Y, Yin Z, Zhu Y, Gu J, Li Y, Wang J. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2019, 58: 587–591
Zhu Y, Guo X, Li Y, Wang J. J Am Chem Soc, 2019, 141: 5511–5517
Guo X, Yuan Z, Zhu Y, Li Z, Huang R, Xia Z, Zhang W, Li Y, Wang J. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2019, 58: 16966–16972
Ball M, Zhong Y, Wu Y, Schenck C, Ng F, Steigerwald M, Xiao S, Nuckolls C. Acc Chem Res, 2015, 48: 267–276
Pun SH, Miao Q. Acc Chem Res, 2018, 51: 1630–1642
Majewski MA, Stępień M. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2019, 58: 86–116
Tan YZ, Yang B, Parvez K, Narita A, Osella S, Beljonne D, Feng X, Müllen K. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2646
Kawasumi K, Zhang Q, Segawa Y, Scott LT, Itami K. Nat Chem, 2013, 5: 739–744
Cheung KY, Chan CK, Liu Z, Miao Q. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2017, 56: 9003–9007
Reger D, Haines P, Heinemann FW, Guldi DM, Jux N. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 5938–5942
Evans PJ, Ouyang J, Favereau L, Crassous J, Fernández I, Perles J, Martín N. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 6774–6779
Hahn U, Maisonhaute E, Nierengarten J-. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 10635–10639
Meng D, Liu G, Xiao C, Shi Y, Zhang L, Jiang L, Baldridge KK, Li Y, Siegel JS, Wang Z. J Am Chem Soc, 2019, 141: 5402–5408
Cruz CM, Márquez IR, Castro-Fernández S, Cuerva JM, Maçôas E, Campaña AG. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2019, 58: 8068–8072
Weber C, Hoogenboom R, Schubert US. Prog Polym Sci, 2012, 37: 686–714
Zhang Q, Weber C, Schubert US, Hoogenboom R. Mater Horiz, 2017, 4: 109–116
Lutz JF, Akdemir Ö, Hoth A. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 13046–13047
Betancourt JE, Rivera JM. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 16666–16668
Wang F, Klaikherd A, Thayumanavan S. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 13496–13503
Ogoshi T, Shiga R, Yamagishi T. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134: 4577–4580
Ogoshi T, Kida K, Yamagishi T. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134: 20146–20150
Wei P, Cook TR, Yan X, Huang F, Stang PJ. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136: 15497–15500
Jung HS, Verwilst P, Sharma A, Shin J, Sessler JL, Kim JS. Chem Soc Rev, 2018, 47: 2280–2297
Baffou G, Quidant R. Laser Photon Rev, 2013, 7: 171–187
Zhang Q, Xu W, Wang X. Sci China Mater, 2018, 61: 905–914
Yavuz MS, Cheng Y, Chen J, Cobley CM, Zhang Q, Rycenga M, Xie J, Kim C, Song KH, Schwartz AG, Wang LV, Xia Y. Nat Mater, 2009, 8: 935–939
Zhang P, Liu F, Liao Q, Yao H, Geng H, Cheng H, Li C, Qu L. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57: 16343–16347
Bisoyi HK, Urbas AM, Li Q. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6: 1800458
Han B, Zhang YL, Chen QD, Sun HB. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28: 1802235
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21871298, 91956118) and the Sun Yat-Sen University. We thank Prof. Dr. Xiaoye Wang from the Nankai University for discussion. Dr. Xiao Zhang and Mr. Zhibin Xiao from the Sun Yat-Sen University are acknowledged for assistance on the calorimetric measurements and photographic recording of the switching process, respectively. We also thank Prof. Wesley R. Browne from the University of Groningen for discussion and proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, S., Zhu, Y., Dou, W. et al. Stimulus-responsive water soluble synthetic nanographene. Sci. China Chem. 64, 576–580 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-020-9916-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-020-9916-7