Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of microwave ablation (MWA) versus lobectomy for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules > 4 cm.
Methods
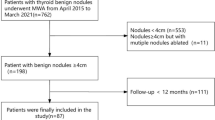
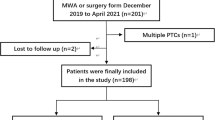
We retrospectively analyzed the data of 48 patients who underwent MWA and 53 patients who underwent lobectomy to treat benign thyroid nodules > 4 cm. The patients were followed up for 12 months. The volume reduction ratio (VRR) was calculated. The operation time, incision length, hospitalization time, complications, thyroid function, symptoms, and cosmetic improvement were analyzed and compared between the two groups.
Results
During the 12-month follow-up, the mean nodule volume in the MWA group was reduced from 36.1 ± 23.1 to 4.0 ± 4.1 ml, and the mean VRR of the nodules was 90 ± 5% in the MWA group, which was comparable with that in the surgery group. No significant postoperative change in thyroid function was observed in the MWA group. Compared with the surgery group, the incidence of complications and postoperative pain in the MWA group were lower, the operation time, incision length, and hospitalization time in the MWA group were shorter, and satisfaction with the esthetic results in the MWA group was greater.
Conclusion
MWA is safe and effective for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules > 4 cm. Moreover, MWA is associated with a faster recovery, fewer complications, better protection of thyroid function, and superior esthetic results relative to thyroid lobectomy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Durante, G. Grani, L. Lamartina, S. Filetti, S.J. Mandel, D.S. Cooper, The diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules: a review. JAMA 319(9), 914–924 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.0898
J. Yan, T. Qiu, J. Lu, Y. Wu, Y. Yang, Microwave ablation induces a lower systemic stress response in patients than open surgery for treatment of benign thyroid nodules. Int. J. Hyperth. 34(5), 606–610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1427286
B.R. Haugen, E.K. Alexander, K.C. Bible, G.M. Doherty, S.J. Mandel, Y.E. Nikiforov, F. Pacini, G.W. Randolph, A.M. Sawka, M. Schlumberger, K.G. Schuff, S.I. Sherman, J.A. Sosa, D.L. Steward, R.M. Tuttle, L. Wartofsky, 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 26(1), 1–133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2015.0020
Y. Korkusuz, O.M. Mader, W. Kromen, C. Happel, S. Ahmad, D. Groner, M. Koca, A. Mader, F. Grunwald, H. Korkusuz, Cooled microwave ablation of thyroid nodules: initial experience. Eur. J. Radiol. 85(11), 2127–2132 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.09.019
W.W. Yue, S.R. Wang, F. Lu, L.P. Sun, L.H. Guo, Y.L. Zhang, X.L. Li, H.X. Xu, Radiofrequency ablation vs. microwave ablation for patients with benign thyroid nodules: a propensity score matching study. Endocrine 55(2), 485–495 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1173-5
I.J. Nixon, P. Angelos, A.R. Shaha, A. Rinaldo, M.D. Williams, A. Ferlito, Image-guided chemical and thermal ablations for thyroid disease: review of efficacy and complications. Head. Neck 40(9), 2103–2115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25181
P. Liang, Y. Wang, X. Yu, B. Dong, Malignant liver tumors: treatment with percutaneous microwave ablation–complications among cohort of 1136 patients. Radiology 251(3), 933–940 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2513081740
J. Yu, P. Liang, X.L. Yu, Z.G. Cheng, Z.Y. Han, X. Zhang, J. Dong, M.J. Mu, X. Li, X.H. Wang, US-guided percutaneous microwave ablation versus open radical nephrectomy for small renal cell carcinoma: intermediate-term results. Radiology 270(3), 880–887 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13130275
L. Sidoff, D.E. Dupuy, Clinical experiences with microwave thermal ablation of lung malignancies. Int. J. Hyperth. 33(1), 25–33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2016.1204630
J. Xu, H. Wu, Z. Han, J. Zhang, Q. Li, J. Dou, C. An, E. Qi, J. Yu, P. Liang, Microwave ablation of benign breast tumors: a prospective study with minimum 12 months follow-up. Int. J. Hyperth. 35(1), 253–261 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1494340
W.J. Wu, X.H. Gong, Q. Zhou, X. Chen, X.J. Chen, B.M. Shi, US-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules. Endocr. J. 64(11), 1079–1085 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0152
X. Zhi, N. Zhao, Y. Liu, J.B. Liu, C. Teng, L. Qian, Microwave ablation compared to thyroidectomy to treat benign thyroid nodules. Int. J. Hyperth. 34(5), 644–652 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1456677
K.L. McCoy, N. Jabbour, J.B. Ogilvie, N.P. Ohori, S.E. Carty, J.H. Yim, The incidence of cancer and rate of false-negative cytology in thyroid nodules greater than or equal to 4 cm in size. Surgery 142(6), 837–844.e833 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2007.08.012
E.J. Ha, J.H. Baek, J.H. Lee et al. Sonographically suspicious thyroid nodules with initially benign cytologic results: the role of a core needle biopsy. Thyroid 23(6), 703–708 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2012.0426
S. Bernardi, C. Dobrinja, B. Fabris, G. Bazzocchi, N. Sabato, V. Ulcigrai, M. Giacca, E. Barro, N. De Manzini, F. Stacul, Radiofrequency ablation compared to surgery for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 934595 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/934595
Z. Cheng, Y. Che, S. Yu, S. Wang, D. Teng, H. Xu, J. Li, D. Sun, Z. Han, P. Liang, US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency versus microwave ablation for benign thyroid nodules: a prospective multicenter study. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 9554 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09930-7
H. Dobnig, K. Amrein, Monopolar radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules: a prospective austrian single-center study. Thyroid. 28(4), 472–480 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0547
C. Vorlander, K. David Kohlhase, Y. Korkusuz, C. Erbelding, W. Luboldt, I. Baser, H. Korkusuz, Comparison between microwave ablation and bipolar radiofrequency ablation in benign thyroid nodules: differences in energy transmission, duration of application and applied shots. Int. J. Hyperth. 35(1), 216–225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2018.1489984
J. Li, Y. Liu, J. Liu, P. Yang, X. Hu, L. Qian, A comparative study of short-term efficacy and safety for thyroid micropapillary carcinoma patients after microwave ablation or surgery. Int. J. Hyperth. 36(1), 640–646 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2019.1626492
P. Del Rio, M. Rossini, C.M. Montana, L. Viani, G. Pedrazzi, T. Loderer, F. Cozzani, Postoperative hypocalcemia: analysis of factors influencing early hypocalcemia development following thyroid surgery. BMC Surg. 18(Suppl 1), 25 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-019-0483-y
D. Ahn, G.J. Lee, J.H. Sohn, Levothyroxine supplementation following hemithyroidectomy: incidence, risk factors, and characteristics. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 26(13), 4405–4413 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07786-x
Y.H. Jung, H.B. Jung, C. Hoon, K.K. Jae, H.L. Jeong, Symptomatic benign thyroid nodules: efficacy of additional radiofrequency ablation treatment session—prospective randomized study. Radiology 263, 909–916 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12111300
B. Wang, Z.Y. Han, J. Yu, Z. Cheng, F. Liu, X.L. Yu, C. Chen, J. Liu, P. Liang, Factors related to recurrence of the benign non-functioning thyroid nodules after percutaneous microwave ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 33(4), 459–464 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2016.1274058
Y.J. Liu, L.X. Qian, D. Liu, J.F. Zhao, Ultrasound-guided microwave ablation in the treatment of benign thyroid nodules in 435 patients. Exp. Biol. Med. 242(15), 1515–1523 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217727477
E. Bandeira-Echtler, K. Bergerhoff, B. Richter, Levothyroxine or minimally invasive therapies for benign thyroid nodules. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (6), CD004098 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD004098.pub2
H. Gharib, L. Hegedus, C.M. Pacella, J.H. Baek, E. Papini, Clinical review: nonsurgical, image-guided, minimally invasive therapy for thyroid nodules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98(10), 3949–3957 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-1806
S.Y. Liu, W.H. Guo, B. Yang, Y.F. Li, X.Y. Huang, X.Q. Wang, J. Chen, D. Xue, X.H. Zhou, Comparison of stress response following microwave ablation and surgical resection of benign thyroid nodules. Endocrine 65(1), 138–143 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01900-5
B. Feng, P. Liang, Z. Cheng, X. Yu, J. Yu, Z. Han, F. Liu, Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of benign thyroid nodules: experimental and clinical studies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 166(6), 1031–1037 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-11-0966
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Finance Department of Jilin Province (No. SCZSY201701) and the Jilin Province Science and Technology Department (No. 20190303140SF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures in studies involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, P., Wu, XL., Sui, GQ. et al. The efficacy and safety of microwave ablation versus lobectomy for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules greater than 4 cm. Endocrine 71, 113–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02338-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02338-w