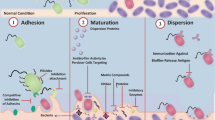
Abstract
Over the last couple of decades, with the crisis of new antimicrobial arsenal, multidrug-resistant clinical pathogens have been observed extensively. In clinical and medical settings, these persistent pathogens predominantly grow as complex heterogeneous structures enmeshed in a self-produced exopolysaccharide matrix, termed as biofilms. Since biofilms can rapidly form by adapting new environmental surroundings and have potential effect on human health, it is critical to study them promptly and consistently. Biofilm infections are challenging in the contamination of medical devices and implantations, food processing and pharmaceutical industrial settings, and in dental area caries, periodontitis and so on. The persistence of infections associated with biofilms has been mainly attributed to the increased antibiotic resistance offered by the cells growing in biofilms. In fact, it is well known that this recalcitrance of bacterial biofilms is multifactorial, and there are several resistance mechanisms that may act in parallel in order to provide an enhanced level of resistance to the biofilm. In combination, distinct resistance mechanisms significantly decrease our ability to control and eradicate biofilm-associated infections with current antimicrobial arsenal. In addition, various factors are known to influence the process of biofilm formation, growth dynamics, and their heterogeneous response towards antibiotic therapy. The current review discusses the contribution of cellular and physiochemical factors on the growth dynamics of biofilm, especially their role in antibiotic resistance mechanisms of bacterial population living in surface attached growth mode. A systematic investigation on the effects and treatment of biofilms may pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat biofilms in healthcare and industrial settings.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato SM and Brynildsen MP 2014 Nutrient transitions are a source of persisters in Escherichia coli biofilms. PLoS One 9 e93110
Anutrakunchai C, Bolscher JGM, Krom BP, Kanthawong S, Chareonsudjai S and Taweechaisupapong S 2018 Impact of nutritional stress on drug susceptibility and biofilm structures of Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia thailandensis grown in static and microfluidic systems. PLoS One 13 e0194946
Armbruster CR and Parsek MR 2018 New insight into the early stages of biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 115 4317–4319
Atkinson S and Williams P 2009 Quorum sensing and social networking in the microbial world. JR Soc. Interface 6 959–978
Bagge N, Schuster M, Hentzer M, Ciofu O, Givskov M, Greenberg EP and Hoiby N 2004 Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms exposed to imipenem exhibit changes in global gene expression and beta-lactamase and alginate production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48 1175–1187
Beebout CJ, Eberly AR, Werby SH, Reasoner SA, Brannon JR, De S, Fitzgerald MJ, Huggins MM, Clayton DB, Cegelski L and Hadjifrangiskou M 2019 Respiratory heterogeneity shapes biofilm formation and host colonization in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. mBio 10 e02400–02418
Berditsch M, Jager T, Strempel N, Schwartz T, Overhage J and Ulrich AS 2015 Synergistic effect of membrane-active peptides polymyxin B and gramicidin S on multidrug-resistant strains and biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59 5288–5296
Bjarnsholt T 2013 The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS 136 1–51
Brackman G, Breyne K, De Rycke R, Vermote A, Van Nieuwerburgh F, Meyer E, Van Calenbergh S and Coenye T 2016 The quorum sensing inhibitor hamamelitannin increases antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms by affecting peptidoglycan biosynthesis and eDNA release. Sci Rep. 6 20321
Bridier A, Sanchez-Vizuete Mdel P, Le Coq D, Aymerich S, Meylheuc T, Maillard JY, Thomas V, Dubois-Brissonnet F and Briandet R 2012 Biofilms of a Bacillus subtilis hospital isolate protect Staphylococcus aureus from biocide action. PLoS One 7 e44506
Brooun A, Liu S and Lewis K 2000 A dose-response study of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44 640–646
Ceri H, Olson ME, Stremick C, Read RR, Morck D and Buret A 1999 The calgary biofilm device: new technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37 1771–1776
Ciofu O, Rojo-Molinero E, Macia MD and Oliver A 2017 Antibiotic treatment of biofilm infections. APMIS 125 304–319
Ciofu O and Tolker-Nielsen T 2019 Tolerance and resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to antimicrobial agents – How P. aeruginosa can escape antibiotics. Front. Microbiol. 10
Ciofu O, Tolker-Nielsen T, Jensen PO, Wang H and Hoiby N 2015 Antimicrobial resistance, respiratory tract infections and role of biofilms in lung infections in cystic fibrosis patients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 85 7–23
Clinton A and Carter T 2015 Chronic wound biofilms: Pathogenesis and potential therapies. Lab. Med. 46 277–284
Costerton JW, Cheng KJ, Geesey GG, Ladd TI, Nickel JC, Dasgupta M and Marrie TJ 1987 Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 41 435–464
Dang H and Lovell CR 2016 Microbial Surface Colonization and Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 80 91–138
Davenport EK, Call DR and Beyenal H 2014 Differential protection from tobramycin by extracellular polymeric substances from Acinetobacter baumannii and Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58 4755–4761
de Kievit TRand Iglewski BH 2000 Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect. Immun. 68 4839–4849
de la Fuente-Núñez C, Reffuveille F, Fernández L and Hancock RE 2013 Bacterial biofilm development as a multicellular adaptation: antibiotic resistance and new therapeutic strategies. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 16 580–589
Demidova-Rice TN, Hamblin MR and Herman IM 2012 Acute and impaired wound healing: pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 1: normal and chronic wounds: biology, causes, and approaches to care. Adv. Skin. Wound. Care 25 304–314
Dötsch A, Eckweiler D, Schniederjans M, Zimmermann A, Jensen V, Scharfe M, Geffers R and Häussler S 2012 The Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptome in planktonic cultures and static biofilms using RNA sequencing. PLoS One 7 e31092
Drenkard E 2003 Antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Microbes Infect. 5 1213–1219
Fagerlind MG, Webb JS, Barraud N, McDougald D, Jansson A, Nilsson P, Harlén M, Kjelleberg S and Rice SA 2012 Dynamic modelling of cell death during biofilm development. J. Theor. Biol. 295 23–36
Fernández-Barat L, Ciofu O, Kragh KN, Pressler T, Johansen U, Motos A, Torres A and Hoiby N 2017 Phenotypic shift in Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations from cystic fibrosis lungs after 2-week antipseudomonal treatment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 16 222–229
Flemming HC, Neu TR and Wozniak DJ 2007 The EPS matrix: the house of biofilm cells. J. Bacteriol. 189 7945–7947
Frank KL, Reichert EJ, Piper KE and Patel R 2007 In vitro effects of antimicrobial agents on planktonic and biofilm forms of Staphylococcus lugdunensis clinical isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 888–895
Furukawa S, Kuchma SL and O’Toole GA 2006 Keeping their options open: Acute versus persistent infections. J. Bacteriol. 188 1211–1217
Ghanbari A, Dehghany J, Schwebs T, Müsken M, Häussler S and Meyer-Hermann M 2016 Inoculation density and nutrient level determine the formation of mushroom-shaped structures in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Sci. Rep. 6 32097
Goltermann L and Tolker-Nielsen T 2017 Importance of the exopolysaccharide matrix in antimicrobial tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa aggregates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61 e02696–e02716
Gothwal R and Thatikonda S 2017 Role of environmental pollution in prevalence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in aquatic environment of river: case of Musi river, South India. Water Environ. J. 31 456–462
Gristina AG, Jennings RA, Naylor PT, Myrvik QN and Webb LX 1989 Comparative in vitro antibiotic resistance of surface-colonizing coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33 813–816
Gu H, Hou S, Yongyat C, De Tore S and Ren D 2013 Patterned biofilm formation reveals a mechanism for structural heterogeneity in bacterial biofilms. Langmuir 29 11145–11153
Haagensen JA, Klausen M, Ernst RK, Miller SI, Folkesson A, Tolker-Nielsen T and Molin S 2007 Differentiation and distribution of colistin- and sodium dodecyl sulfate-tolerant cells in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Bacteriol. 189 28–37
Haddadin RN, Saleh S, Al-Adham IS, Buultjens TE and Collier PJ 2010 The effect of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on virulence factors expressed by Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 108 1281–1291
Hajdu S, Holinka J, Reichmann S, Hirschl AM, Graninger W and Presterl E 2010 Increased temperature enhances the antimicrobial effects of daptomycin, vancomycin, tigecycline, fosfomycin, and cefamandole on staphylococcal biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 54 4078–4084
Hall CW and Mah TF 2017 Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 276–301
Hoffman LR, D’Argenio DA, MacCoss MJ, Zhang Z, Jones RA and Miller SI 2005 Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 436 1171–1175
Hoiby N 2011 Recent advances in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in cystic fibrosis. BMC Med. 9 32
Hunt SM, Werner EM, Huang B, Hamilton MA and Stewart PS 2004 Hypothesis for the role of nutrient starvation in biofilm detachment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70 7418–7425
Hurlow J, Blanz E and Gaddy JA 2016 Clinical investigation of biofilm in non-healing wounds by high resolution microscopy techniques. J. Wound Care 25 S11–22
James GA, Korber DR, Caldwell DE and Costerton JW 1995 Digital image analysis of growth and starvation responses of a surface-colonizing Acinetobacter sp. J. Bacteriol. 177 907–915
Jiang Q, Chen J, Yang C, Yin Y and Yao K 2019 Quorum sensing: a prospective therapeutic target for bacterial diseases. BioMed. Res. Int. 2019 1–15
Jones CJ and Wozniak DJ 2017 Psl Produced by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa contributes to the establishment of biofilms and immune evasion. mBio 8 e00864–e00817
Kim J, Hahn JS, Franklin MJ, Stewart PS and Yoon J 2009 Tolerance of dormant and active cells in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01 biofilm to antimicrobial agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 63 129–135
Kim J, Pitts B, Stewart PS, Camper A and Yoon J 2008 Comparison of the antimicrobial effects of chlorine, silver ion, and tobramycin on biofilm. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 1446–1453
Kırmusaoğlu S 2016 Staphylococcal biofilms: Pathogenicity, mechanism and regulation of biofilm formation by quorum-sensing system and antibiotic resistance mechanisms of biofilm-embedded microorganisms. 2016 189–209. https://doi.org/10.5772/62943
Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ and Collins JJ 2010 How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8 423–435
Kostakioti M, Hadjifrangiskou M and Hultgren SJ 2013 Bacterial biofilms: development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 3 a010306
Koutsoudis MD, D. Tsaltas, Minogue TD and S. B. von Bodman 2006 Quorum-sensing regulation governs bacterial adhesion, biofilm development, and host colonization in Pantoea stewartii subspecies stewartii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103 5983–5988
Kumar A, Alam A, Rani M, Ehtesham NZ and Hasnain SE 2017 Biofilms: Survival and defense strategy for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 307 481–489
Linares JF, Gustafsson I, Baquero F and Martinez JL 2006 Antibiotics as intermicrobial signaling agents instead of weapons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103 19484–19489
Liu J, Martinez-Corral R, Prindle A, Dong-yeon DL, Larkin J, Gabalda-Sagarra M, Garcia-Ojalvo J and Süel GM 2017 Coupling between distant biofilms and emergence of nutrient time-sharing. Science 356 638–642
Machineni L, Rajapantul A, Nandamuri V and Pawar PD 2017 Influence of nutrient availability and quorum sensing on the formation of metabolically inactive microcolonies within structurally heterogeneous bacterial biofilms: An individual-based 3d cellular automata model. Bull. Math. Biol. 79 594–618
Machineni L, Reddy CT, Nandamuri V and Pawar PD 2018 A 3D individual-based model to investigate the spatially heterogeneous response of bacterial biofilms to antimicrobial agents. Math. Method. Appl. Sci. 41
Macia MD, Rojo-Molinero E and Oliver A 2014 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. 20 981–990
Maurice NM, Bedi B and Sadikot RT 2018 Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: host response and clinical implications in lung infections. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 58 428–439
Melaugh G, Hutchison J, Kragh KN, Irie Y, Roberts A, Bjarnsholt T, Diggle SP, Gordon VD and Allen RJ 2016 Shaping the growth behaviour of biofilms initiated from bacterial aggregates. PLoS One 11 e0149683
Meylan S, Andrews IW and Collins JJ 2018 Targeting antibiotic tolerance, pathogen by pathogen. Cell 172 1228–1238
Mulcahy LR, Isabella VM and Lewis K 2014 Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in disease. Microb. Ecol. 68 1–12
Nadell CD, Xavier JB, Levin SA and Foster KR 2008 The evolution of quorum sensing in bacterial biofilms. PLoS Biol. 6 e14
Ng WL and Bassler BL 2009 Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures. Annu. Rev. Genet. 43 197–222
Nguyen D, Joshi-Datar A, Lepine F, Bauerle E, Olakanmi O, Beer K, McKay G, Siehnel R, Schafhauser J, Wang Y, Britigan BE and Singh PK 2011 Active starvation responses mediate antibiotic tolerance in biofilms and nutrient-limited bacteria. Science 334 982–986
Novick RP and Geisinger E 2008 Quorum sensing in staphylococci. Annu. Rev. Genet. 42 541–564
O’Donnell LE, HAlalwan KA, Kean R, Calvert G, Nile CJ, Lappin DF, Robertson D, Williams C, Ramage G and Sherry L 2017 Candida albicans biofilm heterogeneity does not influence denture stomatitis but strongly influences denture cleansing capacity. J. Med. Microbiol. 66 54–60
Olsen I 2015 Biofilm-specific antibiotic tolerance and resistance. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 34 877–886
Owlia P, Nosrati R, Alaghehbandan R and Lari AR 2014 Antimicrobial susceptibility differences among mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. https://doi.org/10.3205/dgkh000233
Pamp SJ, Gjermansen M, Johansen HK and Tolker-Nielsen T 2008 Tolerance to the antimicrobial peptide colistin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms is linked to metabolically active cells, and depends on the pmr and mexAB-oprM genes. Mol. Microbiol. 68 223–240
Park AJ, Murphy K, Krieger JR, Brewer D, Taylor P, Habash M and Khursigara CM 2014 A temporal examination of the planktonic and biofilm proteome of whole cell Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 using quantitative mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell Proteom. 13 1095–1105
Park AJ, Surette MD and Khursigara CM 2014 Antimicrobial targets localize to the extracellular vesicle-associated proteome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown in a biofilm. Front. Microbiol. 5 464
Perumal S and Mahmud R 2013 Chemical analysis, inhibition of biofilm formation and biofilm eradication potential of Euphorbia hirta L. against clinical isolates and standard strains. BMC Complementary Alternat. Med. 13 346
Poole K 2012 Bacterial stress responses as determinants of antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 67 2069–2089
Poudyal B and Sauer K 2018a The ABC of biofilm drug tolerance: the MerR-like regulator BrlR is an activator of ABC transport systems, with PA1874–77 contributing to the tolerance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to tobramycin. Antimicrob. Agents Chem.62 e01981–01917
Poudyal B and Sauer K 2018b The PA3177 Gene encodes an active diguanylate cyclase that contributes to biofilm antimicrobial tolerance but not biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chem.62 e01049–01018
Pu Y, Zhao Z, Li Y, Zou J, Ma Q, Zhao Y, Ke Y, Zhu Y, Chen H, Baker MA, Ge H, Sun Y, Xie XS and Bai F 2016 Enhanced efflux activity facilitates drug tolerance in dormant bacterial cells. Mol. Cell 62 284–294
Queck SY, Jameson M-Lee, Villaruz AE, Bach TH, Khan BA, Sturdevant DE, Ricklefs SM, Li M and Otto M 2008 RNAIII-independent target gene control by the agr quorum-sensing system: insight into the evolution of virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Cell 32 150–158
Quinones B, Dulla G and Lindow SE 2005 Quorum sensing regulates exopolysaccharide production, motility, and virulence in Pseudomonas syringae. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 18 682–693
Rafii F and Hart ME 2015 Antimicrobial resistance in clinically important biofilms. World J. Pharmacol. 4 31–46
Resch A, Rosenstein R, Nerz C and Götz F 2005 Differential gene expression profiling of Staphylococcus aureus cultivated under biofilm and planktonic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 2663–2676
Rice SA, Koh KS, Queck SY, Labbate M, Lam KW and Kjelleberg S 2005 Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. J. Bacteriol. 187 3477–3485
Rochex A and Lebeault JM 2007 Effects of nutrients on biofilm formation and detachment of a Pseudomonas putida strain isolated from a paper machine. Water Res. 41 2885–2892
Sakuragi Y and Kolter R 2007 Quorum-sensing regulation of the biofilm matrix genes (pel) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 189 5383–5386
Santos-Lopez A, Marshall CW, Scribner MR, Snyder D and Cooper VS 2019 Biofilm-dependent evolutionary pathways to antibiotic resistance. bioRxiv: 581611
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton JW and Davies DG 2002 Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 184 1140–1154
Sauer K, Cullen MC, Rickard AH, Zeef LA, Davies DG and Gilbert P 2004 Characterization of nutrient-induced dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 186 7312–7326
Saxena P, Joshi Y, Rawat K and Bisht R 2019 Biofilms: architecture, resistance, quorum sensing and control mechanisms. Indian Microbiol. J. 59 3–12
Singh R, Ray P, Das A and Sharma M 2010 Penetration of antibiotics through Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. J. Antimicrobial Chemother. 65 1955–1958
Singh S, Singh SK, Chowdhury I and Singh R 2017 Understanding the mechanism of bacterial biofilms resistance to antimicrobial agents. Open Microbiol. J. 11 53–62
Sønderholm M, Koren K, Wangpraseurt D, Jensen PØ, Kolpen M, Kragh KN, Bjarnsholt T and Kühl M 2018 Tools for studying growth patterns and chemical dynamics of aggregated Pseudomonas aeruginosa exposed to different electron acceptors in an alginate bead model. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 4 3
Song Z, Wu H, Mygind P, Raventos D, Sonksen C, Kristensen HH and Hoiby N 2005 Effects of intratracheal administration of novispirin G10 on a rat model of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49 3868–3874
Staudinger BJ, Muller JF, Halldorsson S, Boles B, Angermeyer A, Nguyen D, Rosen H, Baldursson O, Gottfreethsson M, Guethmundsson GH and Singh PK 2014 Conditions associated with the cystic fibrosis defect promote chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Am. Respir. J. Crit. Care Med. 189 812–824
Stewart PS and Franklin MJ 2008 Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6 199–210
Stewart PS, Zhang T, Xu R, Pitts B, Walters MC, Roe F, Kikhney J and Moter A 2016 Reaction-diffusion theory explains hypoxia and heterogeneous growth within microbial biofilms associated with chronic infections. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2 16012
Stoitsova S, Paunova-Krasteva T and Borisova D 2016 Modulation of biofilm growth by sub-inhibitory amounts of antibacterial substances. https://doi.org/10.5772/62939
Stoodley P, Dodds I, Boyle JD and Lappin-Scott HM 1998 Influence of hydrodynamics and nutrients on biofilm structure. J. Appl. Microbiol. 85 19S–28S
Stoodley P, Sauer K, Davies DG and Costerton JW 2002 Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 56 187–209
Stoodley P, Wilson S, Hall-Stoodley L, Boyle JD, Lappin-Scott HM and Costerton JW 2001 Growth and detachment of cell clusters from mature mixed-species biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 5608–5613
Subrt N, Mesak LR and Davies J 2011 Modulation of virulence gene expression by cell wall active antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 66 979–984
Tan CH, Koh KS, Xie C, Tay M, Zhou Y, Williams R, Ng WJ, Rice SA and Kjelleberg S 2014 The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. ISME J. 8 1186–1197
Tezel BU, Akçelik N, Yüksel FN, Karatuğ NT and Akçelik M 2016 Effects of sub-MIC antibiotic concentrations on biofilm production of Salmonella infantis. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 30 1184–1191
Trastoy R, Manso T, Fernandez L-Garcia, Blasco L, Ambroa A, Perez MDel L Molino, Bou G, Garcia–Contreras R, Wood TK and Tomas M 2018 Mechanisms of bacterial tolerance and persistence in the gastrointestinal and respiratory environments. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 31 pii: e00023-18
Tseng BS, Zhang W, Harrison JJ, Quach TP, Song JL, Penterman J, Singh PK, Chopp DL, Packman AI and Parsek MR 2013 The extracellular matrix protects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by limiting the penetration of tobramycin. Environ. Microbiol. 15 2865–2878
Tsuneda S, Aikawa H, Hayashi H, Yuasa A and Hirata A 2003 Extracellular polymeric substances responsible for bacterial adhesion onto solid surface. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 223 287–292
Verderosa AD, Dhouib R, Fairfull KE-Smith and Totsika M 2019 Nitroxide functionalized antibiotics are promising eradication agents against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. bioRxiv: 579896
von Bodman SB, Majerczak DR and Coplin DL 1998 A negative regulator mediates quorum-sensing control of exopolysaccharide production in Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 7687–7692
Vu B, Chen M, Crawford RJ and Ivanova EP 2009 Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides involved in biofilm formation. Molecules 14 2535–2554
Wilkins M, Hall L-Stoodley, Allan RN and Faust SN 2014 New approaches to the treatment of biofilm-related infections. Infect. J. 69 S47–S52
Williamson KS, Richards LA, Perez-Osorio AC, Pitts B, McInnerney K, Stewart PS and Franklin MJ 2012 Heterogeneity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms includes expression of ribosome hibernation factors in the antibiotic-tolerant subpopulation and hypoxia-induced stress response in the metabolically active population. Bacteriol. J. 194 2062–2073
Williamson KS, Richards LA, Perez-Osorio AC, Pitts B, McInnerney K, Stewart PS and Franklin MJ 2012 Heterogeneity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms includes expression of ribosome hibernation factors in the antibiotic-tolerant subpopulation and hypoxia-induced stress response in the metabolically active population. J. Bacteriol. 194 2062–2073
Wolska KI, Grudniak AM, Rudnicka Z and Markowska K 2016 Genetic control of bacterial biofilms. J. Appl. Genet. 57 225–238
Wood TK, Knabel SJ and Kwan BW 2013 Bacterial persister cell formation and dormancy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79 7116–7121
Wright GD 2005 Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 57 1451–1470
Xu KD, Stewart PS, Xia F, Huang CT and McFeters GA 1998 Spatial physiological heterogeneity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm is determined by oxygen availability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64 4035–4039
Xue Z, Hessler CM, Panmanee W, Hassett DJ and Seo Y 2013 Pseudomonas aeruginosa inactivation mechanism is affected by capsular extracellular polymeric substances reactivity with chlorine and monochloramine. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 83 101–111
Yang L, Hu Y, Liu Y, Zhang J, Ulstrup J and Molin S 2011 Distinct roles of extracellular polymeric substances in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Environ. Microbiol. 13 1705–1717
Zhang L and Mah TF 2008 Involvement of a novel efflux system in biofilm-specific resistance to antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 190 4447–4452
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Sudha Bhattacharya.
Corresponding editor: Sudha Bhattacharya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machineni, L. Effects of biotic and abiotic factors on biofilm growth dynamics and their heterogeneous response to antibiotic challenge. J Biosci 45, 25 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-9990-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-9990-3