Abstract
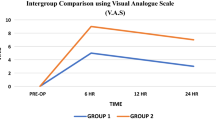
We evaluated the benefit of glossopharyngeal nerve block with long acting local anaesthetic like bupivacaine. It was a randomized prospective study. Sixty-four patients were selected and divided into two groups. Group A received bilateral nerve block and Group B received no block. Pain score using Visual Analog Scale (0–100 mm) was assessed at 30 min, 2, 6 and 12 h. In the immediate post operative period pain scores of Group A at rest and swallowing was significantly lower than Group B (p < 0.001 and p < 0.01). Glossopharyngeal nerve block is an important method of reducing post-tonsillectomy pain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Topal K, Aktan B, Sakat MS, Kilic K, Gozeler MS (2017) Post-operative pain control after tonsillectomy: dexametasone vs tramadol. Acta Otolaryngol 137(6):618–622. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2016.1269945
Kamal SA, Basu S, Kapoor L, Kulandaivelu G, Talpalikar S, Papasthatis D (2006) Harmonic scalpel tonsillectomy: a prospectivestudy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263(449–54):3
Ozkiris M, Kapusuz Z, Saydam L (2013) Comparison of three techniques in adult tonsillectomy. Eur Arch Otorhino-laryngol. 270:1143–1147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2160-y
Ragab SM (2012) Six years of evidence-based adult dissection tonsillectomy with ultrasonic scalpel, bipolar electrocautery, bipolarradiofrequency or ‘cold steel’ dissection. J Laryngol Otol 126:1056–1062
Sarny S, Habermann W, Ossimitz G, Stammberger H (2012) Significant post-tonsillectomy pain is associated with increased risk of hemorrhage. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 121:776–781
Kissin I (2000) Preemptive analgesia. Anesthesiology 93:1138–1143
Hanasono MM, Lalakea ML, Mikulec AA, Shepard KG, Wellis V, Messner AH (2004) Perioperative steroids in tonsillectomy using electrocautery and sharp dissection techniques. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:917–921
Naesh O, Niles LA, Gilbert JG, Ammar MM, Phibbs PW, Phillips AM, Khrapov AV, Robert AJ, McClintock A (2005) A randomized, placebo-controlled study of rofecoxib with paracetamol in early post-tonsillectomy pain in adults. Eur J Anaesthesiol 7(22):768–773
Valijan A (1989) Pain relief after tonsillectomy. Effect of benzydamine hydrochloride spray on postoperative pain relief after tonsillectomy. Anaesthesia 44:990–991
Ginstrom R, Silvola J, Saarnivaara L (2005) Local bupivacaineepinephrine infiltration combined with general anesthesia for adult tonsillectomy. Acta Otolaryngol 125:972–975
Spence AG (1996) Single injection field block of tonsillar fossa. Anaesth Intensive Care 24:621–623
Bruin G (1994) Glossopharyngeal nerve block for tonsillectomy or uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Can J Anaesth 41:1236
Bell KR, Cyna AM, Lawler KM, Sinclair C, Kelly PJ, Millar F, Flood LM (1997) The effect of glossopharyngeal nerve block on pain after elective adult tonsillectomy and uvulopalatoplasty. Anaesthesia 52:597–602
El-Hakim H, Nunez DA, Saleh HA, MacLeod DM, Gardiner Q (2000) A randomised controlled trial of the effect of regional nerve blocks on immediate post-tonsillectomy pain in adult patients. Clin Otolaryngol 25:413–417
Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I (1991) The effect of preincisional infiltration of tonsils with bupivacaine on the pain following tonsillectomy under general anaesthesia. Pain 47:305–308
Park H-P, Hwang J-w, Park S-H, Jeon Y-T, Bahk J-H, Oh Y-S (2007) The effects of glossopharyngeal nerve block on postoperative pain relief after tonsillectomy: the importance of the extent of obtunded gag reflex as a clinical indicator. Anesth Analg 105:267–271
Schoem SR, Watkins GL, Kuhn JJ, Alburger JF, Kim KZ, Thompson DH (1993) Control of early postoperative pain with bupivacaine in adult local tonsillectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 119(3):292–293. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1993.01880150040007
Broadman LM, Patel RI, Feldman BA, Sellman GL, Milmoe G, Camilon F (1989) The effects of peritonsillar infiltration on the reduction of intraoperative blood loss and post-tonsillectomy pain in children. Laryngoscope 99:578–581
Atallah N, Kumar M, Hilali A, Hickey S (2000) Post-operative pain in tonsillectomy: bipolar electrodissection technique vs dissection ligation technique. A double-blind randomized prospective trial. J Laryngol Otol 114(9):667–670
Sharifian HA, Fathololoomi MR, Bafghi AF, Naini SAS (2006) Effect of local bupivacaine infiltration on post-tonsillectomy pain. Tanaffos 5(1):45–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The permission was taken from Institutional Ethics Committee prior to starting the project. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual Participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debasish, G., Anindita, S., Aryabrata, D. et al. Glossopharyngeal Nerve Block with Long Acting Local Anaesthetic Agent (Bupivacaine) and It’s Effect on Early Post-operative Period in Adult Tonsillectomy: A Prospective Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 1), 390–394 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1323-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1323-6