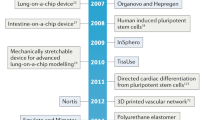
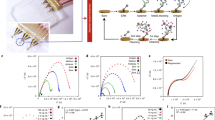
Abstract
The aptamer, known as a chemical antibody, has proven to be of high diagnostic and therapeutic value with the FDA’s first aptamer drug in 2004 and many aptamers under clinical validation. However, the clinical translation of aptamer for therapeutics has been delayed because of the limitation of using the target model during selection and a lack of information on several crucial factors, including their inherent physicochemical characterization and safety, and the function. Three-dimensional (3D) structure tissue provides proof of in-depth functionality due to their maturity and 3D complexity, enabling them to get information on the natural structure of the target for human treatment. The organ-on-a-chip integrates microfluidic technology with 3D cell culture that possesses in vivo-like tissue-based models that have been engineered for validation to transform the commercial drug discovery. Thus, the organ-on-a-chip may offer a promising solution for the addressed problems, enhancing the clinical translation procedure for aptamer-based therapeutics. Motivated by the advantageous function of the aptamer-based organ-on-a-chip system, we update the current technology to generate aptamers using SELEX (Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential Enrichment) and confirm the application of aptamers to various long-term treatments. We can also accurately analyze the advantages of organ-on-a-chips and present the necessity of developing aptamer-based organ-on-a-chip systems. In this regard, the aptamer-based organ-on-a-chip is expected to increase the possibility of creating an aptamer as a therapeutic agent by more accurately selecting and verifying the aptamer that affects specific organ treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellington, A.D., Szostak, J.W.: In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346, 818–822 (1990)
Robertson, D.L., Joyce, G.F.: Selection in vitro of an RNA enzyme that specifically cleaves single-stranded DNA. Nature 344, 467–468 (1990)
Tuerk, C., Gold, L.: Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249, 505–510 (1990)
Kim, S.H., Thoa, T.T.T., Gu, M.B.: Aptasensors for environmental monitoring of contaminants in water and soil. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 10, 9–21 (2019)
Zhou, J., Rossi, J.: Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev Drug Discov. 16, 181–202 (2017)
Stoltenburg, R., Reinemann, C., Strehlitz, B.: SELEX—a (r)evolutionary method to generate high-affinity nucleic acid ligands. Biomol. Eng. 24, 381–403 (2007)
Dunn, M.R., Jimenez, R.M., Chaput, J.C.: Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 1, 0076 (2017)
Taylor, A.I., Holliger, P.: Directed evolution of artificial enzymes (XNAzymes) from diverse repertoires of synthetic genetic polymers. Nat. Protoc. 10, 1625–1642 (2015)
Kimoto, M., Yamashige, R., Matsunaga, K., Yokoyama, S., Hirao, I.: Generation of high-affinity DNA aptamers using an expanded genetic alphabet. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 453–457 (2013)
Leist, M., Hartung, T.: Reprint: Inflammatory findings on species extrapolations: humans are definitely no 70-kg mice. Altex 30, 227–230 (2013)
Chapman, K.L., Holzgrefe, H., Black, L.E., Brown, M., Chellman, G., Copeman, C., Couch, J., Creton, S., Gehen, S., Hoberman, A., Kinter, L.B., Madden, S., Mattis, C., Stemple, H.A., Wilson, S.: Pharmaceutical toxicology: designing studies to reduce animal use, while maximizing human translation. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 66, 88–103 (2013)
Fielden, M.R., Kolaja, K.L.: The role of early in vivo toxicity testing in drug discovery toxicology. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 7, 107–110 (2008)
Olson, H., Betton, G., Robinson, D., Thomas, K., Monro, A., Kolaja, G., Lilly, P., Sanders, J., Sipes, G., Bracken, W., Dorato, M., Deun, K.V., Smith, P., Berger, B., Heller, A.: Concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in humans and in animals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 32, 56–67 (2000)
Richardson, L., Kim, S., Menon, R., Han, A.: Organ-on-chip technology: the future of feto-maternal interface research? Front Physiol. 11, 715 (2020)
Zhang, B., Korolj, A., Lai, B.F.L., Radisic, M.: Advances in organ-on-a-chip engineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 257–278 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Lai, B.S., Juhas, M.: Recent advances in aptamer discovery and applications. Molecules 24, 941 (2019)
Pleiko, K., Saulite, L., Parfejevs, V., Miculis, K., Vjaters, E., Riekstina, U.: Differential binding cell-SELEX method to identify cell-specific aptamers using high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 9, 8142 (2019)
Park, J.W., Tatavarty, R., Kim, D.W., Jung, H.T., Gu, M.B.: Immobilization-free screening of aptamers assisted by graphene oxide. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 48, 2071–2073 (2012)
Shin, S.R., Zhang, Y.S., Kim, D.-J., Manbohi, A., Avci, H., Silvestri, A., Aleman, J., Hu, N., Kilic, T., Keung, W., Righi, M., Assawes, P., Alhadrami, H.A., Li, R.A., Dokmeci, M.R., Khademhosseini, A.: Aptamer-based microfluidic electrochemical biosensor for monitoring cell-secreted trace cardiac biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 88, 10019–10027 (2016)
Wang, D.-L., Song, Y.-L., Zhu, Z., Li, X.-L., Zou, Y., Yang, H.-T., Wang, J.-J., Yao, P.-S., Pan, R.-J., Yang, C.J., Kang, D.-Z.: Selection of DNA aptamers against epidermal growth factor receptor with high affinity and specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 453, 681–685 (2014)
Hung, L.Y., Wang, C.H., Hsu, K.F., Chou, C.Y., Lee, G.B.: An on-chip Cell-SELEX process for automatic selection of high-affinity aptamers specific to different histologically classified ovarian cancer cells. Lab Chip 14, 4017–4028 (2014)
Lee, Y.J., Kim, I.S., Park, S.-A., Kim, Y., Lee, J.E., Noh, D.-Y., Kim, K.-T., Ryu, S.H., Suh, P.-G.: Periostin-binding DNA aptamer inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis. Mol. Ther. 21, 1004–1013 (2013)
Mendonsa, S.D., Bowser, M.T.: In vitro selection of high-affinity DNA ligands for human IgE using capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 76, 5387–5392 (2004)
Bompiani, K.M., Monroe, D.M., Church, F.C., Sullenger, B.A.: A high affinity, antidote-controllable prothrombin and thrombin-binding RNA aptamer inhibits thrombin generation and thrombin activity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 10, 870–880 (2012)
Kim, M.Y., Jeong, S.: In vitro selection of RNA aptamer and specific targeting of ErbB2 in breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 21, 173–178 (2011)
Mi, Z., Guo, H., Russell, M.B., Liu, Y., Sullenger, B.A., Kuo, P.C.: RNA aptamer blockade of osteopontin inhibits growth and metastasis of MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 17, 153–161 (2009)
Jellinek, D., Lynott, C.K., Rifkin, D.B., Janjić, N.: High-affinity RNA ligands to basic fibroblast growth factor inhibit receptor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90, 11227–11231 (1993)
Stoltenburg, R., Reinemann, C., Strehlitz, B.: FluMag-SELEX as an advantageous method for DNA aptamer selection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 383, 83–91 (2005)
Huang, C.J., Lin, H.I., Shiesh, S.C., Lee, G.B.: An integrated microfluidic system for rapid screening of alpha-fetoprotein-specific aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 35, 50–55 (2012)
Hung, L.-Y., Wang, C.-H., Che, Y.-J., Fu, C.-Y., Chang, H.-Y., Wang, K., Lee, G.-B.: Screening of aptamers specific to colorectal cancer cells and stem cells by utilizing on-chip cell-SELEX. Sci. Rep. 5, 10326 (2015)
Ireson, C.R., Kelland, L.R.: Discovery and development of anticancer aptamers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 2957–2962 (2006)
Onakpoya, I.J., Heneghan, C.J., Aronson, J.K.: Correction to: post-marketing withdrawal of 462 medicinal products because of adverse drug reactions: a systematic review of the world literature. BMC Med. 17, 56 (2019)
Paul, S.M., Mytelka, D.S., Dunwiddie, C.T., Persinger, C.C., Munos, B.H., Lindborg, S.R., Schacht, A.L.: How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 203–214 (2010)
Vernetti, L., Gough, A., Baetz, N., Blutt, S., Broughman, J.R., Brown, J.A., Foulke-Abel, J., Hasan, N., In, J., Kelly, E., Kovbasnjuk, O., Repper, J., Senutovitch, N., Stabb, J., Yeung, C., Zachos, N.C., Donowitz, M., Estes, M., Himmelfarb, J., Truskey, G., Wikswo, J.P., Taylor, D.L.: Functional coupling of human microphysiology systems: intestine, liver, kidney proximal tubule, blood-brain barrier and skeletal muscle. Sci. Rep.. 7, 42296 (2017)
Lee, J., Choi, J.H., Kim, H.J.: Human gut-on-a-chip technology: will this revolutionize our understanding of IBD and future treatments? Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 10, 883–885 (2016)
Ingber, D.E.: Reverse engineering human pathophysiology with organs-on-chips. Cell 164, 1105–1109 (2016)
Viravaidya, K., Sin, A., Shuler, M.L.: Development of a microscale cell culture analog to probe naphthalene toxicity. Biotechnol. Prog. 20, 316–323 (2004)
Neff, E.P.: Printing cures: organovo advances with 3D-printed liver tissue. Lab Anim (NY) 46, 57 (2017)
Lind, J.U., Busbee, T.A., Valentine, A.D., Pasqualini, F.S., Yuan, H., Yadid, M., Park, S.-J., Kotikian, A., Nesmith, A.P., Campbell, P.H., Vlassak, J.J., Lewis, J.A., Parker, K.K.: Instrumented cardiac microphysiological devices via multimaterial three-dimensional printing. Nat. Mater. 16, 303–308 (2017)
Miller, P.G., Shuler, M.L.: Design and demonstration of a pumpless 14 compartment microphysiological system. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 113, 2213–2227 (2016)
Ahn, S.I., Sei, Y.J., Park, H.-J., Kim, J., Ryu, Y., Choi, J.J., Sung, H.-J., MacDonald, T.J., Levey, A.I., Kim, Y.: Microengineered human blood-brain barrier platform for understanding nanoparticle transport mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 11, 175 (2020)
Jeong, S., Kim, S., Buonocore, J., Park, J., Welsh, C.J., Li, J., Han, A.: A three-dimensional arrayed microfluidic blood-brain barrier model with integrated electrical sensor array. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65, 431–439 (2018)
Sidorov, V.Y., Samson, P.C., Sidorova, T.N., Davidson, J.M., Lim, C.C., Wikswo, J.P.: I-wire heart-on-a-chip I: three-dimensional cardiac tissue constructs for physiology and pharmacology. Acta Biomater. 48, 68–78 (2017)
Adriani, G., Ma, D., Pavesi, A., Kamm, R.D., Goh, E.L.: A 3D neurovascular microfluidic model consisting of neurons, astrocytes and cerebral endothelial cells as a blood-brain barrier. Lab Chip 17, 448–459 (2017)
Huh, D., Matthews, B.D., Mammoto, A., Montoya-Zavala, M., Hsin, H.Y., Ingber, D.E.: Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 328, 1662–1668 (2010)
Yang, X., Li, K., Zhang, X., Liu, C., Guo, B., Wen, W., Gao, X.: Nanofiber membrane supported lung-on-a-chip microdevice for anti-cancer drug testing. Lab Chip 18, 486–495 (2018)
Stevens, K.R., Ungrin, M.D., Schwartz, R.E., Ng, S., Carvalho, B., Christine, K.S., Chaturvedi, R.R., Li, C.Y., Zandstra, P.W., Chen, C.S., Bhatia, S.N.: InVERT molding for scalable control of tissue microarchitecture. Nat. Commun. 4, 1847 (2013)
Spence, J.R., Mayhew, C.N., Rankin, S.A., Kuhar, M.F., Vallance, J.E., Tolle, K., Hoskins, E.E., Kalinichenko, V.V., Wells, S.I., Zorn, A.M., Shroyer, N.F., Wells, J.M.: Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into intestinal tissue in vitro. Nature 470, 105–109 (2011)
Chi, M., Yi, B., Oh, S., Park, D.-J., Sung, J.H., Park, S.: A microfluidic cell culture device (μFCCD) to culture epithelial cells with physiological and morphological properties that mimic those of the human intestine. Biomed. Microdevices 17, 9966 (2015)
Xiao, S., Coppeta, J.R., Rogers, H.B., Isenberg, B.C., Zhu, J., Olalekan, S.A., McKinnon, K.E., Dokic, D., Rashedi, A.S., Haisenleder, D.J., Malpani, S.S., Arnold-Murray, C.A., Chen, K., Jiang, M., Bai, L., Nguyen, C.T., Zhang, J., Laronda, M.M., Hope, T.J., Maniar, K.P., Pavone, M.E., Avram, M.J., Sefton, E.C., Getsios, S., Burdette, J.E., Kim, J.J., Borenstein, J.T., Woodruff, T.K.: A microfluidic culture model of the human reproductive tract and 28-day menstrual cycle. Nat. Commun. 8, 14584 (2017)
Zhang, Y.S., Aleman, J., Shin, S.R., Kilic, T., Kim, D., Shaegh, S.A.M., Massa, S., Riahi, R., Chae, S., Hu, N., Avci, H., Zhang, W., Silvestri, A., Nezhad, A.S., Manbohi, A., Ferrari, F.D., Polini, A., Calzone, G., Shaikh, N., Alerasool, P., Budina, E., Kang, J., Bhise, N., Ribas, J., Pourmand, A., Skardal, A., Shupe, T., Bishop, C.E., Dokmeci, M.R., Atala, A., Khademhosseini, A.: Multisensor-integrated organs-on-chips platform for automated and continual in situ monitoring of organoid behaviors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114, E2293-e2302 (2017)
Zavyalova, E., Samoylenkova, N., Revishchin, A., Turashev, A., Gordeychuk, I., Golovin, A., Kopylov, A., Pavlova, G.: The evaluation of pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of anti-thrombin DNA Aptamer RA-36. Front Pharmacol. 8, 922 (2017)
Sennino, B., Falcón, B.L., McCauley, D., Le, T., McCauley, T., Kurz, J.C., Haskell, A., Epstein, D.M., McDonald, D.M.: Sequential loss of tumor vessel pericytes and endothelial cells after inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor B by selective aptamer AX102. Cancer Res. 67, 7358–7367 (2007)
Akiyama, H., Kachi, S., Silva, R.L.E., Umeda, N., Hackett, S.F., McCauley, D., McCauley, T., Zoltoski, A., Epstein, D.M., Campochiaro, P.A.: Intraocular injection of an aptamer that binds PDGF-B: a potential treatment for proliferative retinopathies. J. Cell Physiol. 207, 407–412 (2006)
Zboralski, D., Hoehlig, K., Eulberg, D., Frömming, A., Vater, A.: Increasing tumor-infiltrating T cells through inhibition of CXCL12 with NOX-A12 synergizes with PD-1 blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 5, 950–956 (2017)
Hoellenriegel, J., Zboralski, D., Maasch, C., Rosin, N.Y., Wierda, W.G., Keating, M.J., Kruschinski, A., Burger, J.A.: The Spiegelmer NOX-A12, a novel CXCL12 inhibitor, interferes with chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell motility and causes chemosensitization. Blood 123, 1032–1039 (2014)
Macdonald, J., Denoyer, D., Henri, J., Jamieson, A., Burvenich, I.J.G., Pouliot, N., Shigdar, S.: Bifunctional aptamer-doxorubicin conjugate crosses the blood-brain barrier and selectively delivers its payload to EpCAM-positive tumor cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 30, 117–128 (2020)
Glassman, P.M., Myerson, J.W., Ferguson, L.T., Kiseleva, R.Y., Shuvaev, V.V., Brenner, J.S., Muzykantov, V.R.: Targeting drug delivery in the vascular system: focus on endothelium. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. (2020)
Vinores, S.A.: Pegaptanib in the treatment of wet, age-related macular degeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 1, 263–268 (2006)
Mahlknecht, G., Maron, R., Mancini, M., Schechter, B., Sela, M., Yarden, Y.: Aptamer to ErbB-2/HER2 enhances degradation of the target and inhibits tumorigenic growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 8170–8175 (2013)
Hicke, B.J., Stephens, A.W., Gould, T., Chang, Y.-F., Lynott, C.K., Heil, J., Borkowski, S., Hilger, C.-S., Cook, G., Warren, S., Schmidt, P.G.: Tumor targeting by an aptamer. J. Nucl. Med. 47, 668–678 (2006)
Daniels, D.A., Chen, H., Hicke, B.J., Swiderek, K.M., Gold, L.: A tenascin-C aptamer identified by tumor cell SELEX: systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100, 15416–15421 (2003)
Hicke, B.J., Marion, C., Chang, Y.-F., Gould, T., Lynott, C.K., Parma, D., Schmidt, P.G., Warren, S.: Tenascin-C aptamers are generated using tumor cells and purified protein. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 48644–48654 (2001)
Talbot, L.J., Mi, Z., Bhattacharya, S.D., Kim, V., Guo, H., Kuo, P.C.: Pharmacokinetic characterization of an RNA aptamer against osteopontin and demonstration of in vivo efficacy in reversing growth of human breast cancer cells. Surgery 150, 224–230 (2011)
Mongelard, F., Bouvet, P.: AS-1411, a guanosine-rich oligonucleotide aptamer targeting nucleolin for the potential treatment of cancer, including acute myeloid leukemia. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 12, 107–114 (2010)
Bates, P.J., Laber, D.A., Miller, D.M., Thomas, S.D., Trent, J.O.: Discovery and development of the G-rich oligonucleotide AS1411 as a novel treatment for cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 86, 151–164 (2009)
Kang, S.-A., Hasan, N., Mann, A.P., Zheng, W., Zhao, L., Morris, L., Zhu, W., Zhao, Y.D., Suh, K.S., Dooley, W.C., Volk, D., Gorenstein, D.G., Cristofanilli, M., Rui, H., Tanaka, T.: Blocking the adhesion cascade at the premetastatic niche for prevention of breast cancer metastasis. Mol. Ther. 23, 1044–1054 (2015)
Mann, A.P., Somasunderam, A., Nieves-Alicea, R., Li, X., Hu, A., Sood, A.K., Ferrari, M., Gorenstein, D.G., Tanaka, T.: Identification of thioaptamer ligand against E-selectin: potential application for inflamed vasculature targeting. PLoS ONE 5, e13050 (2010)
Roccaro, A.M., Sacco, A., Purschke, W.G., Moschetta, M., Buchner, K., Maasch, C., Zboralski, D., Zöllner, S., Vonhoff, S., Mishima, Y., Maiso, P., Reagan, M.R., Lonardi, S., Ungari, M., Facchetti, F., Eulberg, D., Kruschinski, A., Vater, A., Rossi, G., Klussmann, S., Ghobrial, I.M.: SDF-1 inhibition targets the bone marrow niche for cancer therapy. Cell Rep. 9, 118–128 (2014)
Liu, S.-C., Alomran, R., Chernikova, S.B., Lartey, F., Stafford, J., Jang, T., Merchant, M., Zboralski, D., Zöllner, S., Kruschinski, A., Klussmann, S., Recht, L., Brown, J.M.: Blockade of SDF-1 after irradiation inhibits tumor recurrences of autochthonous brain tumors in rats. Neuro Oncol. 16, 21–28 (2014)
McCauley, T.G., Kurz, J.C., Merlino, P.G., Lewis, S.D., Gilbert, M., Epstein, D.M., Marsh, H.N.: Pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic assessment of anti-TGFbeta2 aptamers in rabbit plasma and aqueous humor. Pharm. Res. 23, 303–311 (2006)
Wlotzka, B., Leva, S., Eschgfäller, B., Burmeister, J., Kleinjung, F., Kaduk, C., Muhn, P., Hess-Stumpp, H., Klussmann, S.: In vivo properties of an anti-GnRH Spiegelmer: an example of an oligonucleotide-based therapeutic substance class. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 8898–8902 (2002)
Leva, S., Lichte, A., Burmeister, J., Muhn, P., Jahnke, B., Fesser, D., Erfurth, J., Burgstaller, P., Klussmann, S.: GnRH binding RNA and DNA Spiegelmers: a novel approach toward GnRH antagonism. Chem. Biol. 9, 351–359 (2002)
Jellinek, D., Green, L.S., Bell, C., Janjić, N.: Inhibition of receptor binding by high-affinity RNA ligands to vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochemistry 33, 10450–10456 (1994)
Shangguan, D., Tang, Z., Mallikaratchy, P., Xiao, Z., Tan, W.: Optimization and modifications of aptamers selected from live cancer cell lines. ChemBioChem 8, 603–606 (2007)
Biesecker, G., Dihel, L., Enney, K., Bendele, R.A.: Derivation of RNA aptamer inhibitors of human complement C5. Immunopharmacology 42, 219–230 (1999)
Rusconi, C.P., Scardino, E., Layzer, J., Pitoc, G.A., Ortel, T.L., Monroe, D., Sullenger, B.A.: RNA aptamers as reversible antagonists of coagulation factor IXa. Nature 419, 90–94 (2002)
Diener, J.L., Daniel Lagasse, H.A., Duerschmied, D., Merhi, Y., Tanguay, J.-F., Hutabarat, R., Gilbert, J., Wagner, D.D., Schaub, R.: Inhibition of von Willebrand factor-mediated platelet activation and thrombosis by the anti-von Willebrand factor A1-domain aptamer ARC1779. J. Thromb. Haemost. 7, 1155–1162 (2009)
Buff, M.C.R., Schäfer, F., Wulffen, B., Müller, J., Pötzsch, B., Heckel, A., Mayer, G.: Dependence of aptamer activity on opposed terminal extensions: improvement of light-regulation efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 2111–2118 (2010)
Waters, E.K., Genga, R.M., Schwartz, M.C., Nelson, J.A., Schaub, R.G., Olson, K.A., Kurz, J.C., McGinness, K.E.: Aptamer ARC19499 mediates a procoagulant hemostatic effect by inhibiting tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood 117, 5514–5522 (2011)
Maasch, C., Buchner, K., Eulberg, D., Vonhoff, S., Klussmann, S.: Physicochemical stability of NOX-E36, a 40mer L-RNA (Spiegelmer) for therapeutic applications. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. Oxf. 52, 61–62 (2008)
Schwoebel, F., van Eijk, L.T., Zboralski, D., Sell, S., Buchner, K., Maasch, C., Purschke, W.G., Humphrey, M., Zöllner, S., Eulberg, D., Morich, F., Pickkers, P., Klussmann, S.: The effects of the anti-hepcidin Spiegelmer NOX-H94 on inflammation-induced anemia in cynomolgus monkeys. Blood 121, 2311–2315 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 2018 Inje University research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, T.T.T., Delgado, A. & Jeong, S. Organ-on-a-Chip: The Future of Therapeutic Aptamer Research?. BioChip J 15, 109–122 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00016-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00016-1