Abstract
Objectives
This study investigated the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a fixed-dose combination (FDC) tablet of olmesartan medoxomil 20 mg and amlodipine 5 mg (CS-8663) in healthy Chinese subjects.
Methods
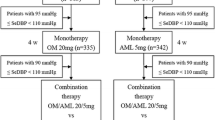
This single-centre, open-label study was conducted in five healthy males and five females aged 18–45 years. Subjects received a single oral dose of an olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg tablet on Day 1 under fasting conditions, and after a wash-out period they received the same dose once daily from Day 15 to Day 24. Serial blood samples were collected at predefined time-points to measure the plasma concentrations of olmesartan and amlodipine during the single-dose and the multiple-dose period. Meanwhile, blood pressure and heart rate were repeatedly taken to delineate the pharmacodynamic profiles. Safety was assessed throughout the study.
Results
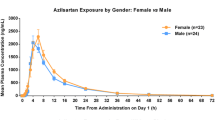
After oral administration, the peak concentrations of olmesartan and amlodipine were reached in a median time of 2 and 6 h, respectively. The elimination half-life of amlodipine is more than twice as long as that of olmesartan. Steady states of both compounds were attained after once-daily dosing for 8 days. Similar significant reductions of systolic and diastolic blood pressure were observed after a single dose of an olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg FDC tablet. In comparison, multiple doses of olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg tablets lowered the daily pre-dose BP level and led to smaller BP changes after the last dose. Heart rate increments were larger and more sustained after multiple doses than during the single-dose period. Females showed more systolic BP reductions than males despite inter-sex similarity in pharmacokinetics. Treatment with olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg FDC tablets was safe and well tolerated.
Conclusion
After single and multiple doses of olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg FDC tablets the pharmacokinetic profiles of olmesartan or amlodipine were comparable to those reported for monotherapy with olmesartan medoxomil or amlodipine, except that the elimination half-life of olmesartan was longer because of the longer time course over which pharmacokinetic blood sampling was carried out in this study. The response profiles of BP indicate a concentration-dependent antihypertensive effect of the olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine 20 mg/5 mg FDC tablet after a single dose and stabilization of such effects after multiple doses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
He J, Whelton PK. Elevated systolic blood pressure and risk of cardiovascular and renal disease: overview of evidence from observational epidemiologic studies and randomized controlled trials. Am Heart J. 1999;138(3 pt 2):S211–9.
Klag MJ, Whelton PK, Randall BL, Neaton JD, Brancati FL, Ford CE, Shulman NB, Stamler J. Blood pressure and end-stage renal disease in men. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:13–8.
Whelton PK, He J. Blood pressure reduction. In: Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Manson JE, Ridker PM, editors. Clinical trials in cardiovascular disease. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1999. p. 341–59.
He J, Klag MJ, Wu Z, Whelton PK. Stroke in the People’s Republic of China. II. Meta-analysis of hypertension and risk of stroke. Stroke. 1995;26:2228–32.
Eastern Stroke and Coronary Heart Disease Collaborative Research Group. Blood pressure, cholesterol, and stroke in eastern Asia. Lancet. 1998;352:1801–7.
He J, Whelton PK, Wu X, Burt VL, Tao S, Roccella EJ, Klag MJ. Comparison of secular trends in prevalence of hypertension in the People’s Republic of China and the United States of America. Am J Hypertens. 1996;9:74A. Abstract.
Gu D, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, Duan X, Muntner P, Huang G, Reynolds RF, Su S, Whelton PK, He J. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in China. Hypertension. 2002;40:920–7.
Writing Group of 2010 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. 2010 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension. Chin J Hypertens. 2011;19(8):701–41.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, et al. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. The JNC7 Report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–72.
Punzi H, Shojaee A, Waverczak WF, Maa JF. Efficacy of amlodipine and olmesartan medoxomil in hypertensive patients with diabetes and obesity. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2011;13:422–30.
Kreutz R. Olmesartan/amlodipine: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011;7:183–92.
Rohatagi S, Lee J, Shenouda M, Haworth S, Bathala MS, Allison M, Rubets I, Heyrman R, Noveck R, Salazar DE. Pharmacokinetics of amlodipine and olmesartan after administration of amlodipine besylate and olmesartan medoxomil in separate dosage forms and as a fixed-dose combination. J Clin Pharmacol. 2008;48:1309–22.
Jiang J, Liu D, Hu P. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of olmesartan medoxomil in healthy Chinese subjects after single and multiple administrations. Pharmazie. 2009;64:323–6.
Park JY, Kim KA, Park PW, Lee OJ, Kim JS, Lee GH, Ha MC, Park JH, O MJ, Ryu JH. Comparative pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics of amlodipine besylate and amlodipine nicotinate in healthy subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;44(12):641–7.
Therapeutic Goods Administration, Department of Health and Ageing, Australian Government. Australian Public Assessment Report for Amlodipine/Valsartan. Page 11, Table 1. Unknown investigators. Study 2311, investigated the pharmacokinetic bioavailability of valsartan and amlodipine followingfixed 5/320 mg combination tablet prototypes (test) and free combination (reference) amlodipine 5 mg and valsartan 320 mg. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Australia Pty. October 2012.
Data on file: Investigator’s Brochure CS-8663. CS8663-A-U112 study. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd; 2008.
Chang Y, Wen A, Li C, Wang Z, Chen S, Zhao P, Wu Y, Jin X, Wang J, Zhu Y, Wang X. Pharmacokinetics of amlodipine besylate/atorvastatin calcium combination tablet in healthy volunteers. Chin Hosp Pharm J. 2008;28(19):1672–6.
Faulkner JK, McGibney D, Chasseaud LF, Perry JL, Taylor IW. The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine in healthy volunteers after single intravenous and oral doses and after 14 repeated oral doses given once daily. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;22:21–5.
Lopez LM, Thorman AD, Mehta JL. Effects of amlodipine on blood pressure, heart rate, catecholamines, lipids and responses to adrenergic stimulus. Am J Cardiol. 1990;66(17):1269–71.
Kloner RA, Sowers JR, DiBona GF, Gaffney M, Wein M. Sex- and age-related antihypertensive effects of amlodipine. The Amlodipine Cardiovascular Community Trial Study Group. Am J Cardiol. 1996;77:713–22.
Ueno K, Sato H. Sex-related differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of anti-hypertensive drugs. Hypertens Res. 2012;36:245–50.
Data on file: Liu DY, Jiang J, Hu P. SS-866 CMB/02 study, investigated the pharmacokinetics of olmesartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide FDC tablet and compared with the mono-drug formulation of olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide, respectively. Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd; 2008.
Acknowledgments
X. Chen, Q. Zhao, J. Jiang and P. Hu contributed to the conception and design of the research; X. Chen, P. Hu, T. Liu and W. Zhong were involved in the acquisition of data or analysis and interpretation of data; X. Chen and Q. Zhao were involved in the initial drafting of the manuscript and all authors critically reviewed and contributed to subsequent drafts. X. Chen, J. Jiang and P. Hu assisted in protocol development. X. Chen and H.Z. Liu were responsible for the evaluation and care of study subjects. The authors deeply appreciated the contributions of the study team during the conduct of this study, which included but were not limited to study nurses Wenying Liang, Shuhui Guo, Zhiyuan Zhang, Xiaowei Li, Chuanqing Yang, Li Sun, Qiqiong Ding, JunWang, Jing Yang; study coordinators Xin Jin, Shuxia Guan; study quality assurance and quality control Haiyan Cheng, Mingli Hu, Ran Li; and study data manager Jinghai Zhou. This study was sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo Pharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd with an assigned protocol code of SS8663-03. The work was supported by a grant from the National Program on Key Research Project of New Drug Innovation (No. 2008ZX09312-016).The authors have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Hu, P., Jiang, J. et al. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiles of a Fixed-Dose Combination of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Amlodipine in Healthy Chinese Males and Females. Clin Drug Investig 32, 783–790 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-012-0026-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-012-0026-0