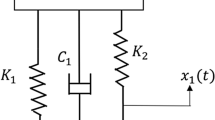
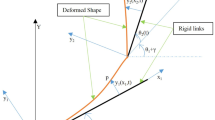
Abstract
Position control and mechanical vibration suppression are still open problems in compliant link mechanisms. Operation and accuracy improvements of manipulators can be made by finding solutions for these problems. This paper presents a comprehensive performance comparison between controllers (two of them robust controllers) to control position and reduce mechanical vibration over a compliant link-manipulator in a three-dimensional environment: (i) linear quadratic regulator, (ii) model predictive controller, (iii) \(H_{\infty }\) loop shaping, and (iv) \(\mu \)-synthesis. The comparisons of controllers are made based on position tracking, vibration damping and control effort in the simulation environment by taking the gravity effect into account. Finally, the paper makes a conclusion by providing some information about main purpose, advantages and disadvantages of each controller in compliant link-manipulator applications.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu C, Pané S, Nelson BJ (2018) Soft micro-and nanorobotics. Annu Rev Control Robot Auton Syst 1:53–75
Watts T, Secoli R, Baena FR (2019) Modelling the deformation of biologically inspired flexible structures for needle steering. In: Rizk R, Awad M (eds) Mechanism, machine, robotics and mechatronics sciences. Springer, Berlin, pp 67–80
Ma G, Xu M, Liu T, Luo Y (2019) The multi-body analysis and vibration control of the second-order mode of a hoop flexible structure. Acta Mech 230(4):1377–1386
Hoshyari S, Xu H, Knoop E, Coros S, Bächer M (2019) Vibration-minimizing motion retargeting for robotic characters. ACM Trans Gr (TOG) 38(4):102
Barjuei ES (2017) Hybrid position/force control of a spatial compliant mechanism. Int J Autom Mech Eng 14:4531–4541
Bernzen W (1999) Active vibration control of flexible robots using virtual spring-damper systems. J Intell Robot Syst 24(1):69–88
Marakakis K, Tairidis GK, Koutsianitis P, Stavroulakis GE (2019) Shunt piezoelectric systems for noise and vibration control: a review. Front Built Environ 5:64
Mishra N, Singh S (2019) Hybrid vibration control of a two-link flexible manipulator. SN Appl Sci 1(7):715
Kumar P, Pratiher B (2019) Nonlinear modeling and vibration analysis of a two-link flexible manipulator coupled with harmonically driven flexible joints. Mech Mach Theory 131:278–299
Williams D, Khodoparast HH, Yang C (2018) Active vibration control of a flexible link robot with the use of piezoelectric actuators. In: MATEC web of conferences, EDP sciences, vol 148, p 11005
Barjuei ES, Boscariol P, Gasparetto A, Giovagnoni M, Vidoni R (2014) Control design for 3d flexible link mechanisms using linearized models. In: Ceccarelli M, Glazunov VA (eds) Advances on theory and practice of robots and manipulators. Springer, Cham, pp 181–188
Benosman M, Le Vey G (2004) Control of flexible manipulators: a survey. Robotica 22(5):533–545
He W, Liu J (2019) Active vibration control and stability analysis of flexible beam systems. Springer, Berlin
Kiang CT, Spowage A, Yoong CK (2015) Review of control and sensor system of flexible manipulator. J Intell Robot Syst 77(1):187–213
Khot S, Yelve NP, Tomar R, Desai S, Vittal S (2012) Active vibration control of cantilever beam by using PID based output feedback controller. J Vib Control 18(3):366–372
Zhang J, He L, Wang E, Gao R (2008) A LQR controller design for active vibration control of flexible structures. In: 2008 IEEE Pacific-Asia workshop on computational intelligence and industrial application, IEEE, vol 1, pp 127–132
Barjuei ES, Boscariol P, Gasparetto A, Giovagnoni M, Vidoni R (2014) Control design for 3D flexible link mechanisms using linearized models. In: Ceccarelli M, Glazunov VA (eds) Advances on theory and practice of robots and manipulators. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–188
Ripamonti F, Orsini L, Resta F (2017) A nonlinear sliding surface in sliding mode control to reduce vibrations of a three-link flexible manipulator. J Vib Acoust 139(5):051005
Zhang S, He W, Huang D (2016) Active vibration control for a flexible string system with input backlash. IET Control Theory Appl 10(7):800–805
Cui L, Zhang J, Gao L, Wang F (2006) A robust controller of a flexible manipulator using genetic algorithm. In: 2006 9th international conference on control, automation, robotics and vision, pp 1–4
Hassan M, Dubay R, Li C, Wang R (2007) Active vibration control of a flexible one-link manipulator using a multivariable predictive controller. Mechatronics 17(6):311–323
Vidoni R, Gasparetto A, Giovagnoni M (2013) Design and implementation of an ERLS-based 3-D dynamic formulation for flexible-link robots. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 29(2):273–282
Levine WS (2018) The control handbook (three volume set). CRC press
Shojaei Barjuei E, Gasparetto A (2015) Predictive control of spatial flexible mechanisms. Int J Mech Control 16(01):85–96
Barjuei ES, Boscariol P, Vidoni R, Gasparetto A (2016) Robust control of three-dimensional compliant mechanisms. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 138(10):101009
Liu KZ, Yao Y (2016) Robust control: theory and applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Abdolshah S, Barjuei ES (2015) Linear quadratic optimal controller for cable-driven parallel robots. Front Mech Eng 10(4):344–351
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for all of their careful, constructive and insightful comments in relation to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shojaei Barjuei, E., Ortiz, J. A comprehensive performance comparison of linear quadratic regulator (LQR) controller, model predictive controller (MPC), \(H_{\infty }\) loop shaping and \(\mu \)-synthesis on spatial compliant link-manipulators. Int. J. Dynam. Control 9, 121–140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00640-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00640-z