Abstract
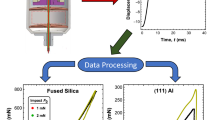
A new method for evaluating modulus and hardness from nanoindentation load/ displacement curves is presented. As a spherical indenter penetrates an elastoplastic half-space, the elastic displacement above the contact line is presumed to diminish in proportion to the total elastic displacement under the indenter. Applying boundary conditions on the elastic and plastic displacements for elastic and rigid plastic contacts leads to an expression that can be best fit to the entire unloading curve to determine E*, the reduced modulus. Justification of the formulation is presented, followed by the results of a preliminary survey conducted on three predominantly isotropic materials: fused quartz, polycrystalline Al, and single crystal W. Diamond tips with radii ranging from 130 nm to 5 μm were used in combination with three different nanoindentation devices. Results indicate that the method gives property values consistent with accepted values for modulus and hardness. The importance of surface roughness and indentation depth are also considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. V. Hainsworth, H. W. Chandler, and T. F. Page, J. Mater. Res. 11, 1987 (1996).
J. L. Loubet, J. M. Georges, and J. Meille, in Nanoindentation Techniques in Materials Science and Engineering, edited by P. T. Blau and B. R. Lawn (ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 1986), pp. 7–89.
H. Hertz, J. Mathematik 92, 156 (1882).
M. F. Doerner and W. D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1580 (1992).
J. S. Field and M. V. Swain, J. Mater. Res. 8, 297 (1993).
R. B. King, Int. J. Solids Structures 23, 1657 (1987).
H. Gao, C-H. Chin, and J. Lee, Int. J. Solids Structures 29, 2471 (1992).
N. A. Stelmashenko, M. G. Walls, L. M. Brown, and Yu. V. Milman, Acta Metall. Mater. 41 (10), 2855 (1993).
T. W. Wu, J. Mater. Res. 6, 407 (1991).
E. T. Lilleodden, W. Bonin, J. Nelson, J. T. Wyrobek, and W. W. Gerberich, J. Mater. Res. 10, 2162 (1995).
N. I. Sneddon, Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
W. W. Gerberich, J. C. Nelson, E. T. Lilleodden, P. Anderson, and J. T. Wyrobek, Acta Mater. 44 (9), 3585 (1996).
T. C. Chou, T. G. Nieh, S. D. McAdams, and G. M. Pharr, Scripta Metall. et Mater. 25, 2203 (1991).
N. R. Moody, Sandia Livermore National Laboratories, private communication.
W. C. Oliver and C. J. McHargue, Thin Solid Films 161, 117 (1988).
J. A. Greenwood and J. H. Tripp, Trans. ASME, E., J. Appl. Mech. 34, 153 (1967).
K. L. Johnson, Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985), pp. 405–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerberich, W.W., Yu, W., Kramer, D. et al. Elastic loading and elastoplastic unloading from nanometer level indentations for modulus determinations. Journal of Materials Research 13, 421–439 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1998.0055
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1998.0055