Abstract
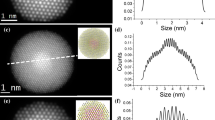
Spherical aberration corrected Atomic Number Contrast Scanning Electron Microscopy (Z-STEM) has recently demonstrated an amazing ability to not only obtain sub-angstrom levels of detail but also yield chemical information at that level as well. With an optimal probe size of 0.8 Å, extremely detailed images of CdSe nanocrystals were obtained showing the lattice structure and surface morphology. As an example of the usefulness of this technique, a sample of CdSe nanocrystals prepared using trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) as the surfactant was compared to a sample of CdSe prepared using a mixture of TOPO and hexadecylamine (HDA) as the surfactant. The TOPO/HDA nanocrystals exhibit a narrower size distribution and several orders of magnitude greater fluorescence compared to that of the TOPO only nanocrystals. Interestingly, the Z-STEM images show a striking difference in nanocrystal morphology as the result of the addition of HDA to the reaction mixture. This result suggests surface morphology can be tuned through judicious choice of surfactant. A second example of Z-STEM imaging involves the characterization of CdSe/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals. The mass contrast afforded by Z-STEM can easily distinguish between core and shell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swofford L. A.; Rosenthal S.J. Molecular and Nanomaterial-Based Photovoltaics, in Molecular Nanoelectronics, E M A T Reed, Editor. 2003, American Scientific Publishers.
N.C. Greenham; X Peng; Alivisatos A. P. Phys. Rev. B, 1996. 54,: p. 17628.
Erwin M. M.; Kadavanich A. V.; McBride J.; Kippeny T.; Pennycook S.; Rosenthal S. J.; Eur. J. Phys. D, 2001. 16: p. 275–277.
Henglein A., Pure Appl. Chem., 1984. 56: p. 1215.
Henglein A., Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 1997. 101: p. 1562.
Nanda J.; Sapra S.; Sarma D.; Chandrasekharan N.; Hodes G.; Chem. of Mater., 2000. 12: p. 1018.
Kho R.; L Nguyen; Torres C. L.-Martinez; Mehra R. K.; Biophys. Res. Commun., 2000. 272: p. 29.
Dubertret B.; Skourides P.; Norris D. J.; Noireaux V.; Brivanlou A. H.; Libchaber A. Science, 2002. 298: p. 1759.
Gerion D.; Parak W. J.; Williams S. C.; Zanchet D.; Micheel C. M.; Alivisatos A.P. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002. 124: p. 7070.
Tomlinson I. D.; Mc J.Bride; Blakely R. D.; Rosenthal S. J.; Biotechnology, in press.
Rosenthal S. J.; Tomlinson I. D.; Adkins E. M.; Schroeter S.; Adams S.; Swafford L. A.; Mc J.Bride; Wang Y.; De Felice L. J.; Blakely R. D.; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002(124): p. 4586.
Wu X.; Liu H.; Lui J.; Haley K. N.; Treadway J.A.; Larson P. J.; Ge N.; Peale F.; Bruchez M. P.; Nature Biotechnology, 2003. 21: p. 41.
Klein D. L.; Roth R.; Lim A. K.; Alivisatos A. P.; McEuen P. L. Nature, 1997. 389: p. 669.
Gao M. Y.; Lesser C.; Kirstein S.; Mohwald H.; Rogach A. L.; Weller H. J. Appl. Phys., 2000. 87: p. 2297.
Konenkamp R.; Hoyer P.; Wahi A. J. Appl. Phys., 1996. 79: p. 7029.
Vlasov Y. A.; Yao N.; Norris D. J. Adv. Mater., 1999. 11: p. 165.
Wange X., Qu L.; Zhang J.; Peng X.; Xiao M. Nano Letters, 2003. 3 (8): p. 1103.
Myung N.; Bae Y.; Bard A.J. Nano Lett., 2003. 3 (6): p. 747.
Manna L.; Scher E. C.; Li L.; Alivisatos A. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002. 124 (24): p. 7136.
Donega C. M.; Hickley S.G.; Wuister S. F.; Vanmaekelbergh D.; Meijerink A. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003. 107: p. 489.
Landes C.; Burda C.; Braun M.; El-Sayed M. A. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001. 105: p. 2981.
A.K.A.M. Kadavanich, Tolbert S. H.; Peng X.; Schlamp M. C.; Lee J. C.; Alivisatos A. P.; Adv. Microcryst. Nanocryst. Semicond. 1996, Symp. 1996.
Shiang J.; Kadavanich A.V.; Grubbs R. K.; Alivisatos A. P.; J. Phys. Chem., 1995. 99: p. 17417.
Peng X. G.; Wickham J.; Alivisatos A. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998. 120: p. 5343.
Talapin D. V.; Rogach A. L.; Kronowski A.; Haase M.; Weller H. Nano Lett., 2001. 1 (4): p. 207.
Peng Z. A.; Peng X. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001. 123: p. 1389.
Reis P.; Bleuse J.; Pron A.; Nano Lett., 2002. 2: p. 781.
Reis P.; Caryon S.; Bleuse J., Pron A.; Synth. Met., 2003. 139: p. 649.
Hines M.; P. G., J. Phys. Chem., 1996. 100.
Dabbousi B.; Rodriguez J.-Viejo; Mikulec F.; Heine J.; Matoussi H.; Ober R.; Jensen K.; Bawendi M.; J. Phys. Chem. B., 1997. 101: p. 9463.
Mattoussi H.; Mauro J. M.; Goldman E. R.; Anderson G. P.; Sundar V.C.; Mikulec F. V.; Bawendi M. G. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000. 122 (49): p. 12142.
Taylor J.; Kippeny T.; Rosenthal S. J. J. Clust. Sci., 2001. 12 (4): p. 571.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Joe Treadway and Quantum Dot Corp. for providing the core/shell nanocrystals and their insight. We would also like to thank Andrew Lupini and the Pennycook research group for assistance with operation of the STEMs. Funding for this research was provided by a Vanderbilt Institute of Nano-Science and Engineering fellowship and by the Department of Energy, grant number (DE-FG0202-ER45957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McBride, J., Kippeny, T.C., Pennycook, S.J. et al. Spherical Aberration Corrected Z-STEM Characterization of CdSe and CdSe/ZnS Nanocrystals. MRS Online Proceedings Library 818, 342–346 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-818-M8.15.1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-818-M8.15.1