Abstract
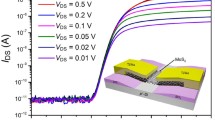
Heterojunction field effect transistors (HFET) for high-frequency and high-power electronics have been an area of active research in recent years as a key enabling technology for applications ranging from wireless communications to power distribution. III-Nitride semiconductors are a leading candidate for fulfilling the material requirements of these devices based on the combination of large bandgap energy, high thermal conductivity, high electron mobility and saturated electron velocity. While III-Nitride HFETs have demonstrated remarkable advances, serious materials related limitations still exist, primarily related to charge states and trapping effects at the semiconductor surface. Several groups have investigated solutions such as the deposition of dielectric passivation layers and asymmetric field-plate gate geometries for controlling the influence of trap states near the metal/semiconductor FET interface. We have demonstrated a metal-oxide semiconductor FET (MOSFET) with a substantially unpinned interface which is capable of establishing substantial charge accumulation under the gate. These III-Nitride MOSFETs may be designed to operate in either depletion mode or enhancement mode. GaN/InGaN heterojunction MOSFETs exhibit enhancement mode peak transconductance at gate voltages Vg>+5V, corresponding to energy greater than the bandgap of the underlying semiconductor which provides strong evidence of an unpinned MOS interface. Additionally III-Nitride MOSFETs eliminate the need for field plate gate structures as the electric field geometry in the gate-drain region changes limiting the tunneling of charge to unfilled surface states. In depletion mode, low-rf dispersion InGaN/GaN MOSFETs exhibit excellent microwave with ft = 8GHz for optically defined gates dimensions.
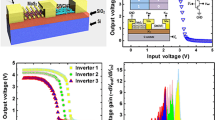
We review the history of compound semiconductor MOSFET development and overlaying these developments with recent advances in the III-Nitride materials and device research. Differences in chemistry of III-Nitrides relative to all other compound semiconductors and the epitaxial deposition of gate-oxides such as Gadolinium Gallium Oxide (GGO), opens the possibility for dramatically improved devices at microwave and mm-wave frequencies as well as power MOSFET rectifiers. Initial III-Nitride MOSFETs results are presented as well as a quaternary thermodynamic framework for the stability of gate-oxide on nitride semiconductors. We also identify key materials related research challenges expected to impact the ongoing development of III-Nitride MOSFETs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
“The Toughest Transistor Yet” L.F. Eastman and U.K. Mishra, IEEE Spectrum, May 2002, p.28–33.
“GaN as Seen by the Industry” J–Y Duboz, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 176, 5 (1999) p 5–14.
“Fabrication and Performance of GaN Electronic Devices” S.J. Pearton, F. Ren, A.P. Zhang, K.P. Lee Materials Science and Engineering, R30 (2000) p. 55–212
“AlGaN/GaN HEMTs—An Overview of Device Operation and Applications” U.K. Mishra, P. Parikh, and Y-F Wu Proc. of the IEEE 90, 6, June 2002 p1022–1031.
“An Assessment of Wide Bandgap Semiconductors for Power Devices” J.L. Hudgins, G.S. Simin, E. Santi, and M.A. Khan, IEEE Trans. on Power Electronics 18, 3, May 2003, p. 907–914.
“Cramming More Components into Integrated Circuits” G.E. Moore, Electronics, 38, 8, April 1965.
A.S. Grove Physics and Technology of Semiconductor Devices (Wiley and Sons: New York) 1967.
S.M. Sze Physics of Semiconductor Devices (Wiley and Sons: New York) 1981.
“Gallium Arsenide MOS Transistors” H. Becke, R. Hall, and J. White Solid-State Electronics (Pergamon Press 1965) Vol. 8, pp. 813–823.
“Initial Oxidation and Oxide/Semiconductor Interface Formation on GaAs” C.W. Wilmsen, B.W. Kee amd K.M. Geib J. Vac Sci. Technol., 15(5) 1979 p 1434–1438.
“Demonstration of an n-Channel Inversion Mode GaAs MISFET” GG. Fountain, R.A. Rudder, S.V. Hattangady, R.J. Markunas, J.A. Hutchby Proc. of IEDM 89 89–889.
“Analysis of Native Oxide Films and Oxide-Substrate Reactions on III-V Semiconductors using Thermochemical Phase Diagrams” G.P. Schwartz Thin Solid Films, 103 (1983) p.3–16.
“Thermal Oxidation and Native Oxide-Substrate Reaction on InAs and InxGa1-xAs” G.P. Schwartz, J.E. Griffiths and G. J. Gualtieri Thin Solid Films, 94 (1982) 213–222.
C.D. Thurmond, G. P. Schwartz, G. W. Kammlott and B. Schwartz, J. Electrochem. Soc., 127 (1980) 1366.
“In-situ fabricated Ga2O3–GaAs structures with low interface recombination velocity” M. Passlack, M. Hong, E.F. Schubert, J.R. Kwo, J.P. Mannaerts, S.N.G. Chu, N. Moriya, and F. A. Thiel, Appl. Phys. Lett. 66(5), January 1995 p. 625–627.
“Low Dit, Thermodynamically Stable Ga2O3–GaAs Interfaces: Fabrication, Characterization, and Modeling” M. Passlack, M. Hong, J.P. Mannaerts, R. L. Opila, S.N.G. Chu, N. Moriya, F. Ren, and J.R. Kwo, IEEE Trans. on Electron Dev., Vol. 44, 2, Feb 1997 p.214–224.
“Gallium Oxide on Gallium Arsenide: Atomic Structure, Materials and Devices” Passlack, M, Yu, Z, Droopad, R, Abrokwah, JK, Braddock, D, Yi, SI Hale, M, Sexton, J, Kummel, AC, III-V Semiconductor Heterostructures: Physics and Devices 2003, ed Cai, WZ (Research Signpost: Trivandrum) 2003.
“Demonstration of Enhancement Mode p- and n- channel GaAs MOSFETs with Ga2O3(Gd2O3) as gate Oxide” Ren, F, Hong, MW, Hobson, WS, Lothian, JR, Mannerts, M Solid-State Electron., 41, 11 (1997) 1751–1753.
“InGaN/GaN/AlGaN-based LEDs and laser diodes” S. Nakamura, M. Senoh, S. Nagahama, N. Iwasa, T. Matushita, T. Mukai, GaN and Rel. Alloys. Symp., 1999, G1.1/14
S. Nakamura, S. Pearton, G. Fasol, Blue Laser Diode 2ed. (Springer: New York) 2000.
“Wide bandgap semiconductor microwave technologies: from promise to practice” Zolper, J.C. IEDM 1999. Technical Digest, 1999, p 389–92.
“Gallium Nitride Based High Power Heterojunction Field Effect Transistors: Process Development and Present Status at UCSB” S. Keller, Y-F Wu, G. Parish, N. Ziang, J.J. Xu, B.P. Keller, S.P. DenBaars, and U.K. Mishra, IEEE Trans. on Eelctron Dev. 48, 3, Mar 2001 p552–559.
“Results, Potential and Challenges of High Power GaN-Based Transistors” L. F. Eastman, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 176, 175 (1999) p175–178.
“Trapping Effects and Microwave Power Performance on AlGaN/GaN HEMTs” S. Binari, K. Ikossi, J. Roussos, W. Kruppa, D. Park, H.B. Dietrich, D.D. Koleske, A.E. Wickenden, R. Henry, IEEE Trans. on Electron Devices, 48 3, Mar 2001 p.465–471.
“The Impact of Surface States on the DC and RF Characteristics of AlGaN/GaN HFETs” R. Vetury, N.Q. Zhang, S. Keller and U.K. Mishra, IEEE Trans. on Electron Dev., Vol. 48 3 Mar 2001, p560–566.
“Power and Linearity Characteristics of Field-Plated Recessed-Gate AlGaN–GaN HEMTs” A. Chini, D. Buttari, R. Coffie, L. Shen, S. Heikman, A. Chakraborty, S. Keller and U.K. Mishra, IEEE Electron Dev. Lett., Vol 25 5, May 2004 p.229–231.
“Application of GaN-Based Heterojunction FETs for Advanced Wireless Communication,” Y. Ohno and M. Kuzuhara IEEE Trans on Electron Dev. 48, 3, Mar 2001 p517–523.
“A Critical Comparison between MBE and MOVPE Growth of III-V Nitride Heterostructures for Opto-Electronic Device Applications,” M.A.L. Johnson, Zhonghai Yu, J.D. Brown, F.A. Koeck, N.A. El-Masry, J.W. Cook, Jr. and J.F. Schetzina, MRS Internet Journal Nitride Semicond. Res. 4S1, G5.10 (1999).
“GaAs surface passivation using in-situ oxide deposition” M. Passlack, M. Hong, R.L. Opila, J.P. Mannaerts, J.R. Kwo Applied Surface Sci. 104/105 (1996) 441–447
“Thermodynamic Assessment of the Gallium-Oxygen System” M. Zinkevich and F. Aldinger J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 87[4] 683–91 (2004) p 683–691.
“Transmission Electron Microscope Study of Epitaxial Gate Oxides on III-N Semiconductor Structures” Y.N. Saripalli, X-Q Liu, D.W. Barlage, M.A.L. Johnson, D. Braddock, N.G. Stoddard, A. Chugh (Presented at the Proceedings of the Materials Research Society Symposium–Dec. 2004)
“Demonstration of Enhancement Mode GaN MOSFETs” D. Barlage K. Dandu, Y. Saripalli, X-Q. Liu, M.A.L. Johnson, W. Sutton and W.D. Braddock, III (Presented at Electronic Materials Conference–June} 20
“Growth and physical properties of Ga2O3 thin films on GaAs(001) substrate by molecular-beam epitaxy Z. Yu, C.D. Overgaard, R. Droopad, M. Passlack and J.K. Abrokwah Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 18 May 2003 p2978–2980.
“A Comparison of Gallium Gadolinium Oxide and Gadolinium Oxide for use as Dielectrics in GaN MOSFETs” B.P. Gila, K.N. Lee, W. Johnson, F. Ren, C.R. Abenathy, S.J. Pearton, M. Hong, J. Kwo, J.P. Mannaerts and K. A. Anselm Proc. of the IEEE. Les Eastman Conference (2000)
“Electron trapping in metal-insulator-semiconductor structures on n-GaN with SiO2 and Si3N4 dielectrics” C. Bae, C. Krug, and G. Lucovsky, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 22(6), Nov/Dec 2004, p2379–2383.
“Effects of Sc2O3 and MgO Passivation Layers on the Output Power of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs” J.K. Gillespie, R.C. Fitch, J. Sewell, R. Dettmer, G.D. Via, A. Crespo, T.J. Jenkins, B. Luo, R. Mehandru, J. Kim, F. Ren, B.P. Gila, A.H. Onstine, C.R. Abernathy, and S.J. Pearton, IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 23, 9 Sept. 2002 p505–507.
“AlGaN/GaN Metal Oxide Semiconductor Heterostructure Field Effect Transistor” M.A. Khan, X. Hu, G. Sumin, A. Lunev, J. Yang, R. Gaska, and M.S. Shur, IEEE Electron Dev. Lett., 21, No. 2, Feb 2000 p63–65.
“A Thermodynamic Approach to Selecting Alternative Gate Dielectrics,” D.G. Schlom and J.H. Haeni, MRS Bulletin 27 (March 2002) 198–204.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank their student and faculty collaborators in the NCSU Photonics and Atomic Resolution Electron Microscopy Labs, most importantly J. Matthews for his expert assistance. One author (DB) thanks collaborators at OSEMI and Univ. of Michigan. This project has been supported by ORAU Powe Faculty Enhancement Award (MJ), SRC Exploratory Development Grant (MJ and DB) and the Navy SBIR Program (Randy Lasiter, Program Manager).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, M.A.L., Barlage, D.W. & Braddock, D. Prospect for III-Nitride Heterojunction MOSFET Structures and Devices. MRS Online Proceedings Library 829, 338–349 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-829-B7.7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-829-B7.7