Abstract
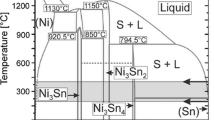
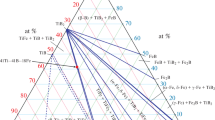
The SHS reaction in the Ni–Ti–B4C system starts with the formation of Ni–Ti and Ni–B intermetallic compounds from the solid interacted reaction among the reactants and, subsequently, the formation of Ni–Ti and Ni–B liquid at the eutectic point. Meanwhile, some C atoms from the reaction between Ni and B4C can dissolve into Ni–Ti liquid to form TiC. The heat generated from these reactions can promote the mutual diffusion of Ni–Ti–C and Ni–B liquid and simultaneously accelerate the formation of Ni–Ti–C–B liquid. Finally the precipitation of TiC and TiB2 occur when the C and B atoms in the liquid become supersaturated. The addition of Ni not only promotes the occurrence of the self-propagating high temperature synthesis (SHS) reaction by forming Ni–Ti liquid, but also accelerates the SHS reaction by forming Ni–B liquid and dissociative C. The early appearance of dissociative C from the reaction between Ni and B4C causes the formation of TiC prior to that of TiB2.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.C. Tjong Z.Y. Ma: Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in-situ metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 29, 49 2000
H. Zhao Y.B. Cheng: Formation of TiB2–TiC composites by reactive sintering. Ceram. Int. 25, 353 1999
M.W. Barsoum B. Houng: Transient plastic phase processing of titanium–boron–carbon composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 1445 1993
P. Mogilevsky, E.Y. Gutmanas, I. Gotman R. Telle: Reactive formation of coatings at boron carbide interface with Ti and Cr powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 15, 527 1995
J.X. Tang, H.Z. Miao Z.Q. Zeng: Analysis of reaction path between Ti and B4C. Acta Metall. Sinica 36, 833 2000
L. Contreras, X. Turrillas, G.B.M. Vaughan, A. Kvick M.A. Rodríguez: Time-resolved XRD study of TiC–TiB2 composites obtained by SHS. Acta Mater. 52, 4783 2004
G.Q. Xiao, Q.C. Fan, M.Z. Gu, Z.H. Wang Z.H. Jin: Dissolution-precipation mechanism of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of TiC–Ni cermet. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 382, 132 2004
J.C. LaSalvia, D.K. Kim, R.A. Lipsett M.A. Meyers: Combustion synthesis in the Ti–C–Ni–Mo system. Part I. Micromechanisms. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26, 3001 1995
J.C. LaSalvia M.A. Meyers: Combustion synthesis in the Ti–C–Ni–Mo system: Part II. Analysis. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 26, 3011 1995
G.Q. Xiao, Q.C. Fan, M.Z. Gu Z.H. Jin: Microstructural evolution during the combustion synthesis of TiC–Al cermet with larger metallic particles. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 425, 318 2006
Y.X. Li, J.D. Hu, H.Y. Wang Z.X. Guo: Dissolution-precipitation mechanism of laser igniting self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of Al/TiC composite. Adv. Eng. Mater. 9, 689 2007
Q.C. Fan, H.F. Chai Z.H. Jin: Role of iron addition in combustion synthesis of TiC–Fe cermet. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 4319 1997
Q.C. Fan, H.F. Chai Z.H. Jin: Mechanism of combustion synthesis of TiC–Fe cermet. J. Mater. Sci. 34, 115 1999
P. Shen, B.L. Zou, S.B. Jin Q.C. Jiang: Reaction mechanism in self-propagating high temperature synthesis of TiC–TiB2/Al composites from an Al–Ti–B4C system. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 454–455, 300 2007
Y.F. Yang, H.Y. Wang, Y.H. Liang, R.Y. Zhao Q.C. Jiang: Effect of Ni content on the reaction behaviors of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis in the Ni–Ti–B4C system. INT. J. Refract. Met. H 26, 77 2008
Powder Diffraction File. Alphabetical Indexes International Center for Diffraction Data Newton Square, PA 2000
T.B. Massalski, H. Okamoto, P.R. Subramanian L. Kacprzak: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed. ASM International Metals Park, OH 1990
Y.F. Yang, H.Y. Wang, Y.H. Liang, R.Y. Zhao Q.C. Jiang: Effect of nickel addition on the thermal reaction of titanium and boron caibide. J. Mater. Res. 22, 169 2007
D. Brodkin, S.R. Kalidindi, M.W. Barsoum A. Zavaliangos: Microstructural evolution during transient plastic phase processing of titanium carbide–titanium boride composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1945 1996
D.L. Hildenbrand W.F. Hall: The decomposition pressure of boron carbide and the heat of sublimation of boron. J. Phys. Chem. 68, 989 1964
D. Emin: Structure and single-phase regime of boron carbides. Phys. Rev. B 38, 6041 1988
G.H. Kwei B. Morosin: Structures of the boron-rich boron carbides from neutron powder diffraction: Implications for the nature of the inter-icosahedral chains. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 8031 1996
R. Lazzari, N. Vast, J.M. Besson, S. Baroni A.D. Corso: Atomic structure and vibrational properties of icosahedral B4C boron carbide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3230 1999
B. Morosin, G.H. Kwei, A.C. Lawson, T.L. Aselage D. Emin: Neutron powder diffraction refinement of boron carbides nature of intericosahedral chains. J. Alloys Compd. 22, 6121 1995
I. Jimenez, D.G.J. Sutherland, T. Van Buuren, J.A. Carlisle, L.J. Terminello F.J. Himpsel: Photoemission and x-ray-absorption study of boron carbide and its surface thermal stability. Phys. Rev. B 57, 13167 1998
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NNSFC) (No. 50531030), The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (MSTC) (Nos. 2006AA03Z566 and 2005CCA00300), and New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET) (No. 06-0308) as well as The Project 985-Automotive Engineering of Jilin University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wang, H., Zhao, R. et al. Reaction mechanism of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis reaction in the Ni–Ti–B4C system. Journal of Materials Research 23, 2519–2527 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2008.0317
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2008.0317