Abstract
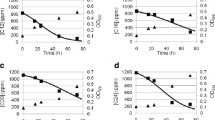
The degradation pathways for cyclic alkanes (c-alkanes) in Rhodococcus sp. NDKK48 were investigated. Strain NDKK48 used dodecylcyclohexane as a sole carbon and energy source, and five metabolites in the dodecylcyclohexane degradation pathway were detected by gas-chromatography/mass spectra. The metabolites were identified as cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, cyclohexylacetic acid, 1-cyclohexene-1-acetic acid, 4-dodecylcyclohexanol, and 4-dodecylcyclohexanone. The strain degrades dodecylcyclohexane via a ring oxidation pathway and an alkyl side chain oxidation pathway. Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid was further oxidized to muconic acid via 1-cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid and benzoic acid, and the muconic acid was finally used by strain NDKK48 for growth. Methylcyclohexane and cyclohexane were co-oxidized with hexadecane by strain NDKK48. Methylcyclohexane was degraded via a ring oxidation pathway, and the degradation pathway contained part of the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation for ring cleavage. Cyclohexane was also degraded by the same pathway as methylcyclohexane. Thus, strain NDKK48 has two pathways for the complete degradation of c-alkanes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott BJ, Gledhill WE (1971) Extracellular accumulation of metabolic products by hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms. Adv Appl Microbiol 14:249–388
Beam HW, Perry JJ (1974) Microbial degradation and assimilation of n-alkyl-substituted cycloparaffins. J Bacteriol 118:394–399
Blakley ER (1978) The microbial degradation of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid by a β-oxidation pathway with simultaneous induction to the utilization of benzoate. Can J Microbiol 24:847–855
Blakley ER, Papish B (1982) The metabolism of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid and 3-cyclohexenecarboxylic acid by Pseudomonas putida. Can J Microbiol 28:1324–1329
Butler CS, Mason JR (1997) Structure-function analysis of the bacterial aromatic ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases. Adv Microb Physiol 38:47–84
Clarke PH (1984) The evolution of degradative pathways. In: Gibson DT (ed) Microbial degradation of organic compounds. Dekker, New York, pp 11–27
Doboghue NA, Norris D, Trudgill PW (1976) The purification and properties of cyclohexanone oxygenase from Nocardia globerula CL1 and Acinetobacter NCIB9871. Eur J Biochem 63:175–192
Dong JZ, Vorkink WP, Lee ML (1993) Origin of long-chain alkylcyclohexanes and alkylbenzenes in a coal-bed wax. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:837–849
Donoghue NA, Trudgill PW (1975) The metabolism of cyclohexanol by Acinetobacter NCIB 9871. Eur J Biochem 60:1–7
Dutta TK, Harayama S (2001) Biodegradation of n-alkylcycloalkanes and n-alkylbenzenes via new pathways in Alcanivorax sp. strain MBIC4326. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1970–1974
Elshahed MS, Bhupathiraju VK, Wofford NQ, Nanny MA, McInerney MJ (2001) Metabolism of benzoate, cyclohex-1-ene carboxylate, and cyclohexane carboxylate by Syntrophus aciditrophicus strain SB in syntrophic association with H2-using microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1728–1738
Fowler MG, Abolins P, Douglas AG (1986) Monocyclic alkanes in Ordovician organic matter. Org Geochem 10:815–823
Griffin M, Trudgill PW (1976) Purification and properties of cyclopentanone oxygenase of Pseudomonas NCIB9872. Eur J Biochem 63:199–209
Hasegawa Y, Nakai Y, Tokuyama T, Iwaki H (2000) Purification and characterization of cyclohexanone 1,2-monooxygenase from Exophiala jeanselmei strain KUIN-6N. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:2696–2698
Kaneda T, Obata H, Tokumoto M (1993) Aromatization of 4-oxocyclohexanecarboxylic acid to 4-hydroxybenzoic acid by two distinctive desaturases from Corynebacterium cyclohexanicum—properties of two desaturases. Eur J Biochem 218:997–1003
Kissin YV (1990) Catagenesis of light cycloalkanes in petroleum. Org Geochem 15:575–594
Ko SH, Lebeault JM (1999) Effect of a mixed culture on co-oxidation during the degradation of saturated hydrocarbon mixture. J Appl Microbiol 87:72–79
Koma D, Sakashita Y, Kubota K, Fujii Y, Hasumi F, Chung SY, Kubo M (2003a) Degradation of car engine base oil by Rhodococcus sp. NDKK48 and Gordonia sp. NDKY76A. Biosci Biochem Bioeng 67:1590–1593
Koma D, Hasumi F, Chung SY, Kubo M (2003b) Biodegradation of n-alkylcyclohexanes by co-oxidation via multiple pathways in Acinetobacter sp. ODDK71. J Biosci Bioeng 95:641–644
Komukai-Nakamura S, Sugiura K, Yamauchi-Inomata Y, Toki H, Venkateswaran K, Yamamoto S, Tanaka H, Harayama S (1996) Construction of bacterial consortia that degrade Arabian light crude oil. J Ferment Bioeng 82:570–574
Kostichka K, Thomas SM, Gibson KJ, Nagarajan V, Cheng Q (2001) Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster for cyclododecanone oxidation in Rhodococcus ruber SC1. J Bacteriol 183:6478–6486
Lal B, Khanna S (1996) Degradation of crude oil by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Alcaligenes odorans. J Appl Bacteriol 81:355–362
Ougham HJ, Trudgill PW (1982) Metabolism of cyclohexaneacetic acid and cyclohexanebutyric acid by Arthrobacter sp. strain CA1. J Bacteriol 150:1172–1182
Perry JJ (1984) Microbial metabolism of cyclic alkanes. In: Atlas RM (ed) Petroleum microbiology. Macmillan, New York, pp 61–98
Rehm H, Reiff I (1981) Mechanism and occurrence of microbial oxidation of long chain alkanes. Adv Biochem Eng 19:175–215
Schumacher JD, Fakoussa RM (1999) Degradation of alicyclic molecules by Rhodococcus ruber CD4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:85–90
Stirling LA, Watkinson RJ (1977) Microbial metabolism of alicyclic hydrocarbons: isolation and properties of a cyclohexane-degrading bacterium. J Gen Microbiol 99:119–125
Swannell RPJ, Lee K, McDonagh M (1996) Field evaluations of marine oil spill bioremediation. Microbiol Rev 60:342–365
Trower MK, Buckland RM, Griffin M (1989) Characterization of an FMN-containing cyclohexanone monooxygenase from a cyclohexane-grown Xanthobacter sp. Eur J Biochem 181:191–206
Williams JA, Dolcater DL, Torkelson BE, Winters JC (1988) Anomalous concentrations of specific alkylaromatics and alkylcycloparaffin components in West Texas and Michigan crude oils. Org Geochem 13:47–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koma, D., Sakashita, Y., Kubota, K. et al. Degradation pathways of cyclic alkanes in Rhodococcus sp. NDKK48. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66, 92–99 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1623-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1623-5