Abstract
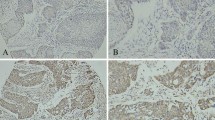
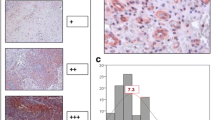
Objective: To study the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and microvessel density (MVD) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and clarify the association of VEGF expression with the angiogenesis and prognostic value of this disease. Methods: Eighty-two cases with primary ESCC treated with radical operation in Department of Surgery from Jan 1981 through May 1994 were enrolled. VEGF expression and MVD value were examined by immunohistochemical staining, the streptavidin-biotin peroxidase complex method (SP method), using anti-VEGF polyclonal antibody and anti-Factor-VIII antibody, respectively. We also analyzed the relationship between VEGF expression and MVD value and postoperative survival rate of patients. Results: Of the 82 cases, 63.4% cases showed positive for VEGF in tumor cells and the median of MVD in tumor was 37 (9–150) ·mm−2. There was a close correlation between MVD and VEGF (P=0.001). The 5-year survival rate of patients with low and high MVD was 34.1% and 12.2%, respectively. The 5-year survival rate was 46.7% in patients with VEGF-negative tumor and 11.5% in patients with VEGF-positive tumor. These differences were statistically significant (P=0.017 and P<0.001, respectively). Conclusion: In ESCC, angiogenesis is mediated mainly by VEGF and VEGF may be associated with tumor progression and increased malignancy via angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toi M, Inada K, Suzuki H, et al. Tumor angiogenesis in breast cancer: its importance as a prognostic indicator and the association with vascular endothelial growth factor expression[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1995; 36:193–204.
Maeda K, Chung YS, Ogawa Y, et al. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric carcinoma[J]. Cancer 1996; 77:858–63.
Abulafia O, Triest WE, Sherer DM. Angiogenesis in malignancies of female genital tract[J]. Gynecol Oncol 1999; 72:220–31.
Sauter ER, Nesbit M, Watson JC, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a marker of tumor invasion and metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck[J]. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5:775–82.
Aikawa H, Takahashi H, Fujimura S, et al. Immunohistochemical study on tumor angiogenic factors in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Anticancer Res 1999; 19:4305–9.
Zhang LJ, Yang GL, Xie YQ, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in primary non-small cell lung carcinoma[J]. Chin J Cancer Res 1999; 11:288–91.
Yano T, Tanikawa S, Fujie T, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and neovascularization in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Eur J Cancer 2000; 36:601–9.
Borre M, Nerstrom B, Overgard J. Association between immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF-expressing neuro-endocrine-differentiated tumor cells, and outcome in prostate cancer patients subjected to watchful waiting[J]. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6:1882–90.
Seo Y, Baba H, Fukuda T, et al. High expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with liver metastasis and a poor prognosis for patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer 2000; 88: 2239–45.
Niedergethmann M, Hildenbrand R, Wolf G, et al. Angiogenesis and cathepsin expression are prognostic factors in pancreatic adenocarcinoma after curative resection[J]. Int J Pancreatol 2000; 28:31–9.
Strohmeyer D, Rossing C, Bauerfeind A, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and its correlation with angiogenesis and p53 expression in prostate cancer[J]. Prostate 2000; 45:216–24.
Inoue K, Slaton JW, Karashima T, et al. The prognostic value of angiogenesis factor expression for predicting recurrence and metastasis of bladder cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy[J]. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6:4866–73.
Straume O, Akslen LA. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, its receptors (FLT-1, KDR) and TSP-1 related to microvessel density and patient outcome in vertical growth phase melanomas[J]. Am J Pathol 2001; 159:223–35.
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, et al. Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992; 84:1875–87.
Bosari S, Lee AK, Delellis RA, et al. Microvessel quantitation and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol 1992; 23:755–61.
Inoue K, Ozeki Y, Suganuma T, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, association with angiogenesis and tumor progression[J]. Cancer 1997; 79:206–13.
Srivastava A, Laidler P, Davies RP, et al. The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76–4.0mm thick) skin melanoma: a quantitative histological study[J]. Am J Pathol 1988; 133:419–23.
Igarashi M, Dhar DK, Kubota H, et al. The prognostic significance of microvessel density and thymidine phosphorylase expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. Cancer 1998; 82:1225–32.
Tanigawa N, Matsumura M, Amaya H, et al. Tumor vascularity correlates with the prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer 1997; 79:220–5.
Kitadai Y, Haruma K, Tokutomi T, et al. Significance of vessel count and vascular endothelial growth factor in human esophageal carcinomas[J]. Clin Cancer Res 1998; 4:2195–200.
Nakagawa S, Nishimaki T, Suzuki T, et al. Tumor angiogenesis as an independent prognostic factor after extended radical esophagectomy for invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. Surgery 2001; 129:302–8.
Ferrara N, Henzel WJ. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1989; 161:851–8.
Tomoda M, Maehara Y, Kakeji Y, et al. Intratumoral neovascularization and growth pattern in early gastric carcinoma[J]. Cancer 1999; 85:2340–6.
Toi M, Bando H, Kuroi K. The predictive value of angiogenesis for adjuvant therapy in breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer 2000;7:311–4.
Han H, Silverman JF, Santucci TS, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer correlates with neoangiogenesis and a poor prognosis[J]. Ann Surg Oncol 2001; 8:72–9.
Koide N, Nishio A, Kono T, et al. Histochemical study of vascular endothelial growth factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. Hepatogastroenterology 1999; 46:952–8.
Ogata Y, Harada Y, Fujii T, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of vascular endothelial growth factor in esophageal cancer[J]. The Kurume Med 1996; 43:157–63.
Uchida S, Shimada Y, Watanabe G, et al. In oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with p53 mutation, advanced stage and poor prognosis[J]. Br J Cancer 1998; 77:1704–9.
Shih CH, Ozawa S, Ando N, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression predicts outcome and lymph node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6:1161–8.
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications[J]. N Engl J Med 1971; 285:1182–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No. 953307900).
Biography: XU Wei-guo(1966–), male, doctor of medicine, associate professor, majors in surgical oncology. Present address: Department of Surgical Oncology, The Affiliated Hospital, North China Coal Medical College, Tangshan, Hebei Province.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Wg., Yang, Gl., Zhou, Lx. et al. Prognostic value of VEGF expression in primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 16, 85–89 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-004-0002-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-004-0002-1