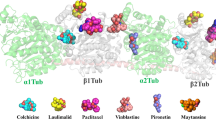
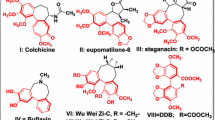
Abstract
Studies on vinca domain binding drugs were done in great details by a number of workers as it is recognized as a potential target for anticancer drug development. Their structures, properties, mode of action, success and failures as potential anticancer drug have been discussed in short details in this review. Among these drugs rhizoxin and maytansine are competitive inhibitors, and bind at the vinblastine binding site of tubulin where as others are non-competitive inhibitors. Besides binding, these drugs also differ in the extent of GTP hydrolysis, GTP exchange and in the stabilization of colchicine binding site. The toxicity level of these drugs towards the host cells and the extent of efflux of drugs by the P-glycoprotein mediated pump are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchison T, Kirschner M: Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature 312: 237-242, 1984
Horio T, Hotani H: Visualization of the dynamic instability of individual microtubules by dark-field microscopy. Nature 321: 605-607, 1986
Hayden JH, Bowser SS, Rieder CL: Kinetochores capture astral microtubules during chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle: Direct visualization in live newt lung cells. J Cell Biol 111: 1039-1045, 1990
Wordeman L, Mitchison TJ: Microtubule dynamics in vivo in microtubules. Hyams & Lloyd, 1994, pp 287-301
Jordan MA, Wilson L: Microtubules and actin filaments: Dynamic targets for cancer chemotherapy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1123-1130, 1998
Wilson L, Jordan MA: Microtubule dynamics: Taking aim at a moving target. Chem Biol 2: 569-573, 1995
Jordan MA, Thrower D, Wilson L: Mechanism of inhibition of cell proliferation by Vinca alkaloids. Cancer Res 51: 2212-2222, 1991
Jordan MA, Thrower D, Wilson L: Effects of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles. Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis. J Cell Sci 102: 401-416, 1992
Jordan MA, Toso RJ, Thrower D, Wilson L: Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by taxol at low concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 9552-9556, 1993
Jordan MA, Wendell K, Gardiner S, Derry WB, Copp H, Wilson L. Mitotic block induced in HeLa cells by low concentrations of paclitaxel (Taxol) results in abnormal mitotic exit and apoptotic cell death. Cancer Res 56: 816-825, 1996
Seed L, Slaughter DP, Limarzi LR: Effect of colchicine on human carcinoma. Surgery 7: 696-709, 1940
Toso RJ, Jordan MA, Farrell KW, Matsumoto B, Wilson L: Kinetic stabilization of microtubule dynamic instability in vitro by vinblastine. Biochemistry 32: 1285-1293, 1993
Wilson L, Jordan MA, Morse A, Margolis RL: Interaction of vinblastine with steady-state microtubules in vitro. J Mol Biol 159: 125-149, 1982
Warfield RKN, Bouck GB: Microtubule-macrotubule transitions: Intermediates after exposure to the mitotic inhibitor vinblastine. Science 186: 1219-1220, 1974
David-Pfeuty T, Simon C, Pantaloni D: Effect of antimitotic drugs on tubulin GTPase activity and self-assembly. J Biol Chem 254: 11696-11702, 1979
Lin CM, Hamel E: Effects of inhibitors of tubulin polymerization on GTP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 256: 9242-9245, 1981
Rai SS, Wolff J: Localization of the vinblastine-binding site on beta-tubulin. J Biol Chem 271: 14707-14711, 1996
Bhattacharyya B, Wolff J: Tubulin aggregation and disaggregation: Mediation by two distinct vinblastine-binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73: 2375-2378, 1976
Wilson L: Properties of colchicine binding protein from chick embryo brain. Interactions with vinca alkaloids and podophyllotoxin. Biochemistry 9: 4999-5007, 1970
Manfredi JJ, Parness J, Horwitz SB: Taxol binds to cellular microtubules. J Cell Biol 94: 688-696, 1982
Iwasaki S, Kobayashi H, Furukawa J, Namikoshi M, Okuda S, Sato Z, Matsuda I, Noda T: Studies on macrocyclic lactone antibiotics. VII. Structure of a phytotoxin 'rhizoxin' produced by Rhizopus chinensis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 37: 354-362, 1984
Tsuro T, Oh-hara T, Iida H, Tsukagoshi S, Sato Z, Matsuda I, Iwaski Okuda S, Shimizu F, Sasagawa K, Fukami M, Fukuda K, Arakawa M: Rhizoxin, a macrocyclic lactone antibiotic, as a new antitumor agent against human and murine tumor cells and their vincristine-resistant sublines. Cancer Res 46: 381-385, 1986
Takashaki M, Iwasaki S, Kobayashi H, Okuda S, Murai T, Sato Y: Rhizoxin binding to tubulin at the maytansine-binding site. Biochim Biophys Acta 926: 215-223, 1987
Wolpert-deFilippes MK, Adamson RH, Cystic RL, Johns DG: Initial studies on the cytotoxic action of maytansine, a novel ansa macrolide. Biochem Pharmacol 24: 751-754, 1975
Takashaki M, Matshumoto S, Iwasaki S, Yahara I: Molecular basis for determining the sensitivity of eucaryotes to the antimitotic drug rhizoxin. Mol Gen Genet 169-175, 1990
Takashaki M, Kobayashi H, Iwasaki S: Rhizoxin resistant mutants with an altered beta-tubulin gene in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 220: 53-59, 1989
Sawada T, Kobayashi H, Hashimoto Y, Iwasaki S: Identification of the fragment photoaffinity-labeled with azidodansyl-rhizoxin as Met-363-Lys-379 on beta-tubulin. Biochem Pharmacol 45: 1387-1394, 1993
Sackett DL: Vinca site agents induce structural changes in tubulin different from and antagonistic to changes induced by colchicine site agents. Biochemistry 34: 7010-7019, 1995
Sackett DL, Varma JK: Molecular mechanism of colchicine action: Induced local unfolding of beta-tubulin. Biochemistry 32: 13560-135655, 1993
Hamel E: Antimitotic natural products and their interactions with tubulin. Med Res Rev 16: 207-231, 1996
Gamble WR, Durso NA, Fuller RW, Westergaard CK, Johnson TR, Sackett DL, Hamel E, Cardellina JH II, Boyd MR: Cytotoxic and tubulin-interactive hemiasterlins from Auletta sp. and Siphonochalina spp. sponges. Bioorg Med Chem: 1611-1615, 1999
Anderson HJ, Coleman JE, Andersen RJ, Roberge M: Cytotoxic peptides hemiasterlin, hemiasterlin A and hemiasterlin B induce mitotic arrest and abnormal spindle formation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 39: 223-226, 1997
Bai R, Durso NA, Sackett DL, Hamel E: Interactions of the sponge-derived antimitotic tripeptide hemiasterlin with tubulin: Comparison with dolastatin 10 and cryptophycin 1. Biochemistry 38: 14302-14310, 1999
Bai R, Schwartz RE, Kepler JA, Pettit GR, Hamel E: Characterization of the interaction of cryptophycin 1 with tubulin: binding in the Vinca domain, competitive inhibition of dolastatin 10 binding, and an unusual aggregation reaction. Cancer Res 56: 4398-4406, 1996
Mandelbaum-Shavit F, Wolpert-DeFilippes MK, Johns DG: Binding of maytansine to rat brain tubulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 72: 47-54, 1976
Bhattacharyya B, Wolff J: Maytansine binding to the vinblastine sites of tubulin. FEBS Lett 75: 159-162, 1977
Pettit GR, Cichacz ZA, Gao F, Herald CL, Boyd MR, Schmidt JM, Hooper JNA: Isolation and structure of spongistatin 1. J Org Chem 58: 1302-1304, 1993
Bai R, Cichacz ZA, Herald CL, Pettit GR, Hamel E: Spongistatin 1, a highly cytotoxic, sponge-derived, marine natural product that inhibits mitosis, microtubule assembly, and the binding of vinblastine to tubulin. Mol Pharmacol 44: 757-766, 1993
Bai R, Taylor GF, Cichacz ZA, Herald CL, Kepler JA, Pettit GR, Hamel E: The spongistatins, potently cytotoxic inhibitors of tubulin polymerization, bind in a distinct region of the vinca domain. Biochemistry 34: 9714-9721, 1995
Uckun FM, Mao C, Vassilev AO, Huang H, Jan ST: Structure-based design of a novel synthetic spiroketal pyran as a pharmacophore for the marine natural product spongistatin 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 541-545, 2000
Huang H, Mao C, Jan ST, Uckun FM: Structure-based design of novel anticancer agents. Tet Lett 41: 1699-1702, 2000
Pettit GR, Herald CL, Boyd MR, Leet JE, Dufresne C, Doubek DL, Schmidt JM, Cerny RL, Hooper JN, Rutzler KC: Isolation and structure of the cell growth inhibitory constituents from the western Pacific marine spong Axinella sp. J Med Chem 34: 3339-3340, 1991
Bai R, Paull KD, Herald CL, Malspeis L, Pettit GR, Hamel E: Halichondrin B and homohalichondrin B, marine natural products binding in the vinca domain of tubulin. Discovery of tubulin-based mechanism of action by analysis of differential cytotoxicity data. J Biol Chem 266: 15882-15889, 1991
Luduena RF, Roach MC, Prasad V, Pettit GR: Interaction of halichondrin B and homohalichondrin B with bovine brain tubulin. Biochem Pharmacol 45: 421-427, 1993
Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Budrow J, Wels BF, Kuznetsov G, Aalfs KK, Wesh S, Zheng W, Seletsk BM, Palme MH, Habgood GJ, Singer LA, Dipietro LV, Wang Y, Chen JJ, Quincy DA, Davis A, Yoshimatsu K, Kishi Y, Yu MJ: In vitro and in vivo anticancer activities of synthetic macrocyclic ketone analogues of halichondrin B. Cancer Res 61: 1013-1021, 2001
Pettit GR, Kamano Y, Herald CL, Tuinman AA, Boettner FE, Kizn H, Schmidt JM, Baczynskyj RJ: The isolation and structure of a remarkable marine animal antineoplastic constituent: Dolastatin 10. J Am Chem Soc 109: 6883-6885, 1987
Bai R, Pettit GR, Hamel E: Dolastatin 10, a powerful cytostatic peptide derived from a marine animal. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization mediated through the vinca alkaloid binding domain. Biochem Pharmacol 39: 1941-1949, 1990
Bai R, Taylor GF, Schmidt JM, Williams MD, Kepler JA, Pettit GR, Hamel E: Interaction of dolastatin 10 with tubulin: Induction of aggregation and binding and dissociation reactions. Mol Pharmacol 47: 965-976, 1995
Ali MA, Rosati R, Pettit GR, Kalemkarian GP: Dolastatin 15 induces apoptosis and BCL-2 phosphorylation in small cell lung cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res 18: 1021-1026, 1998
Kalemkarian GP, Ou X, Adil MR, Rasoti R, Khoulani MM, Madan SK, Pettit GR: Activity of dolastatin 10 against small-cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo: Induction of apoptosis and bcl-2 modification. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 43: 507-515, 1999
Verdier-Pinard P, Kepler JA, Pettit GR, Hamel E: Sustained intracellular retention of dolastatin 10 causes its potent antimitotic activity. Mol Pharmacol 57: 180-187, 2000
Mohammad RM, Pettit GR, Almatchy VP, Wall N, Varterasian M, Al-Katib A: Synergistic interaction of selected marine animal anticancer drugs against human diffuse large cell lymphoma. Anticancer Drugs 9: 149-156, 1998
Mohammad RM, Varterasian M, Almatchy VP, Hannoudi GN, Pettit GR, Al-Katib A: Successful treatment of human chronic lymphocytic leukemia xenografts with combination biological agents auristatin PE and bryostatin 1. Clin Cancer Res 4: 1337-1343, 1998
Poncet J: The dolastatins, a family of promising antineoplastic agents. Curr Pharm Des 5: 139-162, 1999
Panda D, Deluca K, Williams D, Jordon MA, Wilson L: Antiproliferative mechanism of action of cryptophycin-52: Kinetic stabilization of microtubule dynamics by high affinity binding to microtubule ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 9313-9318, 1998
Panda DP, Singh JP, Wilson L: Suppression of microtubule dynamics by LY290181. J Biol Chem 272: 7681-7687, 1997
Bai R, Schwartz RE, Kepler JA, Petit, Hamel E: Tryptostatin A, a specific and novel inhibitor of microtubule. Cancer Res 56: 4398-4406, 1996
Panda D, Ananthnarayan V, Larson G, Shih C, Jordan MA, Wilson L: Interaction of the antitumor compound cryptophycin-52 with tubulin. Biochemistry 39: 14121-14127, 2000
Gelmon KA, Tolcher A, Diab AR, Bally MB, Embree L, Hudon N, Dedhar C, Ayers D, Eisen A, Melosky B, Burge C, Logan P, Mayer LD: Phase I study of liposomal vincristine. J Clin Oncol 17: 697-705, 1999
Sakowicz R, Berdelis MS, Ray K, Blackburn CL, Hopmann C, Faulkner DJ, Goldstein LS: A marine natural product inhibitor of kinesin motors. Science 280: 292-295, 1998
Mayer TU, Kapoor TM, Haggarty SJ, King RW, Schreiber SL, Mitchison TJ: Small molecule inhibitor of mitotic spindle bipolarity identified in a phenotype-based screen. Science 286: 971-974, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Bhattacharyya, B. Antimicrotubular drugs binding to vinca domain of tubulin. Mol Cell Biochem 253, 41–47 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026045100219
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026045100219