Abstract
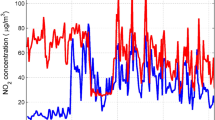
As the health impact of air pollutants existing in ambient addresses much attention in recent years, forecasting of airpollutant parameters becomes an important and popular topic inenvironmental science. Airborne pollution is a serious, and willbe a major problem in Hong Kong within the next few years. InHong Kong, Respirable Suspended Particulate (RSP) and NitrogenOxides NOx and NO2 are major air pollutants due to thedominant diesel fuel usage by public transportation and heavyvehicles. Hence, the investigation and prediction of the influence and the tendency of these pollutants are ofsignificance to public and the city image. The multi-layerperceptron (MLP) neural network is regarded as a reliable andcost-effective method to achieve such tasks. The works presentedhere involve developing an improved neural network model, whichcombines the principal component analysis (PCA) technique and theradial basis function (RBF) network, and forecasting thepollutant levels and tendencies based in the recorded data. Inthe study, the PCA is firstly used to reduce and orthogonalizethe original input variables (data), these treated variables arethen used as new input vectors in RBF neural network modelestablished for forecasting the pollutant tendencies. Comparingwith the general neural network models, the proposed modelpossesses simpler network architecture, faster training speed,and more satisfactory predicting performance. This improvedmodel is evaluated by using hourly time series of RSP, NOx and NO2 concentrations collected at Mong Kok Roadside Gaseous Monitory Station in Hong Kong during the year 2000. By comparing the predicted RSP, NOx and NO2 concentrationswith the actual data of these pollutants recorded at the monitorystation, the effectiveness of the proposed model has been proven.Therefore, in authors' opinion, the model presented in the paper is a potential tool in forecasting air quality parameters and hasadvantages over the traditional neural network methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boznar, M., Lesjak, M. and Mlakar, P.: 1993, 'A neural network-based method for short-term predictions of ambient SO2 concentrations in highly polluted industrial areas of complex terrain', Atmosph. Environ. B27(2), 221-230.
Burnett, R. T., Smith-Doiron, M., Stieb, D., Cakmak, S. and Brook, J. R.: 1999, 'Effects of particulate and gaseous air pollution on cardiorespiratory hospitalizations', Arch. Environ. Health 54(2), 130-139.
Broomhead, D. and Lowe, D.: 1988, 'Multivariable functional interpolation and adaptive networks', Complex Syst. 2, 321-355.
Chan, L. Y. and Kwok, W. S.: 2000, 'Vertical dispersion of suspended particulates in urban area of Hong Kong', Atmosph. Environ. 34, 4403-4412.
Chan, L. Y. and Liu, Y. M.: 2001, 'Carbon monoxide levels in popular passenger commuting modes traversing major commuting routes in Hong Kong', Atmosph. Environ. 35, 2637-2646.
Collet, R. S. and Oduyemi, K.: 1997, 'Air quality modeling: A technical review of mathematical approachs', Meteorolog. Applicat. 4, 235-246.
Comrie, A. C.: 1997, 'Comparing neural networks and regression models for ozone forecasting', J. Air Waste Manage. 47, 653-663.
Fan, H. Y., Lu, W. Z. and Xu, Z. B.: 2000, 'An empirical comparison of three novel genetic algorithms', Engin. Comput. 17(8), 981-1001.
Gardner, M. W. and Dorling, S. R.: 1996, 'Neural Network Modelling of the Influence of Local Meteorology on Surface Ozone Concentrations', Proceedings 1st International Conference on GeoComputation, University of Leeds, pp. 359-370.
Gardner, M. W. and Dorling, S. R.: 1998, 'Artificial neural networks (the multi-layer feed-forward neural networks)-A review of applications in the atmospheric science', Atmosph. Environ. 30(14/15), 2627-2636.
Hadjiiski, L. and Hopke, P. K.: 2000, 'Application of artificial neural network to modeling and prediction of ambient ozone concentrations', J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 50, 894-901.
Harrison, R. M., Smith, D. J. T. and Luhana, L.: 1996, 'Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons collected from urban location in Birmingham, U.K.', Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 825-832.
Harrison, R. M., Deacon, A. R. and Jones, M. R.: 1997, 'Sources and processes affecting concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 particulate matter in Birmingham (U.K.)', Atmosph. Environ. 31(24), 4103-4117.
Hong Kong Environment Protection Department: 1998, 1999, 2000, Environment Hong Kong.
Kaminski, W., Skrzypski, J. and Strumillo, P.: 2000, Forecasting of Air Pollution in Urban Areas by Means of Artificial Neural Networks. Urban Transport and the Environment for the 21st Century, L. J. Sucharov (ed.), WIT Press, Southampton, Boston, pp. 114-124.
Lee, E., Chan, C. K. and Paatero, P.: 1999, 'Application of positive matrix factorization in source apportionment of particulate pollutants', Atmosph. Environ. 33, 3201-3212.
Lu, W. Z., Fan, H. Y., Lo, S. M. and Wong, J. C. K.: 2002, 'Analysis of pollutant levels in Central Hong Kong applying neural network method with particle swarm optimization, Environ. Monit. Assess. 79, 217-230.
Lu, W. Z., Fan, H. Y., Lo, S. M. and Wong, J. C. K.: 2001, 'A Particle-swarm-optimization-based Neural Network Approach and its Application to Environmental Modeling', Proceedings of IAQVEC'2001 I, October, Changsha, P.R. of China, pp. 405-411.
Lu, W. Z., Wang, W. J., Fan, H. Y., Leung, A. Y. T, Lo, S. M., Xu, Z. B. and Wong, J. C. K.: 2002, 'Prediction of pollutant levels in causeway bay area in Hong Kong using an improved neural network model', ASCE J. Environ. Engin. 128(12), 1146-1157, December.
Lu, W. Z.,Wang, W. J., Leung, A. Y. T., Lo, S. M., Yuen, K. K., Xu, Z. B. and Fan, H. Y.: 2002, 'Air Pollutant Parameter Forecasting using Support Vector Machines, IEEE/IJCNN'2002.
Perez, P., Trier, A. and Reyes, J.: 2000, 'Prediction of PM2.5 concentrations several hours in advance using neural networks in Santiago, Chile', Atmosph. Environ. 34, 1189-1196.
Reich, S. L., Gomez, D. R. and Dawidowski, L. E.: 1999, 'Artificial neural network for the identification of unknown air pollution sources', Atmosph. Environ. 33, 3045-3052.
Roadknight, C. M., Balls, G. R., Mills, G. E. and Palmer-Brown, D.: 1997, 'Modeling complex environmental data', IEEE Transact. Neural Networks 8(4), 852-861.
Shi, J. P. and Harrison, R. M.: 1997, 'Regression modeling of hourly and concentrations in urban air in London', Atmosph. Environ. 31(24), 4081-1094.
Song, X. H. and Hopke, P. K.: 1996, 'Solving the chemical mass balance problem using an artificial neural network', Environ. Sci. Technol. 30(2), 531-535.
Spurny, K. R.: 1998, 'On the physics, chemistry and toxicology of ultrafine anthropogenic, atmospheric aerosols (UAAA): New advances', Toxicol. Lett. 96, 253-261.
Thurston, G. D. and Spengler, J. D.: 1985, 'A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate in metropolitan Boston', Atmosph. Environ. 19, 9-25.
Transport Department: 1999, Annual Transport Digest: Hong Kong Printing Department, Hong Kong.
Wang, W. J., Vircent, T., Cheung, T. F., Lam, K. S., Kok, G. L. and Harris, J. M.: 2001, 'The characteristics of ozone and related compounds in the boundary layer of the South China coast: Temporal and vertical variations during autumn season', Atmosph. Environ., 2735-2746.
Wang,W. J., Lu,W. Z., Leung, A. Y. T., Lo, S. M., Xu, Z. B. and Wang, X. K.: 2002, 'Optimal Feed-Forward Neural Networks Based on the Combination of Constructing and Pruning by Genetic Algorithms', IEEE/IJCNN'2002.
Yi, J. and Prybutok, R.: 1996, 'A neural network model forecasting for prediction of daily maximum ozone concentration in an industrialized urban area', Environ. Pollut. 92(3), 349-357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, W.Z., Wang, W.J., Wang, X.K. et al. Using Improved Neural Network Model to Analyze RSP, NOx and NO2 Levels in Urban Air in Mong Kok, Hong Kong. Environ Monit Assess 87, 235–254 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024819309108
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024819309108