Abstract
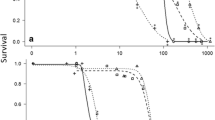
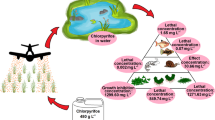
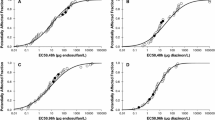
Agricultural activity within coastal watersheds results in estuaries becoming the receiving environment for pesticide inputs. In estuaries, salinity can alter insecticide responses of exposed crustaceans. The acute toxicity of environmentally relevant doses of chlorpyrifos and imidacloprid were examined using the euryhaline amphipod Gammarus lawrencianus at 20 and 30 Practical Salinity Units (PSU). Responses were recorded every 24 h until an incipient (threshold) L(E)C50 was reached. For chlorpyrifos, LC50 ranged from 0.1 to 0.5 µg/L and was two-fold higher at 30 vs. 20 PSU at all time-points over the 96 h exposure. Imidacloprid immobility EC50 ranged from 4 to 40 µg/L over the 144 h exposure. An effect of salinity was only observed at 48 h and the EC50 values showed 1.4 times more potency at 20 PSU compared to 30 PSU. Measured concentrations of both compounds did not differ between salinities. Acetylcholinesterase activity in chlorpyrifos exposed amphipods showed no salinity effect at 96 h. We conclude that salinity level alters G. lawrencianus susceptibility to chlorpyrifos exposure, but not imidacloprid.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatz A, Ashauer R, Brown CD (2014) Imidacloprid perturbs feeding of Gammarus pulex at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:648–653
Bollmohr S, Schulz R, Hahn T (2009) Interactive effect of salinity decrease, salinity adaptation, and chlorpyrifos exposure on an estuarine harpacticoid copepod, Mesochra parva, in South Africa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:756–764
Bousfield EL (1973) Shallow-water gammaridean ampipoda of New England. Comstock-Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Brecken-Folse JA, Mayer FL, Pedigo LE, Marking LL (1994) Acute toxicity of 4-nitrophenol, 2,4-dinitrophenol, terbufos and trichlorfon to grass shrimp (Palaemonetes spp.) and sheepshead minnows (Cyprinodon variegatus) as affected by salinity and temperature. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:67–77
Coffin MRS, Courtenay SC, Knysh KM, Pater CC, van den Heuvel MR (2018) Impacts of hypoxia on estuarine macroinvertebrate assemblages across a regional nutrient gradient. FACETS 3:23–44
Cuevas N, Martins M, Costa PM (2018) Risk assessment of pesticides in estuaries: a review addressing the persistence of an old problem in complex environments. Ecotoxicology 27:1008–1018
Dell’Arciprete ML, Soler JM, Santos-Juanes L, Arques A, Mártire DO, Furlong JP, Gonzalez MC (2012) Reactivity of neonicotinoid insecticides with carbonate radicals. Water Res 46:3479–3489
Delorenzo ME (2015) Impacts of climate change on the ecotoxicology of chemical contaminants in estuarine organisms. Curr Zool 61:641–652
de Waard JR, Ivanova NV, Hajibabaei M, Hebert PDN (2008) Assembling DNA barcodes: analytical protocols. In: Martin CC (ed) Methods in molecular biology: environmental genetics, vol 410. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 275–293
Denning A, Ernst WR, Julien GR, Doe KG, Cook A, Bernier M, Jackman P, Loiser C (2004) An assessment of buffer zone effectiveness in reducing pesticide runoff from potato fields in Prince Edward Island (2001–2002). Environment Canada Surveillance Report: EPS-5-AR-04–05, Atlantic Region.
Fulton MH, Key PB (2001) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition in estuarine fish and invertebrates as an indicator of organophosphorus insecticide exposure and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:37–45
Gallagher DL, Dietrich AM, Reay WG, Hayes MC, Simmons GM Jr (1996) Ground water discharge of agricultural pesticides and nutrients to estuarine surface water. Groundw Monit Remediat 16:118–129
Hall LW, Anderson RD (1995) The influence of salinity on the toxicity of various classes of chemicals to aquatic biota. Crit Rev Toxicol 25:281–346
Hano T, Ito K, Ohkubo N, Sakaji H, Watamabe A, Takashima K, Sato T, Sugaya T, Matsuki K, Onduka T et al (2019) Occurrence of neonicotinoids and fipronil in estuaries and their potential risks to aquatic invertebrates. Environ Pollut 252:205–215
Hothorn T, Bretz F, Westfall P (2008) Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom J 50:346–363
Huang X, Cui H, Duan W (2020) Ecotoxicity of chlorpyrifos to aquatic organisms: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 200:110731
Key PB, Fulton MH (2006) Correlation between 96-h mortality and 24-h acetylcholinesterase inhibition in three grass shrimp larval life stages. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:389–392
Lalonde B, Garron C (2020) Temporal and spatial analysis of surface water pesticide occurrences in the Maritime region of Canada. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 79:12–22
Leclair LA, MacDonald GZ, Phalen LJ et al (2013) The immunological effects of oil sands surface waters and naphthenic acids on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 142–143:185–194
Leight AK, Van Dolah RF (1999) Acute toxicity of the insecticides endosulfan, chlorpyrifos, and malathion to the epibenthic estuarine amphipod Gammarus palustris (bousfield). Environ Toxicol Chem 18:958–964
Liu B, McConnell LL, Torrents A (2001) Hydrolysis of chlorpyrifos in natural waters of the Chesapeake Bay. Chemosphere 44:1315–1323
Morrissey CA, Mineau P, Devries JH, Sanchez-Bayo F, Liess M, Cavallaro M, Liber K (2015) Neonicotinoid contamination of global surface waters and associated risk to aquatic invertebrates: a review. Environ Int 74:291–303
Narra MR (2014) Tissue-specific recovery of oxidative and antioxidant effects of chlorpyrifos in the freshwater crab Barytelphusa guerini. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67:158–166
Pawar AP, Sanaye SV, Shyama S, Sreepada RA, Dake AS (2020) Effects of salinity and temperature on the acute toxicity of the pesticides, dimethoate and chlorpyrifos in post-larvae and juveniles of the whiteleg shrimp. Aquac Reports 16:100240
Podlesińska W, Dąbrowska H (2019) Amphipods in estuarine and marine quality assessment—a review. Oceanologia 61:179–196
R Core Team (2019) A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Ritz C, Baty F, Streibig JC, Gerhard D (2015) Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS ONE 10:e0146021
Roessink I, Merga LB, Zweers HJ, Van den Brink PJ (2013) The neonicotinoid imidacloprid shows high chronic toxicity to mayfly nymphs. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1096–1100
Saranjampour P, Vebrosky EN, Armbrust KL (2017) Salinity impacts on water solubility and n-octanol/water partition coefficients of selected pesticides and oil constituents. Environ Toxicol Chem 36:2274–2280
Schein A, Courtenay SC, Kidd KA, Campbell A, van den Heuvel MR (2013) Food web structure within an estuary of the southern Gulf of St. Lawrence undergoing eutrophication. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 70:1805–1812
Song MY, Brown JJ (1998) Osmotic effects as a factor modifying insecticide toxicity on Aedes and Artemia. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 41:195–202
Steele DH, Steele VJ (1991) Effects of salinity on the survival, growth rate, and reproductive output of Gammarus lawrencianus (crustacea, amphipoda). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 78:49–56
Taylor LJ, Mann NS, Daoud D, Clark KF, van den Heuvel MR, Greenwood SJ (2019) Effects of sublethal chlorpyrifos exposure on postlarval american lobster (Homarus americanus). Environ Toxicol Chem 38:1294–1301
Xie WH, Shiu WY, Mackay D (1997) A review of the effect of salts on the solubility of organic compounds in seawater. Mar Environ Res 44:429–444
Xuereb B, Chaumot A, Mons R, Garric J, Geffard O (2009) Acetylcholinesterase activity in Gammarus fossarum (crustacea amphipoda). Intrinsic variability, reference levels, and a reliable tool for field surveys. Aquat Toxicol 93:225–233
Zeileis A (2006) Object-oriented computation of sandwich estimators. J Stat Softw 1:1–16
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Griffen Wakelin, Christina Pater, and a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC-SGTP 463277-14) grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knysh, K.M., Courtenay, S.C., Grove, C.M. et al. The Differential Effects of Salinity Level on Chlorpyrifos and Imidacloprid Toxicity to an Estuarine Amphipod. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 753–758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03157-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03157-z