Abstract
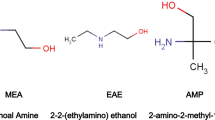
K2CO3 solution is widely used in the CO2-capture industry. In particular, it has advantages for treating CO2 in flue gas under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. However, it has a lower CO2-loading capacity and slower absorption kinetics than those of amines, which are its major disadvantages. Thus, in this study, we investigated ten loading-rate promoters, five primary amines and five secondary amines, to develop higher CO2-loading capacity and faster absorption kinetics. The screening tests of the absorption and desorption processes were conducted at 70 °C and 90 °C, respectively. Based on the results, we concluded that all the amines used improved the CO2-loading and absorption kinetics compared with the use of K2CO3 alone. At a certain value CO2 loading, the respective performance of the primary and secondary amines was twice and thrice better, respectively, than the neat K2CO3 solution. Thus, secondary amines had superior absorption capacity and absorption/desorption rate compared to primary amines. Among the secondary amines, pipecolic acid, sarcosine, and isonipecotic acid were determined as the most effective absorption rate promoters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IPCC, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, Chapters 1 and 2 (2001).
T. E. Rufford, S. Smart, G. C.Y. Watson, B. F. Graham, J. Boxall, J. C. DinizdaCosta and E. F. May, J. Petrol. Sci. Eng., 94–95, 123 (2012).
A. Aroonwilas and A. Veawab, Int. J. Greenh. Con., 2, 143 (2007).
M. Ismael, R. Sahnoun, A. Suzuki, M. Koyama, H. Tsuboi, N. Hatakeyama, A. Endou, H. Takaba, M. Kubo, S. Shimizu, C.A. Del Carpio and A. Miyamoto, Int. J. Greenh. Con., 5, 612 (2009).
R. Hook, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 36, 1779 (1997).
H. J. Song, S. Park, H. Kim, A. Gaur, J.W. Park and S. J. Lee, Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Con., 11, 64 (2012).
S. Lee, T. P. Filbern, M. Gray, J.W. Park and H. J. Song, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 47, 7419 (2008).
Y. E. Kim, J. H. Choi, S. C. Nam and Y. I. Yoon, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 50, 9306 (2011).
J. T. Cullinane and G. T. Rochelle, Chem. Eng. Sci., 59, 3619 (2004).
Y. Liang, D. P. Harrison, R. P. Gupta, D. A. Green and W. J. McMichael, Energy Fuel, 18, 569 (2004).
J.B. Lee, C. K. Ryu, J. I. Baek, J. H. Lee, T. H. Eom and S. H. Kim, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 47, 4465 (2008).
C. Zhao, X. Chen and C. Zhao, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 49, 12212 (2010).
S. C. Lee, B.Y. Choi, C.K. Ryu, Y. S. Ahn, T. J. Lee and J. C. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 23, 374 (2006).
D. M. Muñoz, A. F. Portugal, A. E. Lozano, J.G. De La Campa and J. De Abajo, Energy Environ. Sci., 2, 883 (2009).
S. Ma’mun, H. F. Svendsen, K. A. Hoff and O. Juliussen, Energy Convers. Manage., 48, 251 (2007).
P. Singh and G. F. Versteeg, Process Saf. Environ., 86, 347 (2008).
J. Van Holst, G. F. Versteeg, D.W. F. Brilman and J. A. Hogendoorn, Chem. Eng. Sci., 64, 59 (2009).
J. Oexmann, C. Hensel and A. Kather, Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Con., 2, 539 (2008).
F. Bougie, J. Lauzon-Gauthier and M. Iliuta, Chem. Eng. Sci., 64, 2011 (2009).
J.T. Cullinane and G.T. Rochelle, Chem. Eng. Sci., 54, 3619 (2004).
D. Wappel, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia (2006).
S. Bishnoi and G. T. Rochelle, Chem. Eng. Sci., 55, 5531 (2000).
J. Hetland and T. Christensen., Appl. Therm. Eng., 28, 2030 (2008).
Z. Tanga, W. Feia and Y. OLi, Energy Proc., 4, 307 (2011).
Y. Yonn, S. Nam, S. Jung and Y. Kim, Energy Proc., 4, 267 (2011).
H. Knuutila, O. Juliussen and H. F. Svendsen, Chem. Eng. Sci., 65, 2177 (2010).
J. T. Cullinane and G. T. Rochelle, Fluid Phase Equilib., 227, 197 (2005).
L. Sumin, M. Youguang, Z. Chunying and S. Shuhua, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 15, 842 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Song, HJ., Lee, MG. et al. Screening test for aqueous solvents used in CO2 capture: K2CO3 used with twelve different rate promoters. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 31, 125–131 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0200-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-013-0200-y