Abstract
Purpose of Review
The review provides an update on the diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE).
Recent Findings
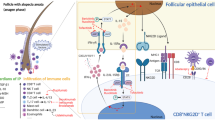
Diagnostic challenges exist in better defining CLE as an independent disease distinct from systemic lupus erythematosus with cutaneous features and further classifying CLE based on clinical, histological, and laboratory features. Recent mechanistic studies revealed more genetic variations, environmental triggers, and immunologic dysfunctions that are associated with CLE. Drug induction specifically has emerged as one of the most important triggers for CLE. Treatment options include topical agents and systemic therapies, including newer biologics such as belimumab, rituximab, ustekinumab, anifrolumab, and BIIB059 that have shown good clinical efficacy in trials.
Summary
CLE is a group of complex and heterogenous diseases. Future studies are warranted to better define CLE within the spectrum of lupus erythematosus. Better insight into the pathogenesis of CLE could facilitate the design of more targeted therapies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Hejazi EZ, Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: an update on pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2016;17:135–46.
Okon LG, Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2013;27:391–404.
Stannard JN, Kahlenberg JM. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: updates on pathogenesis and associations with systemic lupus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28:453–9.
Biazar C, Sigges J, Patsinakidis N, Ruland V, Amler S, Bonsmann G, et al. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: first multicenter database analysis of 1002 patients from the European Society of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (EUSCLE). Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:444–54.
•• Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, Brinks R, Mosca M, Ramsey-Goldman R, et al. European League against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1151–9. Comment: These are the latest guidelines for classification criteria.
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcon GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, et al. Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:2677–86.
Elman SA, Joyce C, Nyberg F, Furukawa F, Goodfield M, Hasegawa M, et al. Development of classification criteria for discoid lupus erythematosus: results of a Delphi exercise. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:261–7.
Samotij D, Szczech J, Kushner CJ, Mowla MR, Danczak-Pazdrowska A, Antiga E, et al. Prevalence of pruritus in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: brief report of a multicenter, multinational cross-sectional study. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3491798.
Albrecht J, Taylor L, Berlin JA, Dulay S, Ang G, Fakharzadeh S, et al. The CLASI (Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index): an outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;125:889–94.
Jolly M, Kazmi N, Mikolaitis RA, Sequeira W, Block JA. Validation of the Cutaneous Lupus Disease Area and Severity Index (CLASI) using physician- and patient-assessed health outcome measures. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:618–23.
Tebbe B, Orfanos C. Epidemiology and socioeconomic impact of skin disease in lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1997;6:96–104.
Durosaro O, Davis MD, Reed KB, Rohlinger AL. Incidence of cutaneous lupus erythematosus, 1965-2005: a population-based study. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:249–53.
Drenkard C, Parker S, Aspey LD, Gordon C, Helmick CG, Bao G, et al. Racial disparities in the incidence of primary chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus in the Southeastern US: the Georgia Lupus Registry. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71:95–103.
Petersen MP, Moller S, Bygum A, Voss A, Bliddal M. Epidemiology of cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the associated risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Lupus. 2018;27:1424–30.
Achtman JC, Werth VP. Pathophysiology of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:182.
Wenzel J. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: new insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:519–32.
Osmola A, Namysl J, Jagodzinski PP, Prokop J. Genetic background of cutaneous forms of lupus erythematosus: update on current evidence. J Appl Genet. 2004;45:77–86.
Fischer GF, Pickl WF, Fae I, Anegg B, Milota S, Volc-Platzer B. Association between chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus and HLA class II alleles. Hum Immunol. 1994;41:280–4.
Pickering MC, Fischer S, Lewis MR, Walport MJ, Botto M, Cook HT. Ultraviolet-radiation-induced keratinocyte apoptosis in C1q-deficient mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:52–8.
Werth VP, Zhang W, Dortzbach K, Sullivan K. Association of a promoter polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and distinct photoregulation of transcription. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:726–30.
Jarvinen TM, Hellquist A, Koskenmies S, Einarsdottir E, Koskinen LL, Jeskanen L, et al. Tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 polymorphisms are associated with discoid and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:123–31.
Kunz M, Konig IR, Schillert A, Kruppa J, Ziegler A, Grallert H, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Exp Dermatol. 2015;24:510–5.
Renauer P, Coit P, Jeffries MA, Merrill JT, McCune WJ, Maksimowicz-McKinnon K, et al. DNA methylation patterns in naive CD4+ T cells identify epigenetic susceptibility loci for malar rash and discoid rash in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci Med. 2015;2:e000101.
Furukawa F, Itoh T, Wakita H, Yagi H, Tokura Y, Norris DA, et al. Keratinocytes from patients with lupus erythematosus show enhanced cytotoxicity to ultraviolet radiation and to antibody-mediated cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999;118:164–70.
Toberer F, Sykora J, Gottel D, Hartschuh W, Werchau S, Enk A, et al. Apoptotic signal molecules in skin biopsies of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: analysis using tissue microarray. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:656–9.
Bashir MM, Sharma MR, Werth VP. UVB and proinflammatory cytokines synergistically activate TNF-alpha production in keratinocytes through enhanced gene transcription. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:994–1001.
Kahlenberg JM, Thacker SG, Berthier CC, Cohen CD, Kretzler M, Kaplan MJ. Inflammasome activation of IL-18 results in endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2011;187:6143–56.
Wang D, Drenker M, Eiz-Vesper B, Werfel T, Wittmann M. Evidence for a pathogenetic role of interleukin-18 in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:3205–15.
Nakamura K, Jinnin M, Kudo H, Inoue K, Nakayama W, Honda N, et al. The role of PSMB9 upregulated by interferon signature in the pathophysiology of cutaneous lesions of dermatomyositis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2016;174:1030–41.
Wenzel J, Worenkamper E, Freutel S, Henze S, Haller O, Bieber T, et al. Enhanced type I interferon signalling promotes Th1-biased inflammation in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Pathol. 2005;205:435–42.
Fredi M, Cavazzana I, Quinzanini M, Taraborelli M, Cartella S, Tincani A, et al. Rare autoantibodies to cellular antigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2014;23:672–7.
Ioannides D, Golden BD, Buyon JP, Bystryn J-C. Expression of SS-A/Ro and SS-B/La antigens in skin biopsy specimens of patients with photosensitive forms of lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:340–6.
• He Y, Sawalha AH. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus: an update on drugs and mechanisms. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30:490–7. Comment: Drug induced lupus is a common, and commonly overlooked, entity and should be recognized. Many common medications are implicated.
Gronhagen CM, Fored CM, Linder M, Granath F, Nyberg F. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and its association with drugs: a population-based matched case-control study of 234 patients in Sweden. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:296–305.
Marano AL, Clarke JM, Morse MA, Shah A, Barrow W, Selim MA, et al. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and dermatomyositis associated with anti-programmed cell death 1 therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181:580–3.
Liu RC, Sebaratnam DF, Jackett L, Kao S, Lowe PM. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus induced by nivolumab. Australas J Dermatol. 2018;59:e152–4.
Michot JM, Fusellier M, Champiat S, Velter C, Baldini C, Voisin AL, et al. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus following immunotherapy with anti-programmed death-(ligand) 1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:e67.
Tarazi M, Aiempanakit K, Werth VP. Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus associated with abatacept. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:698–700.
Tierney E, Kirthi S, Ramsay B, Ahmad K. Ustekinumab-induced subacute cutaneous lupus. JAAD Case Rep. 2019;5:271–3.
Wehrmann C, Sondermann W, Korber A. Secukinumab-induced subacute-cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Hautarzt. 2018;69:64–6.
Borucki R, Werth VP. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus induced by drugs - novel insights. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2019:1–8.
Irizarry-Caro JA, Carmona-Rivera C, Schwartz DM, Khaznadar SS, Kaplan MJ, Grayson PC. Brief report: drugs implicated in systemic autoimmunity modulate neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70:468–74.
• Fairley JL, Oon S, Saracino AM, Nikpour M. Management of cutaneous manifestations of lupus erythematosus: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019; Comment: Recent extensive review of treatment options.
Company-Quiroga J, Alique-Garcia S, Romero-Mate A. Current insights into the management of discoid lupus erythematosus. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019;12:721–32.
Wang X, Zhang L, Luo J, Wu Z, Mei Y, Wang Y, et al. Tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in labial discoid lupus erythematosus: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;55:1221–8.
Pothinamthong P, Janjumratsang P. A comparative study in efficacy and safety of 0.1% tacrolimus and 0.05% clobetasol propionate ointment in discoid lupus erythematosus by modified cutaneous lupus erythematosus disease area and severity index. J Med Assoc Thail. 2012;95:933–40.
Barikbin B, Givrad S, Yousefi M, Eskandari F. Pimecrolimus 1% cream versus betamethasone 17-valerate 0.1% cream in the treatment of facial discoid lupus erythematosus: a double-blind, randomized pilot study. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:776–80.
Kuhn A, Gensch K, Haust M, Schneider SW, Bonsmann G, Gaebelein-Wissing N, et al. Efficacy of tacrolimus 0.1% ointment in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:54–64 64.e51–52.
Tzung TY, Liu YS, Chang HW. Tacrolimus vs. clobetasol propionate in the treatment of facial cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a randomized, double-blind, bilateral comparison study. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:191–2.
Kuhn A, Ruland V, Bonsmann G. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: update of therapeutic options part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:e179–93.
Kuhn A, Aberer E, Bata-Csorgo Z, Caproni M, Dreher A, Frances C, et al. S2k guideline for treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus - guided by the European Dermatology Forum (EDF) in cooperation with the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:389–404.
Wozniacka A, Carter A, McCauliffe DP. Antimalarials in cutaneous lupus erythematosus: mechanisms of therapeutic benefit. Lupus. 2002;11:71–81.
Torigoe M, Sakata K, Ishii A, Iwata S, Nakayamada S, Tanaka Y. Hydroxychloroquine efficiently suppresses inflammatory responses of human class-switched memory B cells via Toll-like receptor 9 inhibition. Clin Immunol. 2018;195:1–7.
Yokogawa N, Eto H, Tanikawa A, Ikeda T, Yamamoto K, Takahashi T, et al. Effects of Hydroxychloroquine in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69:791–9.
Chasset F, Arnaud L, Jachiet M, Monfort JB, Bouaziz JD, Cordoliani F, et al. Changing antimalarial agents after inefficacy or intolerance in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a multicenter observational study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:107–114.e101.
Kishi C, Motegi S-i, Yasuda M, Ishikawa O. Therapeutic efficacy and adverse events of hydroxychloroquine administration in Japanese systemic/cutaneous lupus erythematosus patients. J Dermatol. 2018;45:1020–2.
Mok CC, Penn HJ, Chan KL, Tse SM, Langman LJ, Jannetto PJ. Hydroxychloroquine serum concentrations and flares of systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal cohort analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68:1295–302.
Ugarte A, Porta S, Ríos R, Martinez-Zapico A, Ortego-Centeno N, Agesta N, et al. Combined mepacrine–hydroxychloroquine treatment in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and refractory cutaneous and articular activity. Lupus. 2018;27:1718–22.
Marmor MF, Kellner U, Lai TY, Melles RB, Mieler WF. Recommendations on screening for chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine retinopathy (2016 Revision). Ophthalmology. 2016;123:1386–94.
Wenzel J, Brahler S, Bauer R, Bieber T, Tuting T. Efficacy and safety of methotrexate in recalcitrant cutaneous lupus erythematosus: results of a retrospective study in 43 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:157–62.
Islam MN, Hossain M, Haq SA, Alam MN, Ten Klooster PM, Rasker JJ. Efficacy and safety of methotrexate in articular and cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012;15:62–8.
Sadlier M, Kirby B, Lally A. Mycophenolate mofetil and hydroxychloroquine: an effective treatment for recalcitrant cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:160–1 author reply 161-162.
Gammon B, Hansen C, Costner MI. Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in antimalarial-resistant cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:717–721.e712.
Kreuter A, Tomi NS, Weiner SM, Huger M, Altmeyer P, Gambichler T. Mycophenolate sodium for subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus resistant to standard therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:1321–7.
Cipriani P, Ruscitti P, Carubbi F, Liakouli V, Giacomelli R. Methotrexate: an old new drug in autoimmune disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2014;10:1519–30.
Velo-Garcia A, Ntatsaki E, Isenberg D. The safety of pharmacological treatment options for lupus nephritis. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15:1041–54.
Cortés-Hernández J, Torres-Salido M, Castro-Marrero J, Vilardell-Tarres M, Ordi-Ros J. Thalidomide in the treatment of refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus: prognostic factors of clinical outcome. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:616–23.
Wang D, Chen H, Wang S, Zou Y, Li J, Pan J, et al. Thalidomide treatment in cutaneous lesions of systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter study in China. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35:1521–7.
Kyriakis KP, Kontochristopoulos GJ, Panteleos DN. Experience with low-dose thalidomide therapy in chronic discoid lupus erythematosus. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39:218–22.
Ordi-Ros J, Cortes F, Cucurull E, Mauri M, Bujan S, Vilardell M. Thalidomide in the treatment of cutaneous lupus refractory to conventional therapy. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:1429–33.
Cesbron E, Bessis D, Jachiet M, Lipsker D, Cordel N, Bouaziz J-D, et al. Risk of thromboembolic events in patients treated with thalidomide for cutaneous lupus erythematosus: a multicenter retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:162–5.
Frankel HC, Sharon VR, Vleugels RA, Merola JF, Qureshi AA. Lower-dose thalidomide therapy effectively treats cutaneous lupus erythematosus but is limited by neuropathic toxicity. Inter J Dermatol. 2013;52:1407–9.
Baret I, De Haes P. Thalidomide: still an important second-line treatment in refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus? J Dermatol Treat. 2015;26:173–7.
Tseng S, Pak G, Washenik K, Pomeranz MK, Shupack JL. Rediscovering thalidomide: a review of its mechanism of action, side effects, and potential uses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;35:969–79.
Braunstein I, Goodman NG, Rosenbach M, Okawa J, Shah A, Krathen M, et al. Lenalidomide therapy in treatment-refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus: histologic and circulating leukocyte profile and potential risk of a systemic lupus flare. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:571–82.
Cortés-Hernández J, Ávila G, Vilardell-Tarrés M, Ordi-Ros J. Efficacy and safety of lenalidomide for refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:R265.
Okon L, Rosenbach M, Krathen M, Rose M, Propert K, Okawa J, et al. Lenalidomide in treatment-refractory cutaneous lupus erythematosus: efficacy and safety in a 52-week trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:583–4.
Fennira F, Chasset F, Soubrier M, Cordel N, Petit A, Francès C. Lenalidomide for refractory chronic and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus: 16 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1248–51.
Kindle SA, Wetter DA, Davis MDP, Pittelkow MR, Sciallis GF. Lenalidomide treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus: the Mayo Clinic experience. Inter J Dermatol. 2016;55:e431–9.
van Vollenhoven RF, Hahn BH, Tsokos GC, Wagner CL, Lipsky P, Touma Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, an IL-12 and IL-23 inhibitor, in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a multicentre, double-blind, phase 2, randomised, controlled study. Lancet. 2018;392:1330–9.
Furie R, Khamashta M, Merrill JT, Werth VP, Kalunian K, Brohawn P, et al. Investigators ftCS: Anifrolumab, an anti–interferon-α receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69:376–86.
Furie R, Werth VP, Merola JF, Stevenson L, Reynolds TL, Naik H, et al. Monoclonal antibody targeting BDCA2 ameliorates skin lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:1359–71.
Werth VP, Fiorentino D, Sullivan BA, Boedigheimer MJ, Chiu K, Wang C, et al. Brief report: pharmacodynamics, safety, and clinical efficacy of AMG 811, a human anti–interferon-γ antibody, in patients with discoid lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69:1028–34.
Szepietowski JC, Nilganuwong S, Wozniacka A, Kuhn A, Nyberg F, van Vollenhoven RF, et al. Phase I, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple intravenous, dose-ascending study of sirukumab in cutaneous or systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2661–71.
Stohl W, Schwarting A, Okada M, Scheinberg M, Doria A, Hammer AE, et al. Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: a fifty-two–week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69:1016–27.
Iaccarino L, Bettio S, Reggia R, Zen M, Frassi M, Andreoli L, et al. Effects of belimumab on flare rate and expected damage progression in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res. 2017;69:115–23.
Parodis I, Gomez A, Frodlund M, Jonsen A, Zickert A, Sjowall C, et al. Smoking reduces the efficacy of belimumab in mucocutaneous lupus. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18:911–20.
Quelhas da Costa R, Aguirre-Alastuey ME, Isenberg DA, Saracino AM. Assessment of response to B-cell depletion using rituximab in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1432–40.
Vital EM, Wittmann M, Edward S, Md Yusof MY, MacIver H, Pease CT, et al. Brief report: responses to rituximab suggest B cell–independent inflammation in cutaneous systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2015;67:1586–91.
Hofmann S, Leandro M, Morris S, Isenberg D. Effects of rituximab-based B-cell depletion therapy on skin manifestations of lupus erythematosus – report of 17 cases and review of the literature. Lupus. 2013;22:932–9.
Lowe GC, Henderson CL, Grau RH, Hansen CB, Sontheimer RD. A systematic review of drug-induced subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164:465–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Autoimmunity
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petty, A.J., Floyd, L., Henderson, C. et al. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: Progress and Challenges. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 20, 12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-020-00906-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-020-00906-8