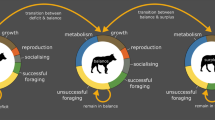
This paper addresses some of the ethical and welfare considerations implicit in the application of general techniques in common use during the course of collecting data in ecological field work. Even if they are not explicitly constructed as manipulative experiments, many field studies involve some degree of intervention during routine monitoring programmes: through disturbance caused merely by the presence of an observer or where specific sampling techniques themselves involve capture, handling and marking. Such interventive techniques may cause discomfort, distress or loss of fitness, even in the extreme may result in incidental mortality — and the ethical scientist should critically evaluate the implications of each methodology before adopting any procedure. The paper reviews by way of example the types of objective information now available for both small and larger mammals in relation to: (i) distress and mortality during capture operations; (ii) mortality or distress caused at the time by marking; (iii) longer-term consequences of handling and marking in terms of subsequent [delayed] mortality or loss of fitness, before considering a formal framework for assessment of costs and benefits of any given field programme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D.W. and Keith, J.O. (1980) The human influence on seabird nesting success: conservation implications Biol. Conserv. 18, 65–80.
Association for the Study of Animal Behaviour (1981) Guidelines for the use of animals in research. Animal Behaviour 29, 1–2.
Bateson, P. (1991) Assessment of pain in animals. Animal Behaviour 42, 827–39.
Bellairs, A. d'A. and Bryant, S.V. (1968) Effects of amputation of limbs and digits of lacertid lizards. Anat. Rec. 161 489–96.
Bender, E.A., Case, T.J. and Gilpin, M.E. (1984) Perturbation experiments in community ecology; theory and practice. Ecology 65, 1–13.
Blanc, C.P. and Carpenter, C.C. (1969) Studies on the Iguanidae of Madagascar. III. Social and reproductive behaviour of Chalarodon madagascariensis. J. Herpetol. 3, 125–34.
Broom, D.M. and Johnson, K.G. (1994) Stress and Animal Welfare. London: Chapman & Hall.
Calvo, B. and Furness, R.W. (1992) A review of the use and the effects of marks and devices on birds. Ringing and Migration 13, 129–51.
Chalmers, G.A. and Barrett, M.W. (1982) Capture myopathy. In Non-infectious Diseases in Wildlife (G.L., Hoff and J.W., Davies, eds.) pp. 84–94. Ames, IA: Iowa State University Press.
Chapman, N.G., Claydon, K., Claydon, M. and Harris, S. (1987) Techniques for the safe and humane capture of free-living muntjac deer (Muntiacus reevesi). Brit. Vet. J. 143, 35–43.
Cockburn, R.H.A. (1976) Catching roe deer alive in long-nets. Deer 3, 434–40.
Cooper, M.E. (1987) An Introduction to Animal Law. London: Academic Press.
Cooper, M.E. (1991) British Mammals and the law. In The Handbook of British Mammals, 3rd edn (G.B., Corbet and S., Harris, eds.) pp. 24–34. Oxford: Blackwell.
Crowell, K.L. and Pimm, S.L. (1976) Competition and niche shifts of mice introduced onto small islands. Oikos 27, 251–8.
Cuthill, I.C. (1990) Field experiments in animal behaviour: methods and ethics. Animal Behaviour 42, 1007–14.
Daugherty, C.H. (1976) Freeze-branding as a technique for marking anurans. Copeia 4, 836–8.
Dawkins, M.S. (1980) Animal Suffering: the Science of Animal Welfare London: Chapman & Hall.
Dawkins, M.S. (1990) From an animal's point of view: motivation, fitness and animal welfare. Behav. Brain Sci. 13, 1–61.
Dawkins, M.S. and Gosling, M. (1992) Ethics in Research on Animal Behaviour. London: Association for the Study of Animal Behaviour/Academic Press.
Diamond, J.M. (1983) Laboratory field and natural experiments. Nature 304, 586–7.
Diamond, J.M., Pimm, S.L., Gilpin, M.E. and LeCroy, M. (1989) Rapid evolution of character displacement in myzomelid honeyeaters. Am. Nat. 134, 675–708.
Duffy, D.C. (1979) Human disturbance and breeding birds. Auk 96, 815–16.
Fairley, J.S. (1982) Short term effects of ringing and toe-clipping on recaptures of woodmice. J. Zool. 197, 295–7.
Farnsworth, E.J. and Rosovsky, J. (1993) The ethics of ecological field experimentation. Conserv. Biol. 7, 463–72.
Ferner, J.W. (1979) A review of marking techniques for amphibians and reptiles. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles; Herpetological Circular 9, 1–41.
Freddy, D.J., Bronaugh, W.M. and Fowler, M.C. (1986) Responses of mule deer to persons afoot and snowmobiles. Wildlife Society Bulletin 14, 63–8.
Fullagar, P.J. and Jewell, P.A. (1965) Marking small rodents and the difficulties of using leg rings. J. Zool. 147, 224–8.
Greenwood, J.J.D. (1994) Research on wild birds: ethical issues of ringing. Proceedings of the International Ornithological Congress, Vienna.
Gurnell, J. and Flowerdew, J.R. (1982) Live Trapping Small Mammals — a Practical Guide. London: Occasional Publications of the Mammal Society.
Haarthorn, A.M., van der, Walt, K. and Young, E. (1976) Possible therapy for capture myopathy in captured wild animals. Nature 247, 577.
Hairston, N.G. (1980) The experimental test of an analysis of field distributions: competition in terrestrial salamanders. Ecology 61, 817–26.
Harrington, R. (1991) Guidelines for the capture and handling of deer. In Methods For the Study of Large Mammals in Forest Ecosystems (G.W.T.A., Groot Bruinderink and S.E.van, Wieren, eds.) pp. 74–87. Arnhem, The Netherlands: Rijksinstituut voor Natuurbeheer.
Hill, S.D. (1985) Influences of large herbivores on small rodents in the New Forest, Hampshire. PhD thesis University of Southampton.
Huntingford, F.A. (1984) Some ethical issues raised by studies of predation and aggression. Animal Behaviour 32, 210–15.
Jeppesen, J.L. (1987) The disturbing effects of orienteering and hunting on roe deer (Capreolus capreolus). Danish Rev. Game Biol. 13, 1–24.
Jones, D.M. (1984) The capture and handling of deer. In The Capture and Handling of Deer (A.J.B., Rudge, ed.) pp. 34–85. Peterborough: Nature Conservancy Council.
Jones, A.R. and Price, S.E. (1992) Measuring the responses of fallow deer to disturbance. In Biology of deer (R.D., Brown. ed.) pp. 211–16. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Kania, W. (1992) Safety of catching adult European birds at the nest. The Ring 14, 5–50.
Kellert, S.R. (1991) Japanese perceptions of wildlife. Conserv. Biol. 5, 297–308.
Kenward, R.E. (1987) Wildlife Radio Tagging: Equipment, Field Techniques and Data Analysis. London, New York: Academic Press.
Moulton, M.P. and Pimm, S.L. (1983) The introduced Hawaiian avifauna: biogeographic evidence for competition. Am. Nat. 121, 669–90.
Moulton, M.P. and Pimm, S.L. (1986) The extent of competition in shaping an introduced avifauna. In Community Ecology (J.M., Diamond and T.J., Case, eds) pp. 80–97. New York: Harper and Row.
Ozoga, J.J. and Clute, R.K. (1988) Mortality rates of marked and unmarked fawns. J. Wildlife Manag. 52, 549–51.
Paine, R.T. (1966) Food web complexity and species diversity. Am. Nat. 100, 65–75.
Paine, R.T. (1969) A note on trophic complexity and community stability. Am. Nat. 103, 91–3.
Putman, R.J. (1990) The care and rehabilitation of injured wild deer. Deer 8, 31–5.
Putman, R.J. and Langbein, J. (1992) Behavioural responses of park red and fallow deer to disturbance and effects on population performance. Animal Welfare 1, 19–38.
Simon, C.A. and Bessinger, B.E. (1983) Paint marking lizards: does it affect survival? J. Herpetol. 17, 184–6.
Smith, R.H. (1980) The capture of deer for radio-tagging. In A Handbook on Biotelemetry and Radiotracking (C.J., Amlaner and D.W., Macdonald, eds) pp. 313–17. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Smith, J. and Boyd, K. (1991) Lives in the Balance: the Ethics of Using Animals in Biomedical Research. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Smith, R.F. and Dobson, H. (1990) Effects of preslaughter experience on behaviour, plasma cortisol and muscle pH in farmed red deer Vei. Rec. 126, 155–8.
Southern, H.N., ed. (1964) The Handbook of British Mammals, 1st edn, Oxford: Blackwell.
Spellerberg, I.F. (1977) Marking live snakes for identification of individuals in population studies. J. App. Ecol. 14, 137–8.
Strauss, S.Y. (1991) Indirect effects in community ecology: their definition, study and importance. Trends Ecol. Evol. 6, 206–10.
Strong, D.R., Simberloff, D., Abele, L.G. and Thistle, A.B. (1984) Ecological Communities: Conceptual Issues and the Evidence. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Sullivan, J.B., De, Young, C.A., Beasom, S.L., Heffelfinger, J.R., Coughlin, S.P. and Hellickson, M.W. (1991) Drive-netting deer-incidence of mortality. Wildlife Society Bulletin 19, 393–6.
Swingland, I.R. (1978) Marking reptiles. In Animal Marking: Recognition Marking of Animals in Research (B., Stonehouse, ed) pp. 119–41. London: Academic Press.
Twigg, G.I. (1975) Marking mammals. Mammal Rev. 5, 101–16.
Tyler, N.J.C. (1991) Short-term responses of Svalbard reindeer to direct provocation by a snowmobile. Biol. Conserv. 56, 179–94.
van der, Zande, A.N., Berkhuizen, J.C., van, Latesteijn, H.C., ter, Keurs, W.J. and Poppelaars, A.J. (1984) Impact of outdoor recreation on the density of a number of breeding bird species in woods adjacent to urban residential areas. Biol. Conserv. 30, 1–39.
White, G.C. and Garrott, R.A. (1990) Analysis of Wildlife Tracking Data. London, New York: Academic Press.
Wiens, J.A. (1989) The Ecology of Bira Communities, Volume 2: Processes and Variations. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wiepkema, P.R. and Koolhaas, J.M. (1992) Stress and animal welfare. Animal Welfare 2, 195–218.
Williams, T.D., Cooke, F., Cooch, E.G. and Rockwell, R.F. (1993). Body condition and gosling survival in mass-banded Lesser Snow geese. J. Wildlife Manag. 57, 555–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Putman, R.J. Ethical considerations and animal welfare in ecological field studies. Biodivers Conserv 4, 903–915 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00056197
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00056197