Abstract
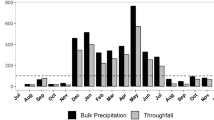
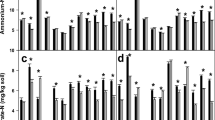
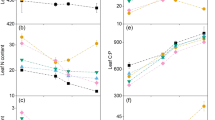
Lysimeter experiments were used to determine atmospheric input to grassland canopies. The combined effect of interception deposition + mineral weathering + mineralization was calculated from input/output budgets. Four types of lysimeters were used, either filled with very pure quartz sand or chalk grassland soil, and either without vegetation or planted with Brachypodium pinnatum (L.) Beauv., Combination of budgets for these four types of lysimeters yielded separate estimates of interception deposition and mineral weathering + mineralization. Ratios between total deposition and bulk deposition were 1.74 and 1.93 for N and S, respectively. Sources and sinks of H+ for lysimeters with chalk grassland soil and planted with Brachypodium (abbrev. CP-lysimeters) were about 10 times larger than for lysimeters without plants and filled with quartz sand. The contribution of atmospheric input to total H+-sources was 80% for bare lysimeters filled with quartz sand, and only 12% for CP-lysimeters. Bulk deposition and total atmospheric deposition of N was 1.25 and 2.18 kmol ha−1 yr−1, respectively, whereas N mineralization of chalk grassland soil yielded 1.62 kmol ha−1 yr−1, ‘Acid rain’ has only a minor influence on H+-transformations within a chalk grassland ecosystem, but N cycling is seriously affected by atmospheric input.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts, R.: 1989, Oikos 56, 31.
Baldocchi, D. D., Hicks, B. B., and Meyers, T. P.: 1988, Ecology 69, 1331.
Bartnicki, J. and Alcamo, J.: 1989, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 47, 101.
Berendse, F. and Aerts, R.: 1984, Acta Oecol./Oecol. Plant 19, 3.
Bobbink, R., Bik, L., and Willems, J. H.: 1988, Acta Botanica Neerlandica 37, 231.
Bobbink, R. and Willems, J. H.: 1987, Biological Conservation 40, 301.
Buijsman, E., Maas, M., and Asman, W. A. H.: 1984, Report V84-20 IMOU
Clark, F. E., Cole, C. V., and Bowman, R. A.: 1980, in Breymeyer, A. I. and Van Duyne, G. M. (eds.), Grasslands, Systems Analysis and Man, Chapter 8: Nutrient cycling. Cambridge University Press.
Colbourn, P., Harper, I. W., and Igbal, M. M.: 1984, J. Soil Sci. 35, 539.
Dowdell, R. J.: 1982, Phil. Trans. Royal Soc., London B296, 363.
Draaijers, G. P. J., Ivens, W. P. M. F., Bos, M. M., and Bleuten, W.: 1989, Environ. Pollut. 60, 55.
Garland, J. A.: 1981, Atmosph. Environm. 15, 787.
Gilliam, F. S.: 1987, Biogeochemistry 4, 203.
Heil, G. W., Werger, M. J. A., de Mol, W., van Dam, D., and Heijne, B.: 1988, Science 239, 764.
Jones, M. B., Delwiche, C. C., and Williams, W. A.: 1977, Agronomy J. 69, 1019.
Kühn, H. and Weller, H.: 1977, Z. Pfanzenernähr. Bodenk. 140, 431.
Mallant, R. K. A. M., ten Brink, H. M., Kos, G. P. A., and de Vate, J. F.: 1983, in Adema, E. H. and van Ham, J. (eds.), Zure Regen: Oorzaken, Effecten en Beleid. Proc. Symp. 17, 18, Nov. 1983, 's-Hertogenbosch.
Minderman, G. and Leeflang, K. W. F.: 1968, Plant and Soil 28, 61.
Mulder, J., van Breemen, N., and Eijck, H. C.: 1989, Nature 337, 247.
Mulder, J., van Dobben, H. F., de Visser, P. B., Booltink, H. W. G., and van Breemen, N.: 1987, Proc. UNESCO-IHP Symp. Acidification and Water Pathways, Vol. 1, Norw. Nat. Committee for Hydrology, Oslo, Norway, pp. 79–89.
Owens, L. D.: 1960, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 24, 372.
Parker, G. G.: 1983, Adv. Ecol. Res. 13, 58.
RIVM: 1986, 1987, 1988, Landelijk Meetnet Luchtkwaliteit. Report nrs. 22802002, 228702006, 228702010, National Institute for Public Health and Environmental Protection, Bilthoven, The Netherlands.
Schneider, T. and Bresser, A. H. M.: 1988, ‘Dutch Priority Programme on Acidification’, Report nr.0006, National Institute for Public Health and Environmental Protection.
Stuyfzand, P. J.: 1984, H 2O17, 152.
van Breemen, N., de Visser, P. H. B., and van Grinsven, J. J. M.: 1986, J. Geol. Soc. London 143, 659.
van Breemen, N., Driscoll, C. T., and Mulder, J.: 1984, Nature 307, 599.
van Breemen, N., Mulder, J., and van Grinsven, J. J. M.: 1987, J. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. 51, 1634.
van Breemen, N., Visser, W. F. J., and Pape, Th.: 1988: Biogeochemistry of a Forested Ecosystem, Agricultural Research Reports 930, Pudoc, Wageningen.
van Dam, D., Heil, G. W., Bobbink, R., and Heijne, B.: 1989, in Brasser, L. J. and Mulder, W. C. (eds.), Man andHisEcosystem, Proc. 8th World Clean Air Congress, The Netherlands, 11–15 September 1989. Vol. 2, 201.
van Dam, D. and Heil, G. W.: 1986, Proc. 7th World Clean Air Congress, Sydney, Australia. 25–29 August 1986. Vol.5, 16.
van Dam, D., Heil, G. W., Bobbink, R., and Heijne, B. 1990a, Biogeochemistry 9, 19.
van Dam, D., Heil, G. W., Bobbink, R., and Heijne, B. 1990b, Oecologia (Berl.), submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Dam, D., Heil, G.W., Bobbink, R. et al. Atmospheric deposition to grassland canopies: Lysimeter budgets discriminating between interception deposition, mineral weathering and mineralization. Water Air Soil Pollut 53, 83–101 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154993
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154993