Summary
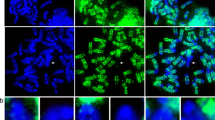
Three different long-arm X isochromosomes and an isodicentric X chromosome were examined by in situ hybridization with X-chromosome-specific α-satellite probes and by quantitation of Southern blots hybridized with proximal short-arm probes. Each chromosome had a unique pericentromeric structure. The isodicentric X chromosome was clearly dicentric, showing two distinct α-satellite hybridization signals and duplication of short-arm material. Two isochromosomes showed a larger than normal, bifid α-satellite signal and also had duplications of different extents of short-arm material. The third X isochromosome could not be distinguished from a classical long-arm isochromosome; it did not have a short-arm duplication and it had a single α-satellite signal. These data indicate that rearrangements responsible for X isochromosome formation can occur at numerous locations in the pericentromeric region and that some X isochromosomes may involve duplications of substantial portions of the short arm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgaonkar DS (1973) An X,isochromosome X (long arm),46 chromosomes. Cytogenetics 12:372
Callen DF, Mulley JC, Baker EG, Sutherland GR (1987) Determining the origin of human X isochromosomes by use of DNA sequence polymorphisms and detection of an apparent i(Xq) with Xp sequences. Hum Genet 77:236–240
Chapelle A de la, Stenstrand K (1974) Dicentric human X chromosomes. Hereditas 76:259–268
Chapelle A de la, Wennström J, Hortling H, Ockey CH (1966) Isochromosome X in man. I. Hereditas 54:260–276
Cohen MM, Rosenmann A, Hacham-Zadeh S, Dahan S (1975) Dicentric X-isochromosome (Xqi dic) and pericentric inversion of no. 2 {inv(2)(p15 q21}) in a patient with gonadal dysgenesis. Clin Genet 8:11–17
Darlington CD (1939) Misdivision and the genetics of the centromere. J Genet 37:341–364
Dewald GW (1983) Isodicentric X chromosomes in humans: origin, segregation behavior, and replication band patterns. In: Sandberg AA (ed) Cytogenetics of the mammalian X chromosome, part A: Basic mechanisms of X chromosome behavior. Liss, New York, pp 405–426
Harbison M, Hassold T, Kobryn C, Jacobs PA (1988) Molecular studies of the parental origin and nature of human X isochromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 47:217–222
Hilliker AJ, Holm DG (1975) Genetic analysis of the proximal region of chromosome 2 of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Detachment of compound autosomes. Genetics 81:705–721
Holm DG (1975) Compound autosomes. In: Novitski E, Ashburner M (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila, vol 1b. Academic Press, New York London, pp 529–561
Hook EB, Warburton D (1983) The distribution of chromosomal genotypes associated with Turner's syndrome: livebirth prevalence rates and evidence for diminished fetal mortality and severity in genotypes associated with structural X abnormalities or mosaicism. Hum Genet 64:24–27
Hsu YF, Paciuc S, David K, Cristian S, Moloshok R, Hirschhorn K (1978) Number of C-bands of human isochromosome Xqi and relation to 45,X mosaicism. J Med Genet 15:222–226
Hurst J, Flavell D, Juelien J-P, Meijer D, Mushynski W, Grosveld F (1987) The human neurofilament gene (NEFL) is located on the short arm of chromosome 8. Cytogenet Cell Genet 45:30–32
Mandel J-L, Willard HF, Nussbaum RL, Romeo G, Puck JM, Davies KE (1989) Report of the committee of the genetic constitution of the X chromosome. (10th International Workshop on Human Gene Mapping) Cytogenet Cell Genet 51:384–437
Manuelidis L (1978) Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma 66:23–32
Masumoto H, Sugimoto K, Okazaki T (1989) Alphoid satellite DNA is tightly associated with centromere antigens in human chromosomes throughout the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res 181:181–196
Mitchell AR, Gosden JR, Miller DA (1985) A cloned sequence, p82H, of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromsomes. Chromosoma 92:369–377
Palmer CG, Reichmann A (1976) Chromosomal and clinical findings in 110 females with Turner syndrome. Hum Genet 35:35–49
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2934–2938
Schmid W, Naef E, Mürset G, Prader A (1974) Cytogenetic findings in 89 cases of Turner's syndrome with abnormal karyotypes. Humangenetik 24:93–104
Simpson JL (1976) Disorders of sexual differentiation. Academic Press, New York London
Therman E, Trunca C, Kuhn EM, Sarto GE (1986) Dicentric chromosomes and the inactivation of the centromere. Hum Genet 72:191–195
Willard HF (1983) Replication of human X chromosomes in fibroblasts and somatic cell hybrids: Cytogenetic analysis and a molecular perspective. In: Sandberg AA (ed) Cytogenetics of the mammalian X chromosome, part A: Basic mechanisms of X chromosome behavior. Liss, New York, pp 427–448
Willard HF (1985) Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. Am J Hum Genet 37:524–532
Willard HF (1990) Molecular cytogenetics of centromeres of human chromosomes. Chromosomes Today 10 (in press)
Willard HF, Smith KD, Sutherland J (1983) Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res 11:2017–2033
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharp, C.B., Bedford, H.M. & Willard, H.F. Pericentromeric structure of human X “isochromosomes”: evidence for molecular heterogeneity. Hum Genet 85, 330–336 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206757
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206757