Summary
-
1.
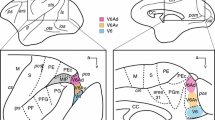
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was injected within the proximal limb and trunk representation zones of the first somatosensory area (SI) of 16 cats. The tangential and laminar distributions of retrogradely labelled neurones (callosal neurones) of the contralateral homotopic cortex were studied. This cortex was explored with microelectrodes on the day after HRP delivery to relate the distribution of callosal neurones to the electrophysiological map of the trunk.
-
2.
Callosal neurones were found in the contralateral SI area mainly in layer III, but also many in layer VI, especially following large HRP injections, and very few in the other layers. Callosal neurones of layer III were mostly pyramidal, those of layer VI pyramidal and non-pyramidal. Many neurones were intensely stained by HRP, and cell details, such as fine dendritic branchings, spines, and axon collaterals, could be seen.
-
3.
Callosal neurones are grouped within two regions located, respectively, in the rostral and caudal parts of the exteroceptive trunk map. The rostral region overlaps the representation of the dorsal midline (cytoarchitectonic field 3b) and the second one that of the ventral body midline (cytoarchitectonic field 2). The cortex intermediate between these two fields contains rare callosal cells and receives afferences from the lateral trunk surface. Few or no callosal cells were found within the proximal limb zones. Neurones recorded from the two midline zones have bilateral receptive fields straddling either the back or the ventral surface of the trunk.
-
4.
It is concluded that the interhemispheric fusion between the two hemibody representations in areas SI is brought about by the mutual callosal links which the two midline zones entertain with their contralateral homologues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J C (1977) Technical considerations in the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neurosci Abstr 2: 141
Barbaresi P, Bellardinelli E, Caminiti R, Manzoni T (1978) Analisi microelettrodica della rappresentazione corporea nell'area SI del gatto. Abstr XXX Ital Physiol Congr, com p 124
Berlucchi G (1972) Anatomical and physiological aspects of visual function of corpus callosum. Brain Res 37: 371–392
Berlucchi G, Gazzaniga M S, Rizzolatti G (1967) Microelectrode analysis of transfer of visual information by the corpus callosum. Arch Ital Biol 105: 583–596
Caminiti R, Manzoni T, Michelini S, Spidalieri G (1976) Callosal transfer of impulses originating from superficial and deep nerves of the cat forelimb. Arch Ital Biol 114: 155–177
Caminiti R, Innocenti G M, Manzoni T (1979) The anatomical substrate of callosal messages from SI and SII in the cat. Exp Brain Res 35: 295–314
Choudhury B P, Witteridge D, Wilson M E (1965) The function of the callosal connections of the visual cortex. Quart J Exp Physiol 50: 214–219
Donaldson L, Hand P J, Morrison A R (1975) Cortical-thalamic relationships in the Rat. Exp Neurol 47: 448–458
Dreyer D A, Loe P R, Metz C B, Whitsel B L (1975) Representation of head and face in postcentral gyrus of the Macaque. J Neurophysiol 38: 714–733
Ebner F F, Myers R E (1965) Distribution of corpus callosum and anterior commissure in cat and raccoon. J Comp Neurol 124: 353–366
Fadiga E, Manzoni T (1969) Relationships between the somatosensory thalamic relay-nuclei of the two sides. Arch Ital Biol 107: 604–632
Garcia-Rill E, Dubrowsky B (1973) Topographical organization of visual input to precruciate motor cortex of cat. Brain Res 56: 151–163
Garey L J, Jones E G, Powell T P S (1968) Interrelationships of striate and extrastriate cortex with primary relay sites of the visual pathways. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 31: 135–157
Hassler R, Muhs-Clement K (1964) Architektonischer Aufbau des sensomotorischen und parietalen Cortex der Katze. J Hirnforsch 6: 377–420
Hekmatpanah J (1961) Organization of tactile dermatomes, C1through L4, in cat. J Neurophysiol 24: 129–140
Hubel D H, Wiesel T N (1967) Cortical and callosal connections concerned with the vertical meridian of the visual field in the cat. J Neurophysiol 30: 1561–1573
Innocenti G M, Fiore L (1976) Morphological correlates of visual field transformation in the corpus callosum. Neurosci Letters 2: 245–252
Innocenti G M, Manzoni T, Spidalieri G (1973) Relevance of the callosal transfer in defining the peripheral reactivity of somesthetic cortical neurones. Arch Ital Biol 111: 187–221
Innocenti G M, Manzoni T, Spidalieri G (1974) Patterns of somesthetic messages transferred through the corpus callosum. Exp Brain Res 19: 447–466
Jones E G, Powell T P S (1968) The commisural connections of the somatic sensory cortex in the cat. J Anat 103: 433–455
Jones E G, Powell T P S (1969) Connexions of the somatic sensory cortex of the rhesus monkey. II. Contralateral cortical connexions. Brain 92: 717–730
Jones E G, Powell T P S (1970) An electron microscopic study of the laminar pattern and mode of termination of afferent fibre pathways in the somatic sensory cortex of the cat. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 257: 45–62
Jones E G, Powell T P S (1973) Anatomical organization of the somatosensory cortex. In: Iggo A (ed) Somatosensory system. Handbook of sensory physiology, vol II, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 579–620
Manzoni T (1976) Intracortical mechanisms influencing the peripheral reactivity of SII convergence neurones. In: Creutzfeldt O (ed). Afferent and intrinsic organization of laminated structures in the brain. Exp Brain Res [Suppl 1]: 431–436 (1976)
Manzoni T, Caminiti R, Spidalieri G, Morelli E (1979a) Anatomical and functional aspects of the associative projections from somatic area SI to SII. Exp Brain Res 34: 453–470
Manzoni T, Spidalieri G, Caminiti R (1979b) Cutaneous and proprioceptive input to the corpus callosum in the cat. In: Steel Russel I, Hof M W van, Berlucchi G (eds) Structure and function of the cerebral commissures Cap. 24. McMillan, London, pp 310–318
Mountcastle V B (1957) Modality and topographic properties of single neurons of cat's somatic sensory cortex. J Neurophysiol 20: 408–434
Mountcastle V, Hennemann E (1949) Pattern of tactile representation in thalamus of cat. J Neurophysiol 12: 85–100
Oscarsson O, Rosén I (1963) Projection to cerebral cortex of large muscle-spindle afferents in forelimb nerves of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 169: 924–945
Oscarsson O, Rosén I (1966) Short-latency projections to the cat's cerebral cortex from skin and muscle afferents in the contralateral forelimb. J Physiol (Lond) 182: 164–184
Pandya D N, Vignolo L A (1969) Interhemispheric projections of the parietal lobe in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res 15: 49–65
Rasmusson D D, Dykes D D, Hoeltzell P B (1979) Segregation of modality information in SI cortex of the cat. Brain Res 166: 409–412
Robinson D L (1973) Electrophysiological analysis of interhemispheric relations in the second somatosensory cortex of the cat. Exp Brain Res 18: 131–144
Rubel E W (1971) A comparison of somatotopic organization in sensory neocortex of newborn kittens and adult cats. J Comp Neurol 143: 447–480
Shanks M F, Rockel A J, Powell T P S (1975) The commissural fibre connections of the primary somatic sensory cortex. Brain Res 98: 166–171
Shatz C (1977) Anatomy of interhemispheric connections in the visual system of Boston Siamese and ordinary cats. J Comp Neurol 173: 497–518
Sur M, Nelson R J, Kaas J H (1978) The representation of the body surface in somatosensory area I of the grey squirrel. J Comp Neurol 179: 425–450
Werner G, Whitsel B L (1973) The functional organization of somatosensory cortex. Iggo A (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol II, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 621–700
Wise S P, Jones E G (1976) The organization and post-natal development of the commissural projection of the rat somatic sensory cortex. J Comp Neurol 168: 313–344
Woolsey C N (1952) Patterns of localization in sensory and motor areas of the cerebral cortex. In: The biology of mental health and disease. Hoeber, New York, pp 192–206
Yorke C H, Jr, Caviness V S, Jr (1975) Interhemispheric neocortical connections of the corpus callosum in the normal mouse: A study based on anterograde and retrograde methods. J Comp Neurol 164: 233–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by funds granted by Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Rome, Italy. Preliminary results were published in abstract form [Exp. Brain Res. 32, R4 (1978)]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manzoni, T., Barbaresi, P., Bellardinelli, E. et al. Callosal projections from the two body midlines. Exp Brain Res 39, 1–9 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237063
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237063