Abstract
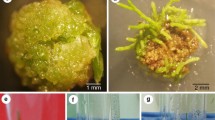
Transgenic calli of Pharbitis nil which grow in the presence of kanamycin were obtained by introduction of plasmid pBI121, which carries kanamycin resistance and the gene for beta-glucuronidase. The calli were shown to have fragments of vector DNA in their genome and high levels of beta-glucuronidase activity. This is the first report of the introduction of T-DNA into P. nil and the T-DNA has been shown to be integrated without apparent rearrangement in its genome. The range of copy numbers was between 3 and 5. The beta-glucuronidase activities measured were about 10 times higher than those of transgenic tobacco by introduction of the same plasmid as previously described by Jefferson et al. (1987). Thus, the widely used CaMV 35S promoter also appears to be very active in P. nil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower Mosaic Virus
- NAA:
-
naphthylacetic acid
- BA:
-
benzylaminopurine
- NPT:
-
neomycinphosphotransferase
- GUS:
-
beta-glucuronidase
- CTX:
-
Cefotaxime
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- 4-MU:
-
4-methylumbelliferone
- NOS:
-
nopaline synthase
- CTAB:
-
hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
References
An G 1987 Methods Enzymol. 153:292–305
An G, Watson BD, Chiang CC 1986 Plant Physiol. 81:301–305
Bevan M 1984 Nucl. Acid Res. 12:8711–8721
Deblaere R, Bytebier B, DeGreve H, Deboeck F, Schell J, Van Montagu M, Leemans J 1985 Nucl. Acid Res. 13:4779–4788
Deblaere R, Reynaerts A, Hofte H, Hernalsteens J-P, Leemans J, Van Montagu M 1987 Methods Enzymol. 153:277–292
Hirano H, Komeda Y, Iino T 1988 Plant Cell Physiol. 29:1153–1157
Hood EE, Helmer GL, Fraley RT, Chilton M-D 1986 J. Bacteriol. 168:1291–1301
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT 1985 Science 227:1229–1231
Imai Y 1931 Genetics 16:26–41
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW 1987 EMBO J. 6:3901–3907
Klee H, Horsch R, Rogers S 1987 Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 38:467–486
Maniatis T, Fritz EF, Sambrook J 1982 Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N. Y., USA.
Murashige T, Skoog F 1962 Physiol. Plant. 15:473–497
Rao RN, Rogers SG 1979 Gene 7:79–82
Rogers SG, Klee HJ, Horsch RB, Fraley RT 1987 Methods Enzymol. 153:253–277.
Takimoto A, Hamner KC 1965 Plant Physiol. 40:852–854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. N. Beachy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Araki, T., Hirano, H., Naito, S. et al. Introduction of foreign genes into Pharbitis nil calli using a vector derived from Agrobacterium pTi. Plant Cell Reports 8, 259–262 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00274124
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00274124