Abstract
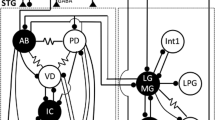
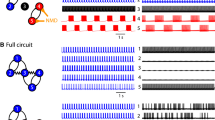
The principles governing neural pattern generation were studied in the pyloric subsystem of lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Quantitative estimates were obtained for repetitive-firing and synaptic-interaction parameters for use in developing quantitative theories (including computer models) of ganglion functioning. 1. The neurons fired tonically to depolarizing current steps, adapting to about 30% of initial frequency along a compound exponential with time-constants around 0.3 and 3.5 s. 2. Both initial and final firing frequencies to depolarizing current steps were approximately logarithmic with current over a substantial current range (2–10 nA). 3. Post-hyperpolarization rebound was exhibited by all cell types. Its magnitude was a linear function of current in some but not all cases. In simple cases build-up followed a compound exponential with time constants similar to those for adaptation. 4. Synaptic potentials were of two general types: sharprising (t peak≃12 ms) and rounded (t peak≃80 ms). 5. Effective synaptic strengths were measured between neuron types. In some cases the strengths were sufficient to expect complete shut-off of moderate activity in postsynaptic elements by moderate activity in presynaptic elements. 6. Certain properties of the system enhance switch-like on/off activity in each cell, which could contribute to burst generation and to appropriate phasing of bursts in the activity cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bidaut, M.R., Russell, D.F., Hartline, D.K.: Distinguishing two types of inhibitory synapses from pacemaker neurons in the pyloric system of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Neurosci. Abstr. 4, 188 (1978)
Brown, M.C., Stein, R.B.: Quantitative studies on the slowly adapting stretch receptor of the crayfish. Kybernetik 3, 175–185 (1966)
Bullock, T.H., Horridge, G.A.: Structure and function in the nervous system of invertebrates. San Francisco: Freeman 1965
Bullock, T.H., Terzuolo, C.A.: Diverse forms of activity in the somata of spontaneous and integrating ganglion cells. J. Physiol. 138, 341–364 (1957)
Conner, J.A., Walter, D., McKown, R.: Neural repetitive firing. Modifications of the Hodgkin-Huxley axon suggested by experimental results from crustacean axons. Biophys. J. 18, 81–102 (1977)
Dando, M.R., Selverston, A.I.: Command fibres from the supraoesophageal ganglion to the stomatogastric ganglion in Panulirus. J. Comp. Physiol 78, 138–175 (1972)
Friesen, W.O., Poon, M., Stent, G.: An oscillatory neural circuit generating a locomotory rhythm. PNAS 73, 3734–3738 (1976)
Govind, C.K., Atwood, H.L., Maynard, D.M.: Innervation and neuromuscular physiology of intrinsic foregut muscles in the blue crab and spiny lobster. J. Comp. Physiol. 96, 185–204 (1975)
Graubard, K., Raper, J.A., Hartline, D.K.: Non-spiking synaptic transmission between spiking neurons. Neurosci. Abstr. 3, 177 (1977)
Hartline, D.K.: Integrative physiology of the lobster cardiac ganglion. Thesis, Harvard University Biology Department (1967)
Hartline, D.K.: SNAX: a language for interactive neuronal modeling and data processing. In: Computer technology in neuroscience, pp. 41–65. Brown, P.B. (ed.). Washington, D.C.: Hemisphere Press 1976a
Hartline, D.K.: Simulation of phase-dependent pattern changes in pertubations of regular firing in crayfish stretch receptor. Brain Res. 110, 245–257 (1976b)
Hartline, D.K.: Quantitative analysis of pyloric network in stomatogastric ganglion. Neurosci. Abstr. 2, 324 (1976c)
Hartline, D.K.: On the pitfalls of modeling and not-modeling. Brain Theory Newslett. 2, 25–27 (1976d)
Hartline, D.K.: Pattern generation in the lobster (Panulirus) stomatogastric ganglion. II. Pyloric network simulation. Biol. Cybernetics 33, 223–236 (1979)
Hartline, D.K., Gassie, D.V., Sirchia, C.D.: Burst reset properties in an endogenously bursting network-driver cell (in preparation)
Hartline, D.K., Maynard, D.M.: Motor patterns in the stomatogastric ganglion of the lobster, Panulirus argus. J. Exp. Biol. 62, 405–420 (1975)
Hartline, D.K., Russell, D.F.: Induction of regenerative properties in neurons of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion by identified neural inputs. Neurosci. Abstr. 4, 195 (1978)
Hodgkin, A.L.: The local electric changes associated with repetitive action in a non-medullated axon. J. Physiol. 107, 165–181 (1948)
King, D.G.: Organization of crustacean neuropil. I. Patterns of synaptic connections in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurocytol. 5, 207–237 (1976a)
King, D.G.: Organization of crustacean neuropil. II. Distribution of synaptic contacts on identified motor neurons in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurocytol. 5, 239–266 (1976b)
Kling, V., Székely, G.: Simulation of rhythmic neurons activities. I. Functions of networks with cyclic inhibitions. Kybernetik 5, 89–103 (1968)
Maynard, D.M.: Direct inhibition in the lobster cardiac ganglion. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Zoology 1955a
Maynard, D.M.: Activity in a crustacean ganglion. II. Pattern and interaction in burst formation. Biol. Bull. 109, 420–436 (1955b)
Maynard, D.M.: Simpler networks. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 193, 59–72 (1972)
Maynard, D.M., Dando, M.R.: The structure of the stomatogastric neuromuscular system in Callinectes sapidus, Homarus americanus, and Panulirus argus (Dcapoda Crustacea). Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London 268, 161–220 (1974)
Maynard, D.M., Selverston, A.I.: Organization of the stomatogastric ganglion of the spiny lobster. IV. The pyloric system. J. Comp. Physiol. 100, 161–182, (1975)
Maynard, D.M., Walton, K.D.: Effects of maintained depolarization of presynaptic neurons on inhibitory transmission in lobster neuropile. J. Comp. Physiol. 97, 215–243 (1975)
Morris, J., Maynard, D.M.: Recordings from the stomatogastric nervous system in intact lobsters. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 33, 969–974 (1970)
Patwardhan, S.S.: On the structure and mechanism of the gastric mill in decapoda. IV. The structure of the gastric mill in Reptantous macrura. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. Sect. B 1, 414–422 (1935)
Russell, D.F.: Central control of pattern generators in the stomatogastric ganglion of the lobster Panulirus interruptus. Thesis, University of California at San Diego, Biology Department 1977
Russell, D.F., Hartline, D.K.: Inputs to the lobster stomatogastric ganglion unmask bursting properties in many of its motorneurons. Neurosci. Abstr. 3, 384 (1977)
Russell, D.F., Hartline, D.K.: Bursting neural networks: a re-examination. Science 200, 453–456 (1978)
Schulman, J.A.: Information transfer across an inhibitor to pacemaker synapse at the crayfish stretch receptor. Thesis, University of California at Los Angeles, Zoology Department 1969
Selverston, A.I., Russell, D.F., Miller, J.P., King, D.G.: The stomatogastric nervous system: structure and function of a small neural network. Progr. Neurobiol. 6, 1–75 (1976)
Sokolove, P.G.: Adaptation in a sensory neuron and the role of sodium transport. Thesis, Harvard University, Department of Biology 1969
Sokolove, P.G., Cooke, I.M.: Inhibition of impulse activity in a sensory neuron by an electrogenic pump. J. Gen. Physiol. 57, 125–163 (1971)
Stevens, C.F.: A quantitative theory of neural interactions. theoretical and experimental investigations. Thesis, Rockefeller University 1964
Terzuolo, C.A., Washizu, Y.: Relation between stimulus strength, generator potential, and impulse frequency in stretch receptor of crustacea. J. Neurophysiol. 25, 56–66 (1962)
Watanabe, A., Obara, S., Toyohiro, A.: Pacemaker potentials for the periodic burst discharge in the heart ganglion of a stomatopod, Squilla oratoria. J. Gen. Physiol. 50, 839–862 (1967)
Wilson, D.M., Waldron, I.: Models for the generation of motor output pattern in flying locusts. Proc. IEEE 56, 1058–1064 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartline, D.K., Gassie, D.V. Pattern generation in the lobster (Panulirus) stomatogastric ganglion. Biol. Cybernetics 33, 209–222 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337410
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337410