Abstract
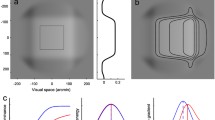
Threshold illumination levels, I t , for visual detection of white light targets, moving across spatially structured background fields, have been measured and it is shown that, for a given background illumination level, I t depends upon the spatial characteristics of the background field structure. Thus, with the background composed of a square-waveform grating of fundamental spatial frequency f cycles/deg, I t is maximum for an intermediate value of f, and falls as f increases or decreases from this value. The relationship between I t and f characterizes the interaction between Movement detection and the background grating, and is designated the IMG function. The parametric properties of the IMG functions are described and it is established that the mechanisms which give rise to these functions are sensitive to the movement, but not the spatial structure of the target. They correspond, therefore, to the movement-sensitive Y-type mechanisms, observed in electrophysiological studies of cat and primate visual pathways. The spatial distribution of sensitivity associated with the IMG functions has been computed by 2-D transform methods, the computation yielding circularly symmetric, centre-surround antagonistic “receptive field” distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbur, J.L., Nunn, B.J.: A simple 8-channel data logger. Photobiol. Bull. 1, 40–50 (1978)
Barbur, J.L.: An arrangement for automatic random stimulus selection and variable speed of presentation in sensory physiology experiments. Photobiol. Bull. 1, 138–142 (1979)
Barbur, J., Ruddock, K.H.: The effects of background structure and target size on movement detection by the foveal and parafoveal retina. Proc. ICO-11 Conference, Madrid. Bescos, J., Hidalgo, A., Plaza, L., Santamaria, J. (eds.) p. 125–128, 1978
Barbur, J.L., Ruddock, K.H.: Spatial characteristics of movement detection mechanisms in human vision. II. Chromatic stimuli. Biol. Cybernetics 37, 93–98 (1980)
Barbur, J.L., Holliday, I.E., Ruddock, K.H., Waterfield, V.A.: Spatial characteristics of movement detection mechanisms in human vision. III. Subjects with abnormal visual pathways. Biol. Cybernetics 37, 99–105 (1980)
Blakemore, C., Campbell, F.W.: On the existence of neurones in the human visual system sensitive to the orientation and size of retinal images. J. Physiol. (London) 203, 237–260 (1969)
Born, M., Wolf, E.: Principles of optics, 4th ed Oxford: Pergamon Press 1979
Boycott, B.B., Wässle, H.: The morphological types of ganglion cells of the domestic cat's retina. J. Physiol. (London) 240, 397–419 (1974)
Bracewell, R.: The Fourier transform and its applications. New York: McGraw-Hill 1965
Burton, G.J., Ruddock, K.H.: Visual adaptation to patterns containing two-dimensional spatial structure. Vision Res. 18, 93–99 (1978)
De Monasterio, F.M., Gouras, P.: Functional properties of ganglion cells of the rhesus monkey retina. J. Physiol. (London) 251, 167–195 (1975)
Duffieux, P.M.: L'intégrale de Fourier et ses applications à l'optique. Rennes: private ed 1946
Enroth-Cuggell, C., Robson, J.G.: The contrast sensitivity of retinal cells of the cat. J. Physiol. (London) 187, 517–552 (1966)
Foster, D.H.: The response of the human visual system to moving spatially-periodic patterns: further analysis. Vision Res. 11, 57–81 (1971)
Gilinsky, A.S.: Orientation-specific effects of patterns of adapting lights on visual acuity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 58, 13–18 (1968)
Goldberg, M.E., Wurtz, R.H.: Activity of superior colliculus in behaving monkey. I. Visual receptive fields of single neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 35, 542–559 (1972)
Hopkins, H.H.: 21st Thomas Young Oration: The application of frequency response techniques in optics. Proc. Phys. Soc. 79, 889–919 (1962)
Hubel, D.H., Wiesel, T.N.: Receptive fields and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex. J. Physiol. (London). 195, 215–243 (1968)
Koenderink, J.J., Bouman, M.A., Mesquita, A.E.B. de, Slappendel, S.: Perimetry of contrast detection thresholds of moving spatial sine wave patterns. II. The far-periphery visual field (eccentricity 0°–50°). J. Opt. Soc. Am. 68, 850–854 (1978)
Kulikowski, J.J.: Effect of eye movements on the contrast sensitivity of spatio-temporal patterns. Vision Res. 11, 261–273 (1971)
Marchand, E.W.: From line to point spread function: the general case. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 55, 352–354 (1965)
Marrocco, R.T.: Sustained and transient cells in monkey lateral geniculate nucleus: conduction velocities and response properties. J. Neurophysiol. 39, 340–353 (1976)
Maudarbocus, A.Y., Ruddock, K.H.: Non-linearity of visual signals in relation to shape-sensitive adaptation processes. Vision Res. 13, 1713–1737 (1973)
Naghshineh, S., Ruddock, K.H: Properties of length-selective and non-length-selective adaptation mechanisms in human vision. Biol. Cybernetics 31, 37–47 (1978)
van Nes, F.L., Bouman, M.A.: Spatial modulation transfer in the human eye. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 57, 401–406 (1967)
Pantle, A.J., Sekuler, R.W.: Velocity-sensitive mechanisms in human vision. Vision Res. 8, 445–450 (1968a)
Pantle, A.J., Sekuler, R.W.: Size-detection mechanisms in human vision. Sci. N.Y. 162, 1146–1148 (1968b)
Reichardt, W., Varju, D.: Übertragungseigenschaften im Auswertesystem für das Bewegungsehen. Z. Naturforsch. 146, 674–689 (1959)
Robson, G.J.: Spatial and temporal contrast sensitivity functions of the visual system. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 56, 1141–1142 (1966)
Ruddock, K.H., Wigley, E.: Inhibitory binocular interaction in human vision and a possible mechanism subserving stereoscopic fusion. Nature (London) 260, 604–606 (1976)
Ruddock, K.H., Waterfield, V.A., Wigley, E.: The response characteristics of an inhibitory binocular interaction in human vision. J. Physiol. (London) 290, 37–49 (1979)
Schiller, P.H., Koerner, F.: Discharge characteristics of single units in superior colliculus of the alert rhesus monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 920–936 (1971)
Schiller, P.H., Finlay, B.L., Volman, S.F.: Quantitative studies of single-cell properties in monkey striate cortex. I. Spatio temporal organisation of receptive fields. J. Neurophysiol. 39, 1288–1319 (1976)
Tolhurst, D.J., Sharpe, C.R. Hart, G.: The analysis of the drift rate of moving sinusoidal gratings. Vision Res. 13, 2545–2556 (1973)
Wynne, C.G.: Simple Fourier transform lenses. I.. Opt. Commun. 12, 266–269 (1974a)
Wynne, C.G.: Simple Fourier transform lenses. II. Opt. Commun. 12, 270–274 (1974b)
Zeki, S.M.: Functional organisation of a visual area in the posterior bank of the superior temporal sulcus. J. Physiol. (London) 236, 549–573 (1974)
Zeki, S.M.: Uniformity and diversity of structure and function in rhesus prestriate visual cortex. J. Physiol. (London) 277, 273–290 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbur, J.L., Ruddock, K.H. Spatial characteristics of movement detection mechanisms in human vision. Biol. Cybernetics 37, 77–92 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364247
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364247