Abstract
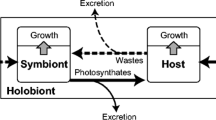
Rates of oxygen and carbon-dioxide exhange were measured in symbiotic and aposymbiotic specimens of the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima while fed and starved under light or dark conditions. Respiratory quotients indicated that fed anemones switched from a carbohydrate to a fat catabolism when starved, with the exception that symbiotic individuals starved in the light showed a pronounced carbohydrate catabolism for over 1 month. The source of the carbohydrate was probably photosynthate translocated by the dinoflagellate Symbiodinium (=Gymnodinium) microadriaticum (Freudenthal) living in the anemones' tissues. The starved symbiotic anemones maintained in the light had lipid levels not significantly different from fed controls and 44 to 61% higher than starved aposymbiotic anemones after 1 month. Thus, the quality and quantity of the metabolic flux from the symbionts to the sea anemone were sufficient to conserve the host's lipid reserves.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Beyers, R. J.: A pH-carbon dioxide method for measuring aquatic primary productivity. Bull. Ga Acad Sci. 28, 55–68 (1970)
Blanquet, R. S., J. C. Nevenzel and A. A. Benson: Acetate incorporation into the lipids of the anemone Anthopleura elegantissima and its associated zooxanthellae. Mar. Biol. 54, 185–194 (1979)
Buchner, P.: Endosymbiosis of animals with plant microorganisms, 909 pp. New York: Wiley Interscience 1965
Childress, J. J. and M. N. Nygaard: Chemical composition and buoyancy of midwater crustaceans as a function of depth of occurrence off Southern California. Mar. Biol. 27, 225–238 (1974)
Ciereszko, L. S. and T. K. B. Karns: Comparative biochemistry of coral reef coelenterates. In: Biology and geology of coral reefs, Vol. II. pp 183–203. Ed. by O. A. Jones and R. Endean. New York: Academic Press 1973
Droop, M.: Algae and invertebrates in symbiosis. Symp. Soc. gen Microbiol. 13, 171–199 (1963)
Dubois, M., K. A. Gilles, J. K. Hamilton, P. A. Rebers and F. Smith: Colorometric method for the determination of sugars and related substances. Analyt. Chem. 28, 350–356 (1956)
Fankboner, R. V.: Intracellular digestion of symbiotic zooxanthellae by host amoebocytes in giant clams (Bivalvia: Tridacnidae), with a note on the nutritional role of the hypertrophied siphonal epidermis. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole, 141, 222–234 (1971)
Folch, J., M. Lees and G. H. Sloane Stanley: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1956)
Franzisket, L.: Riffcorallen können autroph leben. Naturwissenschaften 56, p. 144 (1969)
Giese, A. C.: Lipids in the economy of marine invertebrates. Physiol. Rev. 46, 244–298 (1966)
Goreau, T. F. and N. I. Goreau: Distribution of labeled carbon in reef-building corals with and without zooxanthellae. Science, N. Y. 131, 668–670 (1960)
Holt, C. von, and M. von Holt: The secretion of organic compounds by zooxanthellae isolated from various types of Zoanthus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 24, 83–92 (1968a)
Holt, C. von, M. von Holt: Transfer of photosynthetic products from zooxanthellae to coelenterate hosts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 24, 73–81 (1968b)
James, W. O. Plant respiration, 282 pp. Oxford: Clarendon Press 1953
Jennison, B. L.: An analyses of the environmental factors which influence gametogenesis, spawning, and nutrient storage in the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima (Brandt, 1935), 194 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of California at Berkeley 1977
Kleiber, M.: The fire of life, 454 pp. New York: John Wiley & Sons 1961
Kleiber, M.: Respiratory exchange and metabolic rate. In: Respiration, Vol. II. pp 927–938. Ed. by W. O. Fern and H. Rahn. Washington D.C.: American Physiological Society 1965
Lewis, D. H. and D. C. Smith: The autotrophic nutrition of symbiotic marine coelenterates with special reference to hermatypic corals. I. Movement of photosynthetic products between the symbionts. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 178, 111–129 (1971)
Lowry, O. H., H. J. Rosenborough, A. L. Farr and R. J. Randall: Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
McCloskey, L. R., D. S. Wethey and J. W. Porter: Measurement and interpretation of photosynthesis and respiration in reef corals. Monogr. oceanogr. Methodol. (UNESCO) 5, 379–396 (1978)
McLaughlin, J. A. and P. A. Zahl: Endozoic algae. In: Symbiosis, Vol. 1. pp 257–297. Ed. by S. M. Henry. New York: Academic Press 1966
Muscatine, L.: Symbiosis in marine and freshwater coelenterates. In: The biology of hydra, pp 255–268. Ed. by H. Lenhoff and W. F. Loomis. Miami: University of Miami Press 1961
Muscatine, L.: Glycerol excretion by symbiotic algae from corals and Tridacna and its control by the host. Science, N.Y. 156, 519–520 (1967)
Muscatine, L.: Nutrition in corals. In: Biology and geology of coral reefs, Vol. II. pp 77–115. Ed. by O. A. Jones and R. Endean. New York: Academic Press 1973
Muscatine, L. and E. Cernichiari: Assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by a reef coral. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 137, 506–523 (1969)
Muscatine, L. and C. Hand: Direct evidence for the transfer of materials from symbiotic algae to the tissues of coelenterates. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 44, 1259–1263 (1958)
Muscatine, L., R. R. Pool, and E. Cernichiari: Some factors influencing selective release of soluble organic material by zooxanthellae from reef corals. Mar. Biol. 13, 298–308 (1972)
Muscatine, L. and J. W. Porter: Reef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor environments. BioSci. 27, 454–460 (1977)
Nicol, J. A. C.: Biology of marine animals, 699 pp. London: Pitman 1960
Pardy, R. L.: The production of aposymbiotic hydra by the photodestruction of green hydra zoochlorellae. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Wood Hole 151, 225–235 (1976)
Pardy, R. L. and B. N. While: Metabolic relationships between green hydra and its symbiotic algae. Biol. Bull mar. biol. Lab., Wood Hole 153, 228–236 (1977)
Richardson, H. B.: The respiratory quotient. Physiol. Rev. 9, 61–125 (1929)
Roffman, B.: Patterns of oxygen exchange in some Pacific corals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 27, 405–418 (1968)
Shick, J. M., W. I. Brown, E. G. Dolliver and S. R. Kayer: Oxygen uptake in sea anemones: effects of expansion, contraction, and exposure to air and the liminations of diffusion. Physiol. Zoöl. 52, 50–62 (1979)
Smith, D. C., L. Muscatine and D. H. Lewis: Carbohydrate movement from autotrophs to heterotrops in parasitic and mutualistic symbiosis. Biol. Rev. 44, 19–90 (1969)
Svoboda, A. and T. Porrmann: Oxygen preduction and uptake by symbiotic Aiptasia diaphana (Rapp), (Anthoroa, Coelenterata) adapted to different light intensities. In: Nutrition in lower metazoa, Vol. I. Ed. by Y. Tiffon. New York: Pergamon Press (In press)
Taylor, D. L.: On the regulation and maintenance of algal numbers in zooxanthellae-coelenterate symbiosis, with a note on the relationship in Anemonia sulcata. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 49, 1057–1065 (1969)
Taylor, D. L.: Algal symbionts of invertebrates. A. Rev. Microbiol. 27, 171–187 (1973)
Trench, R.K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. I. The assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177, 225–235 (1971a)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. II. Liberation of fixed 14C by zooxanthellae in vitro. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177, 237–250 (1971b)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. III. The effect of homogenates of host tissues on the excretion of photosynthetic products in vitro by zooxanthellae from two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177, 251–264 (1971c)
Trench, R. K.: Nutritional potentials in Zoanthus sociatus (Coelenterata: Anthozoa). Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 26, 174–216 (1974)
Trench, R. K.: The cell biology of plant-animal sybiosis. A. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 30, 485–531 (1979)
Wethey, D. S. and J. W. Porter: Sun and shade differences in productivity of reef corals. Nature, Lond. 262, 281–282 (1976)
Young, S. D., J. D. O'Connor and L. Muscatine: Organic material from scleractinian coral skeletons. II. Incorporation of 14C into protein, chitin, and lipid. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 40, 945–958 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N. D. Holland, La Jolla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitt, W.K., Pardy, R.L. Effects of starvation, and light and dark on the energy metabolism of symbiotic and aposymbiotic sea anemones, Anthopleura elegantissima . Mar. Biol. 61, 199–205 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386660
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386660