Summary
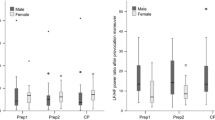
The effects of different physical training regimes on the plasma catecholamine values at rest and the density and responsiveness of adrenergic receptors at rest were investigated. The changes during well-defined training periods of swimmers, long-distance runners, weight lifters and wrestlers were compared with untrained male volunteers. The training of swimmers and long-distance runners, building up endurance, resulted in a significantly lower basal plasma norepinephrine (NE) concentration and a significantly or possibly lower ratio NE∶EPI (epinephrine). Both values indicated reduced sympathetic activity and resulted also in a significantly lower β-receptor density and a higher α 2-receptor sensitivity compared with the other groups investigated. However, swimming-specific characteristics provoked labile hypertensive blood pressure regulation with an unchanged heart rate in swimmers. Static training of weight lifters, building up power, also led to a lower NE concentration compared with untrained subjects, whereas β-receptor density was unchanged and α2-receptor density and sensitivity were decreased. Elevated blood pressure values were observed in weight lifters and swimmers due to a reduced baroreceptor sensitivity. The dynamic training of wrestlers affected only basal heart rate and α 2-receptor sensitivity, both of which were decreased. Different kinds of physical training caused various adaptations of the basal activity of the autonomic nervous system in which adrenergic receptors also became adapted. In this context, the stronger adrenergic circulatory component of overall sympathetic activity at rest in swimmers and long-distance runners resulted in lower β-receptor density, and the reduced noradrenergic component sensitized α2-receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarons RD, Molinoff PB (1982) Changes in the density of beta adrenergic receptors in rat lymphocytes, heart and lung after chronic treatment with propranolol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 221:439–443
Aarons RD, Nies AS, Gerber JG, Molinoff PB (1983) Decreased beta adrenergic receptor density on human lymphocytes after chronic treatment with agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:1–6
Bedford TB, Tipton CM (1987) Exercise training and the arterial baroreflex. J Appl Physiol 63:1926–1932
Bieger W, Zittel R, Zappe H, Weicker H (1982) Einfluß körperlicher Aktivität auf die Katecholaminrezeptor-Regulation. In: Heck H, Hollmann W, Liesen H, Rost R (eds) Sport: Leistung und Gesundheit. Kongreßband Deutscher Sportärztekongress, Cologne, pp 271–275
Brodde OE, Engel G, Hoyer D, Bock KD, Weber F (1981) The beta-adrenergic receptor in human lymphocytes: subclassification by the use of a new radioligand, (±)125iodocyanopindolol. Life Sci 29:2189–2198
Brodde OE, Kretsch R, Ikezono K, Zerkowski HR, Reidemeister JC (1986) Human β-adrenoceptors: relation of myocardial and lymphocyte β-adrenoceptor density. Science 231:1584–1585
Butler J, O'Brien M, O'Malley K, Kelly JG (1982) Relationship of β-adrenoceptor density to fitness in athletes. Nature 298:60–62
Ekblom B, Kilborn A, Saltysiak J (1973) Physical training, bradycardia and autonomic nervous system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 32:251–256
Fraser J, Nadeau J, Robertson D, Wood AJJ (1981) Regulation of human leukocyte beta receptors by endogenous catecholamines. J Clin Invest 67:1777–1784
Galant SP, Duriseti L, Underwood S, Insel PA (1978) Decreased β-adrenergic receptors in polymorphnuclear leukocytes after adrenergic therapy. N Engl J Med 299:933–936
Goldstein DS, McCarty R, Polinsky RJ, Kopin IJ (1983) Relationship between plasma norepinephrine and sympathetic neural activity. Hypertension 5:552–559
Greenacre JK, Conolly ME (1978) Desensitization of the beta adrenoceptor of lymphocytes from normal subjects and patients with pheochromocytoma: studies in vivo. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5:191–197
Guezennec Y, Leger L, Aymonod H, Pesgries PC (1986) Hormone and metabolic response to weight-lifting training sessions. Int J Sports Med 7:100–105
Hagberg JM, Hickson RC, McLane IA, Elsani AA, Winder WW (1979) Disappearance of norepinephrine from the circulation following strenuous exercise. J Appl Physiol 47:1311–1314
Hammond HK, White FC, Brunton LL, Longhurst JC (1987) Association of decreased myocardial β-receptors and chronotropic response to isoproterenol and exercise in pigs following chronic exercise. Circ Res 60:720–726
Hertting G (1979) Das sympathische Neuron: Regelwege für Synthese, Freisetzung und Wirkung des Transmitters. Klin Wochenschr 57:593–598
Kjaer M, Christensen J, Sonne R, Richter EA, Galbo H (1985) Effect of exercise on epinephrine turnover in trained and untrained male subjects. J Appl Physiol 59:1061–1067
Landmann R, Bürgisser E, Bühler FR (1983) Human lymphocytes as a model for beta-adrenergic receptors in clinical investigation. J Recept Res 3:71–88
Lehmann M, Keul J (1984) Häufigkeit der Hypertonie bei 810 männlichen Sportlern. Z Kardiol 73:137–141
Lehmann M, Keul J (1986) Free plasma catecholamines, heart rates, lactate levels and oxygen uptake in competition weight lifters, cyclists and untrained control-subjects. Int J Sports Med 7:18–21
Lehmann M, Dickhut MH, Schmid P, Porzig H, Keul J (1984) Plasma catecholamines, β-adrenergic receptors and isoproterenol sensitivity in endurance trained and non-endurance trained volunteers. Eur J Appl Physiol 52:362–369
Lehmann M, Bergdolt E, Hasler K, Hasenfuss G, Holubarsch C, Kaper W, Keul J (1985a) Adrenalin-induzierte Plättchenaggregation bei Patienten mit koronarer Herzkrankheit sowie gesunden trainierten und untrainierten Kontrollpersonen. Dtsch Z Sportmed 11:334–339
Lehmann M, Schmid P, Keul J (1985b) Zum Verhalten von Alpha-Adrenoceptoren an intakten Thrombozyten bei Ausdauertrainierten, untrainierten Kontrollpersonen und Kraftsportlern. In: Franz IW, Mellerowicz H, Noack W (eds) Training und Sport zur Prävention u. Rehabilitation in der technisierten Umwelt. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 367–371
Lehmann M, Hasler K, Bergdolt E, Keul J (1986) Alpha-2- adrenoceptor density on intact platelets and epinephrine induced platelet aggregation in endurance and nonendurance trained subjects. Int J Sports Med 7:172–176
Lockette W, McCurdy R, Smith S, Carretero O (1987) Endurance training and human α2-adrenergic receptors on platelets. Med Sci Sports Exerc 19:7–10
Macfarlane DE, Wright BL, Stump DC (1981) Use of [methyl3H] yohimbine as a radioligand for alpha-2-adrenoceptors on intact platelets. Comparison with dihydroergocryptine. Thromb Res 24:31–43
Mc Pherson GA (1985) Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. J Pharmacol Methods 14:213–228
Meyer R, Meyer U, Weiss M, Weicker H (1988) Sympathoadrenergic regulation of metabolism and cardiocirculation during and following running exercises of different intensity and duration. Int J Sports Med 9 [Suppl 2]: 132–140
Michel G, Vocke T, Fiehn W, Weicker H, Schwarz W, Bieger WR (1984) Bidirectional alteration of insulin receptor affinity in circulating monocytes and erythrocytes following different forms of physical exercise. Am J Physiol 246:153–159
Michel G, Lenz T, Weicker H, Werle E, Lehnhardt U (1987) Sulfoconjugated catecholamines: lack of β-adrenoceptor binding and adenylate cyclase stimulation in human mononuclear leukocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 143:179–188
Moore RL, Riedy M, Gollnick PD (1982) Effect of training on β-adrenergic receptor number in rat heart. J Appl Physiol 52:1133–1137
Motulsky HJ, Insel PA (1982) Adrenergic receptors in man: direct identification, physiologic regulation and clinical alterations. N Engl J Med 307:18–29
Motulsky HJ, Shattil S, Insel PA (1980) Characterisation of α2-adrenergic receptors on human platelets using 3H-yohimbine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 97:1562–1570
Munson PJ, Rodbard D (1980) Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand binding. Anal Biochem 107:220–239
Peronnet F, Cleroux J, Perrault H, Cousineau D, Champlain T de, Nadeau R (1981) Plasma norepinephrine response to exercise before and after training in humans. J Appl Physiol 51:812–815
Pollert R (1987) Hormonelle, metabolische und kardiozirkulatorische Antwort auf verschiedene Schwimmbelastungen im Freizeitund Leistungssportbereich, Arm- und Beinbelastung, Gymnastik und horizontales Eintauchen bei verschiedenen Wassertemperaturen. Dissertation, University of Heidelberg
Weicker H (1986) Bestimmung der freien und konjugierten Katecholamine mit HPLC und amperometrischer Detektion. Lab Med 10:31–44
Weiss M, Weicker H (1985) Gibt es eine Schwimmer-Hypertonie? Schweiz Z Sportmed 33:122–132
Werle E, Michel G, Lenz T, Kather H, Schneider B, Weicker H (1988) Restricted alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor affinity of sulfoconjugated catecholamines in human mononuclear leukocytes, platelets and fat cells and reduction of the postreceptor mechanism. Int J Sports Med 9 [Suppl 2]:93–102
Williams RS, Eden RS, Moll M, Lester RM, Wallace AG (1981) Autonomic mechanism of training bradycardia: β-adrenergic receptors in humans. J Appl Physiol 51:1232–1237
Williams RS, Schaible TT, Bishop T, Morey M (1984) Effects of endurance training on cholinergic and adrenergic receptors of rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 16:395–403
Winder WW, Hagberg JM, Hickson RC, Ehsani AA, McLane JA (1978) Time course of sympathoadrenal adaptation to endurance exercise training in man. J Appl Physiol 45:370–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jost, J., Weiß, M. & Weicker, H. Comparison of sympatho-adrenergic regulation at rest and of the adrenoceptor system in swimmers, long-distance runners, weight lifters, wrestlers and untrained men. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 58, 596–604 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00418505
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00418505