Summary
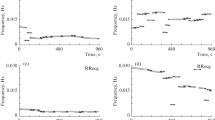
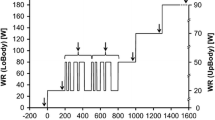
The influence of the degree of coupling between the breathing and cycling rhythms (K) on oxygen uptake \(\dot V_{O_2 } \) was examined in 30 volunteers. They cycled on an ergometer with a load equal to 50% of their work capacity 170 in two experimental runs with spontaneous breathing rhythm, and in a further two runs with acoustically triggered breathing. K was continuously ascertained. \(\dot V_{O_2 } \) and other respiratory parameters were measured by an automatic “breath-by-breath analysis” system.
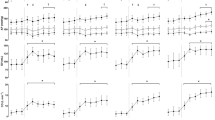
In 16 subjects, \(\dot V_{O_2 } \)-differences between runs were correlated with the differences in K. In the majority of these subjects (12), \(\dot V_{O_2 } \) decreased significantly with increasing K. In 14 subjects, \(\dot V_{O_2 } \) -and K-variations within individual runs were analyzed. Phases with higher K were regularly accompanied by a decrease in \(\dot V_{O_2 } \).
It is concluded that coupling the breathing and cycling rhythms reduces \(\dot V_{O_2 } \) for a given moderate work load, although the magnitude of the \(\dot V_{O_2 } \)-reduction varies considerably between individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostoni E, D'Angelo E (1976) The effect of limb movement on the regulation of depth and rate of breathing. Respir Physiol 27:33–52
Anders P (1928) über den individuellen Eigenrhythmus beim menschlichen Gange und seine Beziehungen zum Rhythmus der Herz- und AtemtÄtigkeit. Arch Ges Physiol 220:287–299
Astrand PO, Rodahl K (1977) Textbook of work physiology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bechbache RR, Duffin J (1977) The entrainment of breathing frequency by exercise rhythm. J Physiol [Lond] 272:553–561
Benson H, Dryer T, Hartley LH (1978) Decreased oxygen consumption during exercise with elicitation of the relaxation response. J Human Stress 4:38–42
Böning D, Gönen Y, Maassen N (1984) Relationship between work load, pedal frequency, and physical fitness. Int J Sports Med 5:92–97
Boutellier U, Gomez U, Koller EA (1982) Verbessertes Atmungsanalysesystem. Anwendung am Beispiel der Sauerstoffaufnahmekinetik (\(\dot V_{O_2 } \)). Swiss Med 4:31–33
Bramble DM, Carrier DR (1983) Running and breathing in mammals. Science 219:251–256
Bühlmann A (1965) Klinische Funktionsprüfung des Herzens. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 95:1327–1332
Cohen MI (1979) Neurogenesis of respiratory rhythm in the mammal. Physiol Rev 59:1105–1173
Hildebrandt G, Daumann FJ (1965) Koordination von Pulsund Atemrhythmus bei Arbeit. Int Z Angew Physiol 21:27–48
Holst von, E (1939) Die relative Koordination als PhÄnomen und als Methode zentralnervöser Funktionsanalyse. Ergeb Physiol 42:228–306
Iscoe S, Polosa C (1976) Synchronization of respiratory frequency by somatic afferent stimulation. J Appl Physiol 40:138–148
JÄger M (1979) über die Beziehungen zwischen Tret- und Atmungsrhythmus in der Fahrradergometrie. Inaug Dissertation, Zürich
Jasinskas CL, Wilson BA, Hoare J (1980) Entrainment of breathing rate to movement frequency during work at two intensities. Respir Physiol 42:199–209
Kohl J, Koller EA, JÄger M (1981) Relation between pedalling- and breathing rhythm. Eur J Appl Physiol 47:223–237
Löllgen H, Ulmer HV (1972) Zum Problem der Tretgeschwindigkeit in der Ergometrie. In: Mellerowicz H, Hansen G (eds) III. Internationales Seminar für Ergometrie. Berlin, pp 130–135
Panda A, Senapati JM, Parida B, Fahim M (1979) Role of cerebellum on ventilatory change due to muscle-receptor stimulation in the dog. J Appl Physiol REEP 47:1062–1065
Pietsch P (1984) Das rechnerunterstützte Atmungsanalysesystem des Physiologischen Instituts Zürich. Inaug Dissertation, Zürich
Saunders JA (1947) Respiratory rhythm and rhythm of body movement in the human. J Physiol [Lond] 106:25
Schwarz G (1973) über die VerÄnderungen der Herz- und Atemperiodenstreuung bei Tretarbeit mit verschiedenen Frequenzen und ihre Beziehung zum Trainingszustand. Inaug Dissertation, Marburg
Sjöstrand T (1960) Functional capacity and exercise tolerance in patients with impaired cardiovascular function. In: Clinical cardiopulmonary physiology. Grune and Stratton, New York
Stegemann J, Ulmer HV, Heinrich KW (1968) Die Beziehung zwischen Kraft und Kraftempfindung als Ursache für die Wahl energetisch ungünstiger Tretfrequenzen beim Radsport. Int Z Angew Physiol 25:224–234
Tesch PA, Kaiser P (1983) Effects of beta-adrenergic blockade on O2 uptake during submaximal and maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol REEP 54:901–905
Viala D, Vidal C, Freton E (1979) Coordinated rhythmic bursting in respiratory and locomotor muscle nerves in the spinal rabbit. Neurosci Lett 11:155–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garlando, F., Kohl, J., Koller, E.A. et al. Effect of coupling the breathing- and cycling rhythms on oxygen uptake during bicycle ergometry. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 54, 497–501 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422959
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422959