Abstract
The fluorescence properties of ribonuclease labelled at its active site with N-(iodoacetylamino)-ethyl-5-naphthylamine-1-sulfonic acid have been studied at different temperatures and in the presence of acrylamide. The rate constant for the quenching of the fluorescence of labelled ribonuclease by acrylamide is apparently not limited by the “accessibility” of the probe: similar values are obtained for the native and denatured states of the protein. Instead, acrylamide seems to be a rather inefficient quencher of this fluorescent group ((acetamidoamino) ethyl-5-naphtylamine-1-sulfonic acid), as shown by non-linear Stern-Volmer representations, biphasic decay kinetics, and a low value of the rate constant.
The fluorescence intensity of the native state of the labelled protein is highly sensitive to temperature and exhibits a 20% decrease for an increase of temperature of from 10°C to 30°C, independent of solvent viscosity. This thermal quenching is specific for the native conformation and disappears when the protein is unfolded. When the fluorescence life-time of the label is shortened by addition of acrylamide, the effect of temperature becomes identical for native and unfolded structures. This suggests that the cause of the thermal quenching is the presence of conformational fluctuations within the native protein which apparently take place in the time range from 35 to 200 ns.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
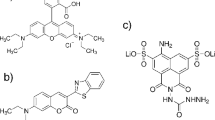
- 1,5-IAEDANS:
-
N-(iodoacetylamino)ethyl-5-naphthylamine-1-sulfonic acid
- AEDANS:
-
(acetamidoamine)-ethyl-5-naphthylamine-1-sulfonic acid
- RNase:
-
bovine pancreatic ribonuclease
- AEDANS-RNase:
-
RNase labelled with AEDANS
- ME-AEDANS:
-
(hydroxyethylthioacetamido)ethyl-5-naphthylamine-1-sulfonic acid: the product of the reaction between 1,5-IAEDANS and β-mercaptoethanol (Hudson and Weber 1973)
- Gu-HCl:
-
guanidine hydrochloride
References
Brochon JC (1980) Protein structure and dynamics by polarized pulse fluorometry. In: Ishiwata S (ed) Protein dynamics and energy transduction. Proceedings of the Sixth Taniguchi International Symposium, Biophysics Division, pp 163–189
Cooper A (1981) Spurious conformational transitions in proteins? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3551–3553
Eftink MR, Ghiron CA (1981) Fluorescence quenching studies with proteins. Anal Biochem 114:199–227
Eftink MR, Ghiron CA (1984) Indole fluorescence quenching studies on proteins and model systems: use of the inefficient quencher succinimide. Biochemistry 23:3891–3899
Fenichel IR, Horowitz SB (1965) Diffusional specificity in water. Ann NY Acad Sci 125:290–297
Gratton E, Jameson DM, Weber G, Alpert B (1984) A model of dynamic quenching of fluorescence in globular proteins. Biophys J 45:789–803
Grinvald A, Steinberg IZ (1974) On the analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics by the method of least-squares. Anal Biochem 59:583–598
Hudson EN, Weber G (1973) Synthesis and characterization of two fluorescent sulfhydryl reagents. Biochemistry 12: 4154–4161
Jullien M, Garel J-R (1981) Fluorescent probe of ribonuclease A conformation. Biochemistry 20:7021–7026
Parker CA (1968) Photoluminescence of solutions. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Wahl P (1979) Time-resolved fluorometry. In: Chen RF, Edelhoch H (eds) Biochemical fluorescence concepts. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–41
Yguerabide J (1972) Nanosecond fluorescence spectroscopy of macromolecules. In: Hirs CHW, Timasheff SN (eds) Methods in enzymology, Vol 26. Academic Press, New York, pp 498–578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jullien, M., Garel, J.R., Merola, F. et al. Quenching by acrylamide and temperature of a fluorescent probe attached to the active site of Ribonuclease. Eur Biophys J 13, 131–137 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542558
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542558