Summary
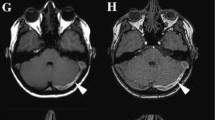
Six patients with a dural arteriovenous malformation (dural AVM) involving the cavernous sinus were followed up with magnetic resonance imaging in order to assess change in the lesions. Spin-echo (SE) imaging of three patients in whom the AVM appeared to have closed at least 1 month earlier (two of them spontaneously, and one after external carotid artery embolization) showed neither apparent flow void in the involved cavernous sinus nor evidence of venous thrombosis. SE images of the other three patients who had not been cured by external carotid artery embolization (two of whom were examined within a week of treatment), detected persisting arteriovenous shunts, including high-flow cortical venous drainage, seen as flow void. Two-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography (2D TOF MRA) was performed simultaneously in three patients. Whereas shunting blood and the normal cavernous sinus were of high intensity, presumed thrombosed cavernous sinuses were isointense with stationary brain tissue. SE imaging can confirm the resolution of arteriovenous shunts, but poorly delineates ver acute and chronic thrombosis of the draining veins. In contrast, 2D TOF MRA directly demonstrates flowing blood, permitting the diagnosis of venous thrombosis; it should be included in follow-up of a dural AVM involving the cavernous sinus when venous thrombosis is suspected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirabuki N, Miura T, Mitomo M, Harada K, Hashimoto T, Kawai R, Kozuka T (1988) MR imaging of dural arteriovenous malformations with ocular signs. Neuroradiology 30:390–394
Komiyama M, Fu Y, Yagura H, Yasui T, Hakuba A, Nishimura S (1990) MR imaging of dural AV fistulas at the cavernous sinus. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:397–401
Viñuela F, Fox AJ, Debrun GM, Peerless SJ, Drake CG (1984) Spontaneous carotid-cavernous fistulas: clinical, radiological, and therapeutic considerations. J Neurosurg 60:976–984
Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, Ter-Brugge K, Tolia A, Hurth M, Berenstein M (1986) Neurological manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64:724–730
Hirabuki N, Mitomo M, Miura T, Hashimoto T, Kawai R, Kozuka T (1990) External carotid artery embolization of arteriovenous malformations involving the cavernous sinus: outcome and role of venous thrombosis. Acta Radiol 31:197–201
Tsai FY, Hieshima GB, Mehringer CM, Grinnell V, Pribram HW (1983) Delayed effects in the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas. AJNR 4:357–361
Seeger JF, Gabrielsen TO, Giannotta SL Lotz PR (1980) Carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas and venous thrombosis. AJNR 1:141–148
Sergott RC, Grossman RI, Savino PJ, Bosley TM, Schatz MJ (1987) The syndrome of paradoxical worsening of dural cavernous sinus arteriovenous malformations. Ophthalmology 94:205–212
Litt AW, Eidelman EM, Pinto RS, Riles TS, McLachlan SJ Schwartzenberg S, Weinreb JC, Kricheff II (1991) Diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis: comparison of 2DFT time-of-flight MR angiography with contrast angiography in 50 patients. AJNR 12:149–154
Sevick RJ, Tsuruda JS, Schmalbrock P (1990) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography in the evaluation of cerebral aneurysms. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14:874–881
Mattle HP, Wentz KU, Edelman RR, Wallner B, Finn JP, Barnes P, Atkinson DJ, Kleefield J, Hoogewoud HM (1991) Cerebral venography with MR. Radiology 178:453–458
Bonneville JF, Cattin F, Racle A, Bouchareb M, Boulard D, Potelon P, Tang YS (1989) Dynamic CT of the laterosellar extradural venous spaces. AJNR 10:535–542
Daniels DL, Czervionke LF, Bonneville JF, Cattin F, Mark LP, Pech P, Hendrix LE, Smith DF, Haughton VM, Williams AL (1988) MR imaging of the cavernous sinus: value of spin echo and gradient recalled echo images. AJNR 9:947–952
Halbach VV, Hieshima GB, Higashida RT, Reicher M (1987) Carotid cavernous fistulae: indication for urgent treatment. AJNR 8:627–633
Macchi PJ, Grossman RI, Gomori JM, Goldberg HI, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1986) High-field MR imaging of cerebral venous thrombosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 10:10–15
McMurdo SK, Brant-Zawadzki M, Bradley WG, Chang GY, Berg BO (1986) Dural sinus thrombosis: study using intermediate field strength MR imaging. Radiology 161:83–86
Bauer WB, Einhaupl K, Heywang SH, Vogl T, Seiderer M, Clados D (1987) MR of venous sinus thrombosis: a case report. AJNR 8:713–715
Hulcelle PJ, Dooms GC, Mathurin P, Cornelis G (1989) MRI assesement of unsuspected dural sinus thrombosis. Neuroradiology 31:217–221
Bradley WG (1988) Flow phenomenon in MR imaging. AJR 150:983–994
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1985) Intracranial hematomas: imaging by high-field MR. Radiology 157:87–93
Nadel L, Braun IF, Kraft KA, Fatouros PP, Laine FJ (1990) Intracranial vascular abnormalities: value of MR phase imaging to distinguish thrombus from flowing blood. AJNR 11:1133–1140
Sze G, Simmons B, Krol G, Walker R, Zimmerman RD, Deck MDF (1988) Dural sinus thrombosis: verification with spin-echo techniques. AJNR 9:679–686
Atlas SW, Mark AS, Fram EK, Grossman RI (1988) Vascular intracranial lesions: applications of gradient-echo MR imaging. Radiology 169:455–461
Anderson CM, Saloner D, Tsuruda JS, Shapeero LG, Lee RE (1990) Artifacts in maximum-intensity-projection display of MR angiograms. AJR 154:623–629
Chakeres DW, Schmalbrock P, Brogan M, Yuan C, Cohen L (1990) Normal venous anatomy of the brain: demonstration with gadopentetate dimeglumine in enhanced 3-D MR angiography. AJNR 11:1107–1118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirabuki, N., Fujita, N., Hashimoto, T. et al. Follow-up MRI in dural arteriovenous malformations involving the cavernous sinus: emphasis on detection of venous thrombosis. Neuroradiology 34, 423–427 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00596507
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00596507