Abstract
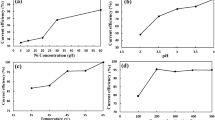
Zinc deposits contaminated with lead were found to have characteristic morphologies and orientations which were dependent on the amount of lead present in the zinc deposits and to a lesser extent on the presence of other impurities such as antimony and glue in the deposits. Increasing lead in the zinc deposits progressively changed the orientations from (1 1 2) to (1 0 1) to (1 0 0) to finally a poorly crystalline (0 0 2) structure. The lead content of the zinc deposits was dependent on both the concentration and chemical composition of lead added to the electrolyte, the current density and also on the presence of antimony or glue in the electrolyte. A relationship was shown to exist between the effect of lead contamination on zinc deposit morphology and orientation and on the overpotentials associated with zinc electrodeposition in the presence of lead.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. Robinson and T. J. O'Keefe,J. Appl. Electrochem. 6 (1976) 1.
B. A. Lamping and T. J. O'Keefe,Metall. Trans. 7B (1976) 551.
R. C. Kerby, H. E. Jackson, T. J. O'Keefe and Y. -M. Wang,ibid 8B (1977) 661.
D. J. MacKinnon and J. M. Brannen,J. Appl. Electrochem. 7 (1977) 451.
H. Fukubayashi, T. J. O'Keefe and W. C. Clinton, U.S.B.M. Report of Investigations, RI 7966 (1974) p. 26.
R. C. Kerby and T. R. Ingraham, Mines Branch Research Report R243, Department of Energy, Mines and Resources, Ottawa, Canada, April (1971) p. 35.
U. F. Turonshina and V. V. Stender,J. Appl. Chem. USSR 28 (1955) 151.
Idem, ibid 28 (1955) 347.
Idem, ibid 28 (1955) 447.
A. D'Este and R. Guerriero,Montovecchio 16 (1965) 1.
F. S. Weiner, G. T. Wever and R. J. Lapee, ‘Zinc’ (Ed. C. H. Mattewson) Reinhold, New York, (1959) Ch. 6.
C. L. Mantell, ‘Electrochemical Engineering’, McGraw-Hill Book Co, New York (1960) p. 218.
G. Haensel,Neue Huette 7 (1962) 356.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackinnon, D.J., Brannen, J.M. & Kerby, R.C. The effect of lead on zinc deposit structures obtained from high purity synthetic and industrial acid sulphate electrolytes. J Appl Electrochem 9, 55–70 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620587
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620587