Summary
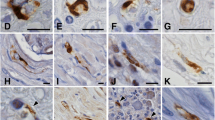
Light and electron microscopic studies were made on the anterior horn cells in a case of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eosinophilic inclusions of Bunina type were observed almost selectively in the motor neurons of spinal cord, as well as of brain stem, at the light microscopic level. Fine structural study revealed the presence of two types of cytoplasmic inclusions. The first, mainly corresponding to the light microscopic inclusions, were homogeneous, electron-dense, round- or oval-shaped bodies with vesicular or tubular rims and ribosome particles, about 2–5 μ in diameter, which contained filaments or other cytoplasmic components in the clear areas within them. The second were lamellar structures (laminated cytoplasmic bodies, Morales) which appeared to be originating from endoplasmic reticulum. There was no distinct transition in these two types of inclusions and the relationship to each other is not clear. The significance of Bunina body is unknown, but some manifestation of a primary disorder, e.g., protein metabolism, rather than a secondary degenerative change in the motor neurons in amyotorophic lateral sclerosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bunina, T. L.: On intracellular inclusions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Korsakow. J. Neuropath. Psychiat.62, 1293–1299 (1962)
Doolin, P. F., Barron, K. D., Kwak, S.: Ultrastructural and histochemical analysis of cytoplasmic laminar bodies in lateral geniculate neurons of adult cat. Am. J. Anat.121, 601–622 (1967)
Field, E. J., Narang, H. K.: An electron-microscopic study of scrapie in the rat: Further observations on “inclusion bodies” and virus-like particles. J. neurol. Sci.17, 347–364 (1972)
Gross, B. G.: Annulate lamellae in the axillary apocrine glands of adult man. J. Ultrastr. Res.14, 64–73 (1966)
Harrison, G. A.: Some observations on the presence of annulate lamellae in alligator and sea gull adrenal cortical cells. J. Ultrastr. Res.14, 158–166 (1966)
Hart, M. N., Cancilla, P. A., Frommes, S. P.: Ultrastructure of “Bunina bodies”. 52nd Annual Meeting of American Neuropathologists, 1976
Hart, M. N., Cancilla, P. A., Frommes, S. and Hirano, A.: Anterior horn cell degeneration and Bunina-type inclusions associated with dementia. Acta neuropath.38, 225–228 (1977)
Herman, M. M., Ralston, H. J.: Laminated cytoplasmic bodies and annulate lamellae in the cat ventrobasal and posterior thalamus. Anat. Rec.167, 183–196 (1970)
Hirano, A.: Pathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In: Gadjusek, D. C., Gibbs, C. J. and Alpers, M. (Eds.). Slow, latent, and temperate virus infections. NINDB Monograph No. 2, p. 23 Washington: National Institute of Health, 1965
Hirano, A., Llena, J. F., Streifler, M., Cohn, D. F.: Anterior horn cell changes in a case of neurolathyrism. Acta neuropath.35, 277–283 (1976)
Hirano, A., Kurland, L. T., Sayre, G. P.: Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch. Neurol.16, 232–243 (1967)
Hirano, A.: Changes of the neuronal endoplasmic reticulum in the peripheral nervous system in mutant hamsters with hind leg paralysis and normal controls. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.37, 75–84 (1978)
Kepes, J. J., Chou, S. M., Price, L. W.: Progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy with 10-year survival in a patient with nontropic sprue. Report of a case with unusual light and electron microscopic features. Neurology25, 1006–1012 (1975)
Kessel, R. G.: Intranuclear and cytoplasmic annulate lamellae in tunicate oocytes. J. Cell Biol.24, 471–487 (1965)
Kruger, L., Maxwell, D. S.: Cytoplasmic laminar bodies in the striate cortex. J. Ultrastr. Res.26, 387–390 (1969)
Martinez, A. J., Ohya, T., Jabbour, J. T., Duenas, D.: Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE). Reappraisal of nuclear, cytoplasmic and axonal inclusions. Ultrastructural study of eight cases. Acta neuropath.28, 1–13 (1974)
Mendell, J. R., Markesbery, W. R.: Neuronal intracytoplasmic hyalin inclusions. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.30, 233–239 (1971)
Merkow, L., Leighton, J.: Increase numbers of annulate lamellae in myocardium of chick embryo incubated at abnormal temperatures. J. Cell Biol.28, 127–137 (1966)
Morales, R. D., Duncan, D., Rehmet, R.: A distinctive laminated cytoplasmic body in the lateral geniculate body neurons of the cat. J. Ultrastr. Res.10, 116–123 (1964)
Morales, R., Duncan, D.: Multilaminated bodies and other unusual configurations of endoplasmic reticulum in the cerebellum of the cat. An electron microscopic study. J. Ultrastr. Res.15, 480–489 (1966)
Morecki, R., Zimmerman, H. M.: Human rabies encephalitis. Fine structure study of cytoplasmic inclusions. Arch. Neurol.20, 599–604 (1969)
Nakamura, H., Takahashi, K., Nakashima, R., Kamoto, T.: Demyelinating encephalitis associated with progressive systemic scleroderma. Clin. Neurol. (Tokyo)14, 672–677 (1974)
Norman, M. G.: Hyalin (“colloid”) cytoplasmic inclusions in motoneurons in association with familial microencephaly, retardation and seizures. J. neurol. Sci.23, 63–70 (1974)
Novikoff, A. B.: Lysosomes in nerve cells. In: Hydén, H. (Ed.): The cell, p. 319. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1967
Peters, A., Palay, S. L.: The morphology of laminae A and Al of the dorsal nucleus of the lateral geniculate body of the cat. J. Anat.100, 451–486 (1966)
Schochet, S. S., Hardman, J. M., Ladeweg, P. P., Earle, K. M.: Intraneuronal conglomerates in sporadic motor neuron disease: A light and electron microscopic study. Arch. Neurol.20, 548–553 (1969)
Sung, J. H., Hayano, M., Mastri, A. R., Okagaki, T.: A case of human rabies and ultrastructure of the Negri body. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.35, 541–559 (1976)
Szlachta, H. L., Habel, R. E.: Inclusions resembling Negri bodies in the brains of nonrabid cats. Cornell Veterinarian,43, 207–212 (1953), cited by Doolin et al. (1962)
Takahashi, K., Nakamura, H., Okada, E.: Hereditary amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Histochemical and electron microscopic study of hyalin inclusions in motor neurons. Arch. Neurol.27, 292–299 (1972)
Takahashi, K., Nakamura, H., Agari, M., Yamasaki, I.: Demyelinating myelitis with painful tonic seizures. Report of an autopsy case. Clin. Neurol. (Tokyo)16, 117–123 (1976)
Takei, Y., Mirra, S. S.: Intracytoplasmic hyalin inclusion bodies in the nerve cells of the hypoglossal nucleus in human autopsy material. Acta neuropath.17, 14–23 (1971)
Wisotzkey, H. M., Mossy, J.: Hyalin (“colloid”) cytoplasmic inclusions in neurons of human hypoglossal nuclei. Arch. Path. (Chic.)93, 61–70 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomonaga, M., Saito, M., Yoshimura, M. et al. Ultrastructure of the Bunina bodies in anterior horn cells of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 42, 81–86 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690971
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690971