Summary
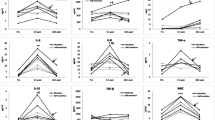
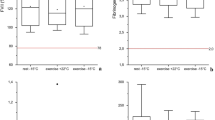
The effect of a test marathon race on plasma fibrinolytic activity (FA) was studied in 16 endurance athletes before, immediately after, 3 h, and 31 h after the run. Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) activity increased about 31-fold immediately after the run. Similar increases were found in t-PA antigen concentration. Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) was not detectable immediately after the race and was significantly decreased 3 h (P < 0.05) and 31 h (P < 0.01) later. Bβ15–42 peptide increased by 0.63 pmol · ml−1 (P<0.001),d-dimer by 68.3 ng · ml−1 (P< 0.05). Euglobulin lysis time (ELT) was reduced from 109 to 18 min (P<0.001). The increased t-PA activity and t-PA antigen concentration disappeared in the course of the first 3 h after exertion. ELT also reached its pre-exercise levels at this time. Thirty-one hours after the race ELT and t-PA antigen levels were slightly but significantly reduced (P<0.05), whereas Bβ15–42 peptide remained increased (P<0.05). t-PA activity was unchanged compared with pre-exercise values. It seems that the exercise-induced FA is mainly caused by the marked increase of t-PA antigen and t-PA activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew M, Carter C, O'Brodovich H, Heigenhauser G (1986) Increases in factor VIII complex and fibrinolytic activity are dependent on exercise intensity. J Appl Physiol 60:1917–1922
Astrup T (1956) Fibrinolysis in the organism. Blood 11:781–806
Bennett NB, Ogston CM, Ogston D (1968) The effect of prolonged exercise on the components of the blood fibrinolytic enzyme system. J Physiol 198:479–485
Biggs R, Macfarlane RG, Pilling J (1947) Observations on fibrinolysis. Lancet 1:402–405
Brommer EJP, Barett-Bergshoeff MM, Allen RA, Schlicht I, Bertina RM, Schalekamp MADH (1982) The use of desmopressin acetate (DDAVP) as a test of the fibrinolytic capacity of patients. Analysis of responders and non-responders. Thromb Haemost 48:156–161
Cash JD, Woodfield DG, Allan AGE (1970) Adrenergic mechanisms in the systemic plasminogen activator response to adrenaline in man. Br J Haematol 18:487–494
Chan KL, Davies RA, Chambers RJ (1984) Coronary thrombosis and subsequent lysis after a marathon. J Am Coll Cardiol 4:1322–1325
Cohen RJ, Epstein SE, Cohen SL, Dennis LH (1968) Alterations of fibrinolysis and blood coagulation induced by exercise and the role of beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation. Lancet 11:1264–1266
Collen D, Semeraro N, Tricot JP, Vermylen J (1977) Turnover of fibrinogen, plasminogen, and prothrombin during exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 42:865–873
Davis GL, Abildgaard FC, Bernauer EM, Britton M (1976) Fibrinolytic and hemostatic changes during and after maximal exercise in males. J Appl Physiol 40:287–292
Egeberg O (1963) The effect of exercise on the blood clotting system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 15:8–13
Ferguson EW, Guest MM (1974) Exercise, physical conditioning, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh 31:663–671
Ferguson EW, Barr CF, Bernier LL (1979) Fibrinogenolysis and fibrinolysis with strenuous exercise. J Appl Physiol 47:1157–1166
Hawkey CM, Britton BJ, Wood WG, Peele M, Irving MH (1975) Changes in blood catecholamine levels and blood coagulation and fibrinolytic activity in response to graded exercise in man. Br J Haematol 29:377–384
Hyers TM, Martin BJ, Pratt DS, Dreisin RB, Franks JJ (1980) Enhanced thrombin and plasmin activity with exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 48:821–825
Iatridis SG, Ferguson JH (1963) Effect of physical exercise on blood clotting and fibrinolysis. J Appl Physiol 18:337–344
Karp JE, Bell R (1974) Fibrinogen-fibrin degradation products and fibrinolysis following exercise in humans. Am J Physiol 227:1212–1215
Langleben D, Moroz LA (1985) Participation of blood cells in exercise-induced fibrinolysis. Thromb Res 39:733–740
Lill H (1987) Biochemische und physiologische Grundlagen zum Gewebeplasminogenaktivator (t-PA). Z Gesamte Inn Med 42:478–486
Mandalaki T, Dessypris A, Louizou C, Bossinakou I, Panayotopoulou A, Antonopoulou A (1977) Marathon run. I. Effects on blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 37:444–450
Marsh NA, Gaffney PJ (1980) Some observations on the release of extrinsic and intrinsic plasminogen activators during exercise in man. Haemostasis 9:238–247
Marsh NA, Gaffney PJ (1982) Exercise-induced fibrinolysis — fact or fiction. Thromb Haemost 48:201–203
Paques EP, Heimburger N (1986) Das fibrinolytische System. Hämostaseologie 6:139–147
Röcker L (1983) Der Einfluß korperlicher Leistungen auf Laborbefunde. Kassenarzt 23:35–45
Röcker L (1984) Gerinnung und Fibrinolyse bei ergometrischen Leistungen. Ärztl Lab 30:316–318
Röcker L, Drygas WK, Heyduck B (1986) Blood platelet activation and increase in thrombin activity following a marathon race. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:374–380
Sachs L (1974) Angewandte Statistik, Planung und Auswertung, Methoden and Modelle, 4th ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Stötzer K-E, Amiral J, Spanuth E (1988) Neue Methoden zur spezifischen Bestimmung von Fibrinspaltprodukten (d-Dimere). Lab Med 12:51–59
Strauss MB, Davis RK, Rosenbaum JD, Rossmeisl EC (1951) Water diuresis produced during recumbency by the intravenous infusion of isotonic saline solution. J Clin Invest 30:862–868
Wilman B, Mellbring G, Ranby M (1983) Plasminogen activator release during venous stasis and exercise as determined by a new specific assay. Clin Chim Acta 127:279–288
Winckelmann G, Meyer G, Roskamm H (1968) Der Einfluß korperlicher Belastung auf Blutgerinnung und Fibrinolyse bei untrainierten Personen und Hochleistungssportlern. Klin Wochenschr 46:712–716
Wybitul K, Thiel M, Keller E, Lindermaier M, Merten R (1983) Der plotzliche Tod beim Sport. Med Welt 34:1098–1102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Röcker, L., Taenzer, M., Drygas, W.K. et al. Effect of prolonged physical exercise on the fibrinolytic system. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 60, 478–481 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705040
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705040