Abstract
Joint hypocenter determination is performed for intermediate and deep earthquakes of the Tyrrhenian Sea region.
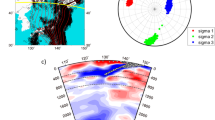
This analysis allowed us to obtain a catalogue of 70 well-located events in this peculiar Benioff zone, which is characterized by quite low seismic activity, compared to the Pacific deep earthquake regions. The method used for the analysis is that ofFrohlich (1979), a variant of the successive approximation technique, which allows use of a great number of events and stations but saves computer memory. The results show a spoon-shaped Benioff zone, dipping NW in the Tyrrhenian Sea to 500km depth. 32 reliable fault-plane solutions have been determined using these new earthquake locations, confirming the predominance of down-dip compression in the central part of the slab and more complex motion along the borders of the zone, as previously suggested byGasparini et al. (1982).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boccaletti, M. andGuazzone, G. (1972),Gli archi appenninici, il Mar Ligure ed il Tirreno nel quadro della tettonica dei bacini marginali retroarco, Mem. Soc. Geol. It.,11, 201–216.
Bolt, B. A. (1960),The revision of earthquake epicenters, focal depth and origin times using a high-speed computer, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc.3, 433–440.
Caputo, M., Panza, G. F. andPostpischl, D. (1970),Deep structure of Mediterranean basin. J. Geophys. Res.75, 4919–4923.
Del Pezzo, E., Guerra, I. andScarpa, R. (1981),The crust and upper mantle structure beneath Southern Italy by earthquakes and DSS data. Pure Appl. Geophys.119, 1134–1143.
Dziewonski, A. M., Chou, T. A. andWoodhouse, J. H. (1981),Determination of earthquake source parameters from waveform data for studies of global and regional seismicity, J. Geophys. Res.86, 2825–2852.
Frohlich, C. (1979),An efficient method for joint hypocenter determination for large groups of earthquakes. Comput. Geosci.5, 387–389.
Gasparini, C., Iannaccone, G., Scandone, P. andScarpa, R. (1982),Seismotectonics of the Calabrian arc.Tectonophysics 82, 267–286.
Gasparini, C., Iannaccone, G. andScarpa, R. (1985),Fault-plane solutions and seismicity of the Italian peninsula, Tectonophysics117, 59–78.
Ghisetti, F., Scarpa, R. andVezzani, L. (1982),Seismic activity, deep structures and deformation processes in the Calabrian arc, Southern Italy, Earth Evol. Sci.3, 248–260.
Jeffreys, H. andBullen, K. E. (1940),Seismological tables. British Ass. Adv. Sci., London.
Mantovani, E. (1982),Some remarks on the driving forces in the evolution of the Tyrrhenian basin and Calabrian arc. Earth Evol. Sci.3, 266–270.
Martini, M. andScarpa, R. (1983),Earthquakes in Italy in the last century, Proc. Int. School of Physics ‘E.Fermi’, LXXXV Course on ‘Earthquakes: observation, theory and interpretation’, North Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 473–487.
Ninkovich, D. andHays, J. D. (1972),Mediterranean island arcs and origin of high potash volcanoes. Earth Plan. Sci. Lett.,16, 331–345.
Pavlis, G. L. andBooker, J. R. (1983),Progressive multiple event location (PMEL), Bull. Seism. Soc. Am.43, 1753–1777.
Ritsema, A. R. (1979),Active or passive subduction in the Calabrian arc. Geol. Mijnbouw58, 127–134.
Scandone, P. (1979),Origin of the Tyrrhenian sea and Calabrian arc, Boll. Soc. Geol. It.98, 27–34.
Wezel, F. C. (1982)The Tyrrhenian sea: a rifted Krikogenic-swell basin. Mem. Soc. Geol. It.24, 531–568.
Vickens, A. J. andHodgson, J. H. (1967),Computer re-evaluation of earthquake mechanism solutions. Pub. Dom. Obs. Ottawa33, 1–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iannaccone, G., Scarcella, G. & Scarpa, R. Subduction zone geometry and stress patterns in the tyrrhenian sea. PAGEOPH 123, 819–836 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876972
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876972